UK economy had zero growth between July and September

- Published
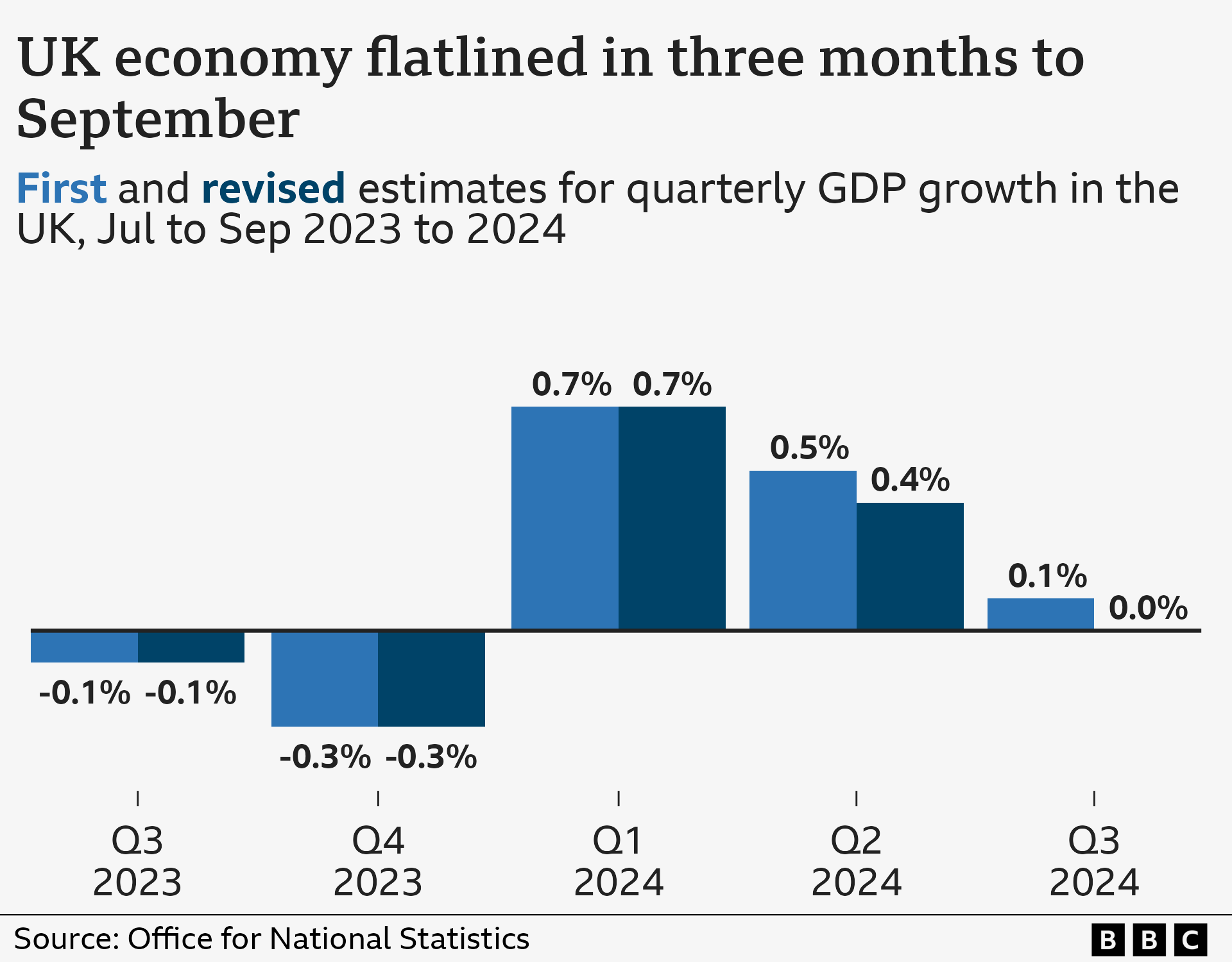
The UK economy had zero growth between July and September, revised official figures show.
The revised data comes after a series of disappointing figures including inflation rising at its fastest pace for eight months and the economy unexpectedly shrinking in October.
One of the UK's leading business groups, the CBI, said its latest company survey suggested "the economy is headed for the worst of all worlds".
Chancellor Rachel Reeves said the challenge to fix the economy "after 15 years of neglect is huge", while shadow chancellor Mel Stride said Monday's figures showed "growth has tanked on Labour's watch".
Initial figures had suggested the economy had grown by just 0.1% between July and September - and shrank during September itself. But that figure has now been revised down to 0%.
This will be a blow to the government which has made boosting the economy its top priority.
Labour has promised to deliver the highest sustained economic growth in the G7 group of the world's richest nations.
Businesses have already warned that measures announced in October's Budget including a rise in employer national insurance contributions (NICs) and a higher minimum wage could push them into cutting jobs and raising prices.
These Budget changes come into effect in April. But Stride said the latest figures from the three months before the October Budget signal "the warning lights are flashing" on how the economy will fare into 2025.
Reeves said Labour's Budget would "deliver sustainable long-term growth, putting more money in people's pockets through increased investment and relentless reform."
Liberal Democrat treasury spokesperson, Daisy Cooper called on the government to reverse the national insurance tax hike on small businesses and scrap the business rates system.
Job cuts and price rises
The CBI, which claims to represent 170,000 firms, said its survey based on responses of 899 firms between 25 November and 12 December, found private sector businesses across all industries expected a "steep decline in activity" in the first three months in 2025.
"Expectations are now at their weakest in over two years," said Alpesh Paleja, the CBI's interim deputy chief economist.
A separate survey by the British Retail Consortium, which represents UK retailers ranging from Marks and Spencer to Tesco, suggested a "January spending squeeze on the horizon" for consumers.
It said "public confidence in the state of the economy took a nosedive" this month, according to its consumer sentiment survey.
"With sales growth unable to keep pace, retailers will have no choice but to raise prices or cut costs – closing stores and freezing recruitment," said Helen Dickinson, chief executive of the BRC.

Mick Dore, general manager of the Alexander pub in Wimbledon, said its costs would rise in April due to the rise in national insurance contributions it makes for its 50 to 60 staff.
"All of December we've been crazy busy with loads and loads of work parties," he told BBC Breakfast. "There are cost implications going forward and we have to have a good Christmas to insulate ourselves against that."
But he said he was optimistic about business next year.
"I generally think as a whole we are going to be ok. I've been around a long time now and each time they've told me the end is nigh it never has been."
'Teeing up a recession?'
Paul Dales, chief economist at Capital Economics, said there was "no doubt that some business and households put spending and investment on hold around the Budget". But he said it was "too soon to see any genuine effect of Labour policies".
He said it would be a matter of time before the drag from higher interest rates gave way to a boost from lower rates but he expected to see an improvement in the second half of next year.
Simon French, chief economist at Panmure Liberum said the revised figures were consistent "with a lot of other indicators we've seen since the July general election that've shown a loss of momentum in the economy".
He said there was a question over whether this was a typical slowdown as seen after previous general elections which later picked up or "whether this is something more problematic teeing up a recession next year".
The Bank of England voted to hold interest rates on Thursday, stating it thought the UK economy had performed worse than expected, with no growth at all between October and December.
The UK economy is measured by gross domestic product - a measure of all the economic activity of companies, governments and people in the country.
The ONS puts out initial estimates on the UK's economic performance and revises them once it receives more data.
On Monday it also revised down growth figures for April to June to 0.4% from 0.5%.
It said the economy was weaker than initially estimated as bars and restaurants, legal firms and advertising firms performed less well.
"Real household disposable income per head showed no growth," ONS director of economic statistics Liz McKeown said.
Get in touch
Have you been impacted by this? Get in touch