New study on moons of Uranus raises chance of life

Artwork: Uranus and its five largest moons had been thought to be inactive and sterile.
- Published
The planet Uranus and its five biggest moons may not be the dead sterile worlds that scientists have long thought.
Instead, they may have oceans, and the moons may even be capable of supporting life, scientists say.
Much of what we know about them was gathered by Nasa’s Voyager 2 spacecraft which visited nearly 40 years ago.
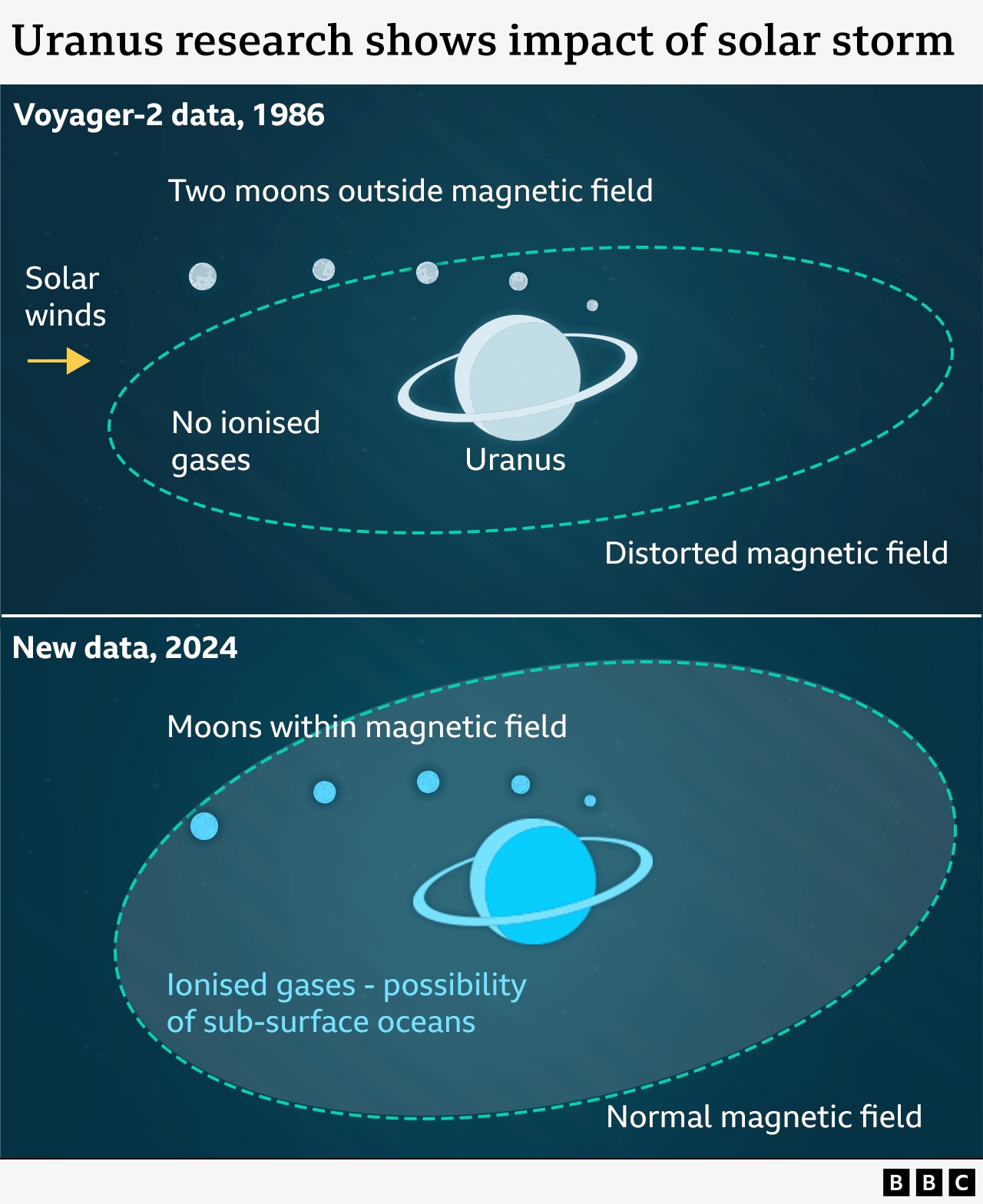
But a new analysis shows that Voyager's visit coincided with a powerful solar storm, which led to a misleading idea of what the Uranian system is really like.
Uranus is a beautiful, icy ringed world in the outer reaches of our solar system. It is among the coldest of all the planets. It is also tilted on its side compared to all the other worlds – as if it had been knocked over – making it arguably the weirdest.
We got our first close-up look at it in 1986, when Voyager 2 flew past and sent back sensational pictures of the planet and its five major moons.
But what amazed scientists even more was the data Voyager 2 sent back indicating that the Uranian system was even weirder than they thought.
The measurements from the spacecraft’s instruments indicated that the planets and moons were inactive, unlike the other moons in the outer solar system. They also showed that Uranus’s protective magnetic field was strangely distorted. It was squashed and pushed away from the Sun.
A planet’s magnetic field traps any gases and other material coming off the planet and its moons. These might be from oceans or geological activity. Voyager 2 found none, suggesting that Uranus and its five largest moons were sterile and inactive.
This came as an enormous surprise because it was unlike the solar system’s other planets and their moons.
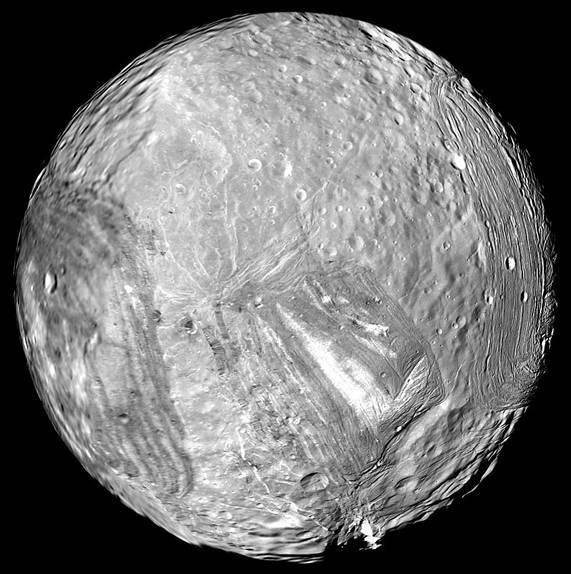
Miranda, one of the moons of Uranus, photographed by Voyager 2. The new research says the moon possibly has a sub-surface ocean and may even be home to life
Voyager 2 was launched in 1977 to study Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune
But the new analysis has solved the decades-long mystery. It shows that Voyager 2 flew past on a bad day.
The new research shows that just as Voyager 2 flew past Uranus, the Sun was raging, creating a powerful solar wind that might have blown the material away and temporarily distorted the magnetic field.
So, for 40 years we have had an incorrect view of what Uranus and its five largest moons are normally like, according to Dr William Dunn of University College London.
“These results suggest that the Uranian system could be much more exciting than previously thought. There could be moons there that could have the conditions that are necessary for life, they might have oceans below the surface that could be teeming with fish!”.

The first picture of Uranus was sent back by Voyager 2 in 1986
Linda Spilker was a young scientist working on the Voyager programme when the Uranus data came in. She is now still serving as the project scientist for the Voyager missions. She said that she was delighted to hear about the new results, which have been published in the Journal Nature Astronomy., external
“The results are fascinating, and I am really excited to see that there is potential for life in the Uranian system,” she told BBC News.
“I’m also so pleased that so much is being done with the Voyager data. It’s amazing that scientists are looking back at the data we collected in 1986 and finding new results and new discoveries”.
Dr Affelia Wibisono of the Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, who is independent of the research team, described the results as “very exciting”.
“It shows how important it is to look back at old data, because sometimes, hiding behind them is something new to be discovered, which can help us design the next generation of space exploration missions”.
Which is exactly what Nasa is doing, partly as a result of the new research.
It has been nearly 40 years since Voyager 2 last flew past the icy world and its moons. Nasa has plans to launch a new mission, the Uranus Orbiter and Probe, to go back for a closer look in 10 years’ time.
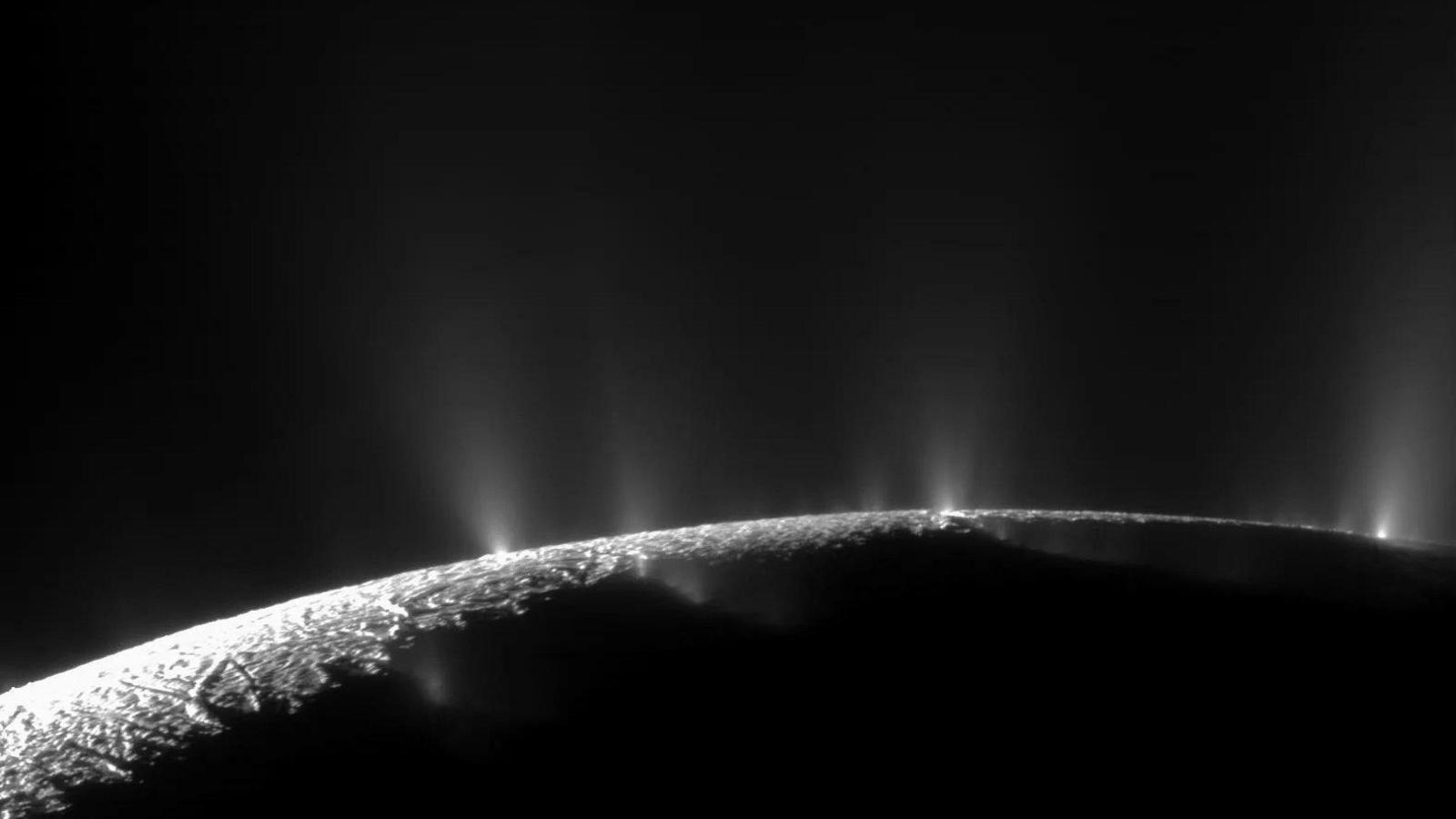

Plumes of material coming from Enceladus, one of the moons of Saturn, indicating a possible sub-surface ocean. Could the same be true of the Uranian moons?
According to Nasa’s Dr Jamie Jasinski, whose idea it was to re-examine the Voyager 2 data, the mission will need to take his results into account when designing its instruments and planning the scientific survey.
“Some of the instruments for the future spacecraft are very much being designed with ideas from what we learned from Voyager 2 when it flew past the system when it was experiencing an abnormal event. So we need to rethink how exactly we are going to design the instruments on the new mission so that we can best capture the science we need to make discoveries”.
Nasa’s Uranus probe is expected to arrive by 2045, which is when scientists hope to find out whether these far-flung icy moons, once thought of as being dead worlds, might have the possibility of being home to life.