The Nigerian queer parties that offer liberation
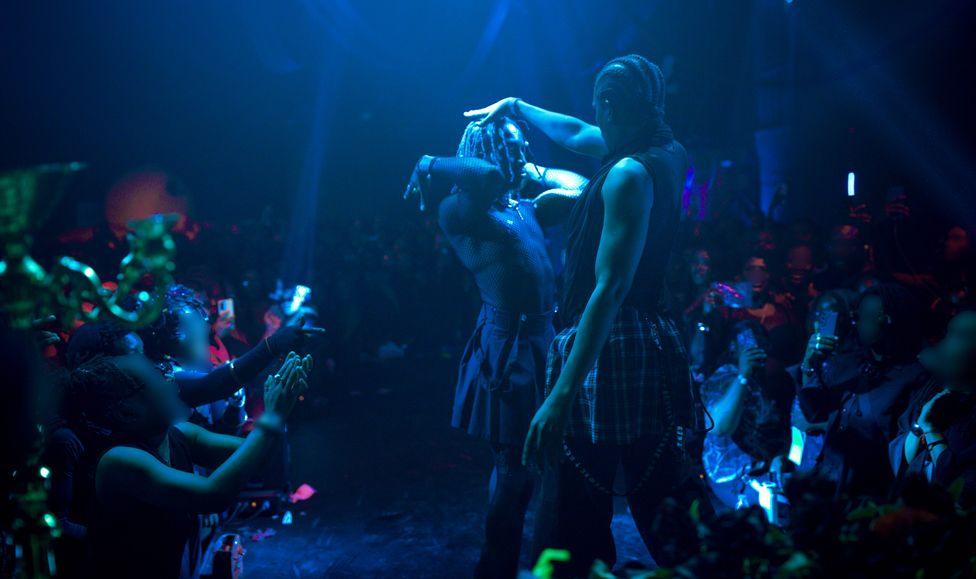
- Published
The location of the celebratory ball had to be kept a secret.
This was a queer event and in Nigeria, where same-sex relationships or public displays of affection are illegal, anything that is dedicated to embracing this culture is in danger.
Marking Pride month in any way here is an act of defiance.
The organisers of the Fola Francis Ball – named in honour of a transgender woman who died last year - only released the venue details with just hours to go before it opened.
But this did not deter the more than 500 people who turned up in a district close to the thriving waterfront area of Nigeria’s commercial heartland, Lagos.
Around the gated venue were abandoned car parts and warehouses known for rave parties.
A thumping bassline could be heard through the door and crossing the threshold felt like stepping into an alternative reality.
Inside was Lagos’s queer community, the venue, a cloak shielding them from the world outside.
For safety reasons, many LGBTQ+ Nigerians use the word "queer" as a broad term to encompass their identities.
Excited chatter and laughter coursed through the air. This was the joy of shedding fear.
Everyone was dressed to fit the neo-gothic theme.
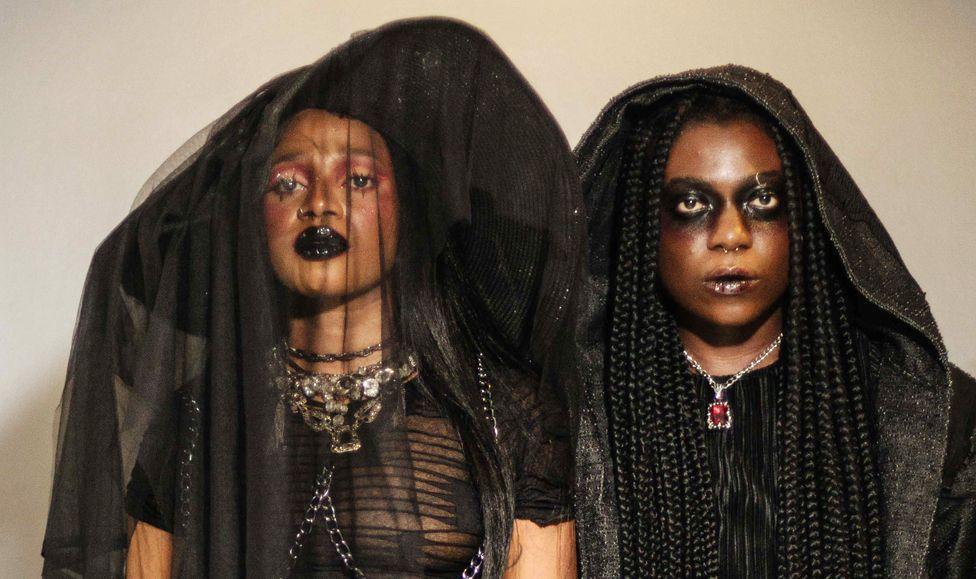

Uyaiedu Ikpe-Etim (L) and Ayo Lawson (R) organised the ball
In the dimly lit hall, strobe lights painted the skin of attendees in different colours. The flashes caught figures in different poses - a kaleidoscope of movement.
Androgyny and eccentricity reigned supreme. A woman with a shaved head and sparkling make-up strutted confidently next to a man in a flowing black dress.
People who, beyond the walls of the party, had to conform to a view of how a man should look felt empowered to wear wigs and bodycon dresses, and use their faces as a canvas for glitter and bold hues.
The creative duo behind the ball - Ayo Lawson and Uyaiedu Ikpe-Etim – were inspired by a similar event they had been to.
“We thought we were very queer and very out there, but going to experience a ball really changed our perspective of what it is to be queer and what queer joy really is,” Lawson told the BBC.
Last year’s first edition of the event was held to celebrate their queer-themed movie 14 Years and a Day, but this year they wanted to honour Fola Francis.
Until she drowned close to a Lagos beach at the end of last year, she had been at the heart of the burgeoning underground ballroom scene.
She hosted, organised and invited queer people to all the major parties.
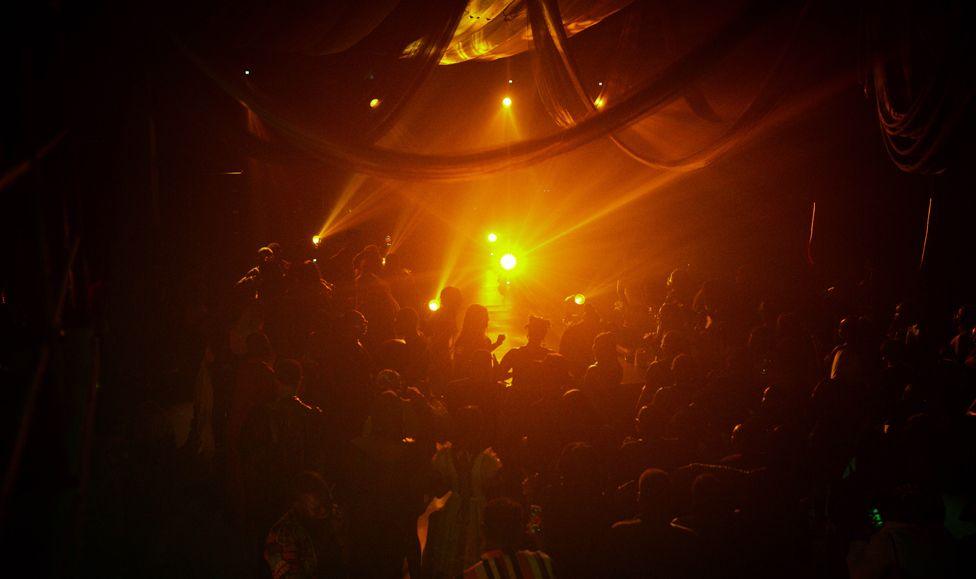

The ball offered a safe place for people to be who they wanted to be
For many, the Fola Francis ball was an opportunity to pay their respects.
“I want to celebrate Fola,” said one of the platform-heeled revellers, who was wearing a black choker, a dark corset, and lace leggings under a red checkered mini-skirt that matched her nails.
“When I first started going out, she was always telling me: ‘You look so good’, and it got to my head. It made me confident in being myself,” she said.
Fola Francis had a big impact on the entire queer community in the country. But for many trans and non-binary people, her death was personal, and honouring the life she lived was important.
A trans, non-binary person wearing an African-print gown said that Fola helped them realise the importance of showing up authentically. “Her existence gave me freedom,” they added with a sense of pride.
Another of the trans women, who was attending her first ball, told the BBC that the event was a “dream come true”.
She was forced to relocate to Lagos after facing transphobic violence in northern Nigeria and Fola Francis had offered to help her find safe housing.
The LGBTQ+ ballroom culture can be traced to the US and underground African-American drag events in the mid-19th Century. It has since blossomed across the US, and beyond, with a well-developed infrastructure including “houses”, which provide support networks and the basis for competitions.
TV shows like RuPaul’s Drag Race, Legendary and Pose have also brought the concept into the mainstream.
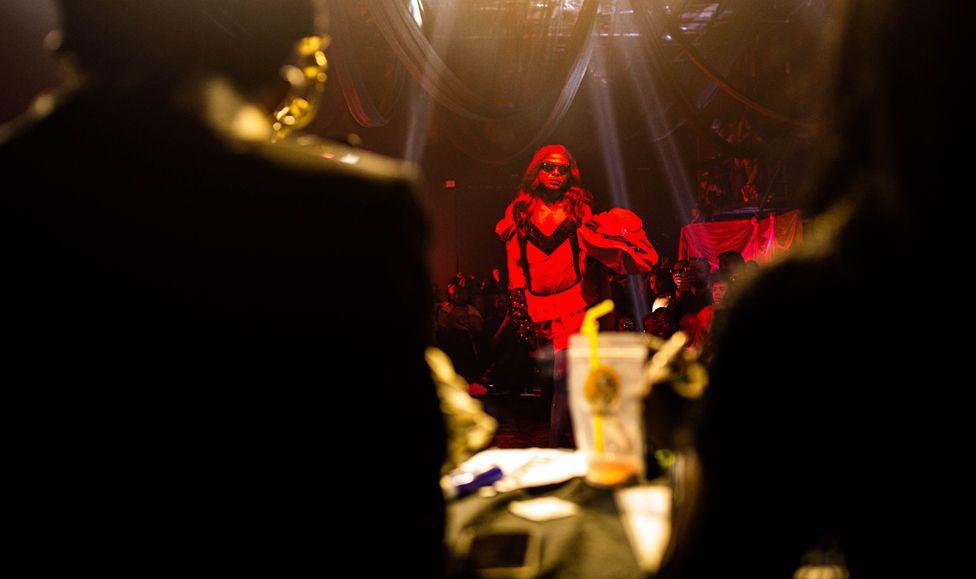

Participants came on to the catwalk stage to compete in various categories
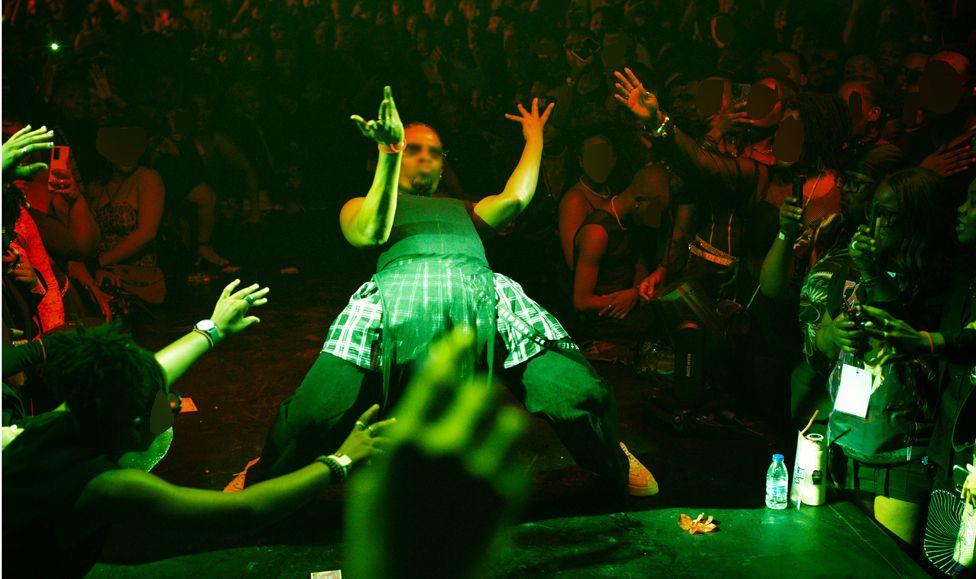

People clapped and cheered the contestants
At the Fola Francis Ball, some of those who came competed against each other in several categories - butch queen realness, femme queen realness, body, face, voguing and best-dressed.
The audience chanted and clapped as people danced and walked on the stage.
For the organisers, the purpose of a ball in Nigeria is clear: to be a space for self-expression and to celebrate the beauty of diversity, even in the face of fear.
And that fear is never far away as it feels like the 2014 Same-Sex Marriage Prohibition Act criminalises who they are.
“I’m not 100% relaxed or secure. One minute you can be safe, and another minute you’re busted,” a gay man at the venue told the BBC, citing cases in the past where the police arrested people at an all-male party.
Amid the fun he reflected on those who did not want to turn up.
“A lot of my friends would have been here tonight, but because of that fear [of arrest], they chose not to come.
“It makes me sad because ballroom culture, queer culture, is our way of celebrating who we are,” he added.
“I don’t get to experience it fully with them. It also makes me angry because there’s no reason why we should be living in fear when we can just express ourselves, be ourselves, and just live and be happy.”
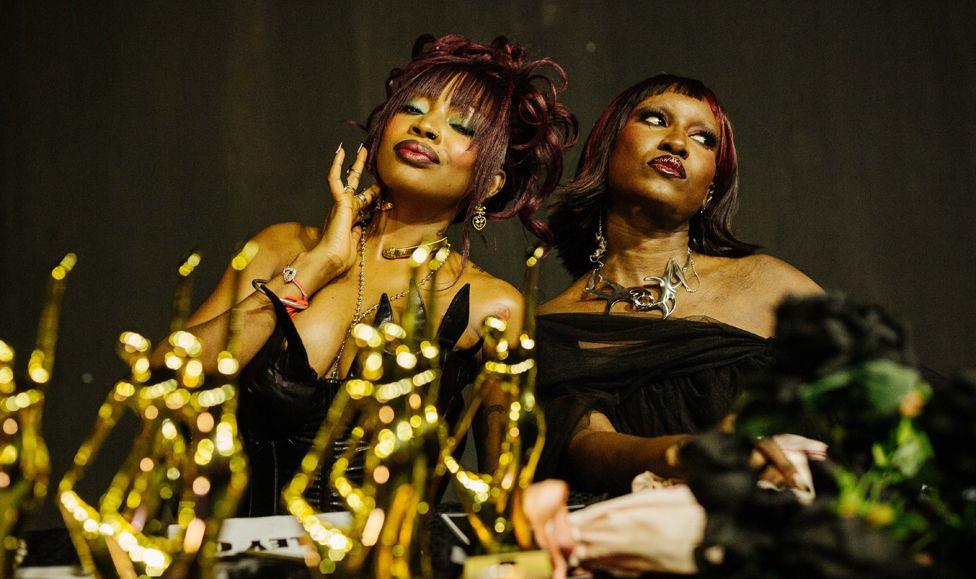

Ashley Okoli (L) and writer-designer Ozzy Etomi (R), both mainstream figures in Nigeria, supported the event as competition judges
But the organisers did all they could to create a safe environment.
Some of the safety measures included providing changing rooms for those who wanted to dress as their most authentic selves but needed to avoid homophobic and transphobic violence on their way to the venue.
They also worked with a private security firm that was committed to inclusion.
There was some criticism that the organisers were allowing cisgendered and straight people to come into queer spaces but they insisted they wanted allies, families and friends to attend.
“Queer joy is one of the biggest forms of resistance,” Ikpe-Etim said, and they wanted people to experience the culture.
“We want to push the narrative that queer people exist. Changing the narrative of what queer people are seen as in Nigeria.”
Author Eloghosa Osunde, who was one of the judges, saw the Fola Francis Ball and others like it as “spaces where people feel less shame”.
“There’s no one identity that’s greater than the other just because it is validated by the law. I really believe we can create legitimacy for ourselves, and that’s one way for our world to grow.”
And the underground ball scene looks set to expand further in Lagos as more queer people feel the support from the community.
“Spaces like this are so important,” said another of the judges, fashion designer Weiz Dhurm Franklyn.
“Knowing you actually have space you can call home, and be free, and be yourself without judgement, without prejudice. It is utterly important not just for the sake of having fun, but for the sake of living.”
You may also be interested in:

Go to BBCAfrica.com, external for more news from the African continent.
Follow us on Twitter @BBCAfrica, external, on Facebook at BBC Africa, external or on Instagram at bbcafrica, external