Government borrowing higher than expected in February

- Published
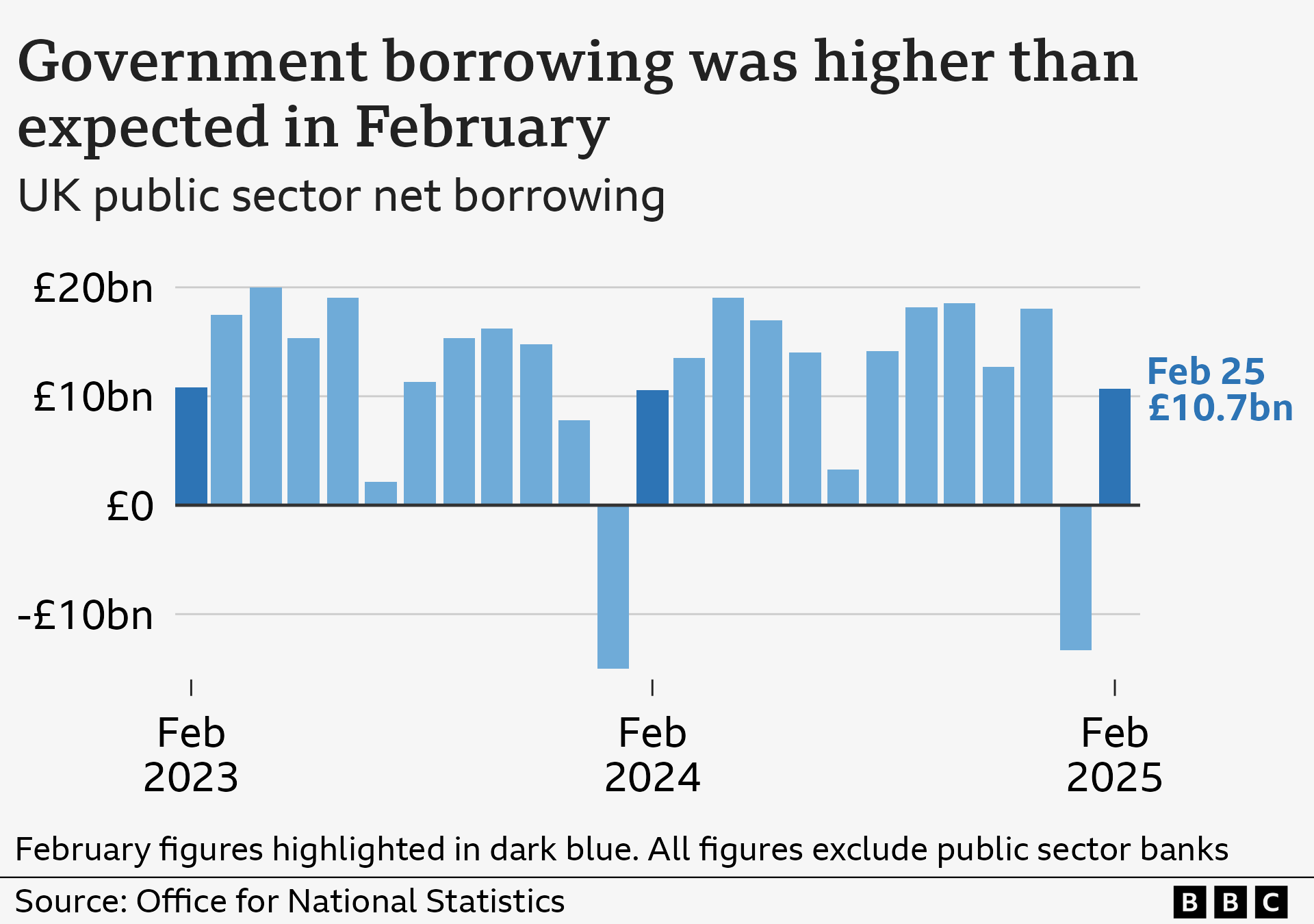
UK government borrowing was higher than expected in February, adding pressure to Chancellor Rachel Reeves ahead of her Spring Statement next week.
Borrowing - the difference between spending and income from taxes - was £10.7bn last month, according to official figures.
The government's independent forecaster had predicted that borrowing would be £6.5bn for the month.
Reeves is expected to announce spending cuts next week to meet her self-imposed rules for the economy, which the Treasury reiterated were "non-negotiable".
"We must go further and faster to create an agile and productive state that works for people," said Darren Jones, chief secretary to the Treasury, adding that the government "will never play fast and loose with the public finances".
However, economists have warned the higher-than-expected borrowing last month "puts more pressure" on the Chancellor ahead of the Spring Statement on Wednesday.
What will be in the chancellor's Spring Statement?
- Published26 March
Dennis Tatarkov, senior economist at KPMG, said the latest borrowing figures raised the risk of Reeves missing her self-imposed borrowing rules.
Most governments in wealthy nations have such rules, which are designed to reassure investors and maintain credibility with financial markets.
Reeves's two main rules are: not to borrow to fund day-to-day public spending; and to get debt falling as a share of the UK economic output by 2029/30.
Isabel Stockton, senior researcher for the Institute for Fiscal Studies think tank, said Reeves had "boxed herself in with promises to meet her fiscal targets, not to raise taxes further and not to return to austerity for public services".
She added that "easy or risk-free options for the Chancellor are in short supply".
Alex Kerr, UK economist at Capital Economics, said he expected further spending cuts "on top of the welfare cuts already unveiled".
At the Budget in October, the government's official forecaster the Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) indicated Reeves had £9.9bn available to spend against her borrowing rules.
But next week the OBR will be likely to conclude the chancellor's buffer has been "wiped out", Mr Kerr added.
Pantheon Macroeconomics, said the UK's "weak public finances mean spending cuts in the Spring Statement", and added that "taxes will rise in October".
This week the government revealed plans for major changes to the benefits system aimed generating savings of £5bn a year in response to the UK's growing welfare bill.
Policies include stricter tests for personal independence payments (Pip), which will affect hundreds of thousands of claimants, and a freeze on incapacity benefits in cash terms at £97 per week until 2029/30.
The prime minister has also announced NHS England will be scrapped, along with some other arms-length government bodies.
But aside from spending cuts, the government has said it will increase defence spending, though the funds are being reallocated from the international aid budget.
Liberal Democrat Treasury spokesperson Daisy Cooper MP said the latest borrowing figures were "yet another major blow to the Chancellor's faltering plan for growth, and show her approach is simply not working".
She added National Insurance increases for employers, set to come into effect in April, would "hammer small businesses".
The BBC has contacted the Conservative Party for comment.