Ukraine front could 'collapse' as Russia gains accelerate, experts warn

- Published
President Biden’s decision to provide anti-personnel mines to Ukraine, and allow the use of long-range missiles on Russian territory comes as the Russian military is accelerating its gains along the front line.
Data from the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) shows that Russia has gained almost six times as much territory in 2024 as it did in 2023, and is advancing towards key Ukrainian logistical hubs in the eastern Donbas region.
Meanwhile, Ukraine's surprise incursion into Russia's Kursk region is faltering. Russian troops have pushed Kyiv's offensive backwards. Experts have questioned the success of the offensive, with one calling it a "strategic catastrophe" given manpower shortages faced by Ukraine.
These developments come at a time of heightened uncertainty with a second Donald Trump administration looming. The US president-elect has vowed to bring the war to a close when he takes office in January, with some fearing he could cut future military aid to Ukraine.
Russia advances in eastern Ukraine
In the first few months of the war the front line moved quickly, with Russia gaining ground quickly before being pushed back by a Ukrainian counteroffensive. But in 2023 neither side made any major gains - with the conflict largely sliding into a stalemate.
But new ISW figures suggest the story in 2024 is more favourable for Russia. The ISW bases its analysis on confirmed social media footage and reports of troop movements.
The ISW data shows Moscow’s forces have seized around 2,700 sq km of Ukrainian territory so far this year, compared with just 465 sq km in the whole of 2023, a near six-fold increase.
Dr Marina Miron, a defence researcher at Kings College London, suggested to the BBC that there was a possibility the Ukrainian eastern front “might actually collapse” if Russia continued to advance at pace.
More than 1000 sq km was taken between 1 September and 3 November, suggesting the push accelerated in recent months. Two areas bearing the brunt of these advances are Kupiansk in Kharkiv region, and Kurakhove, a stepping stone to the key logistical hub of Pokrovsk in Donetsk region.
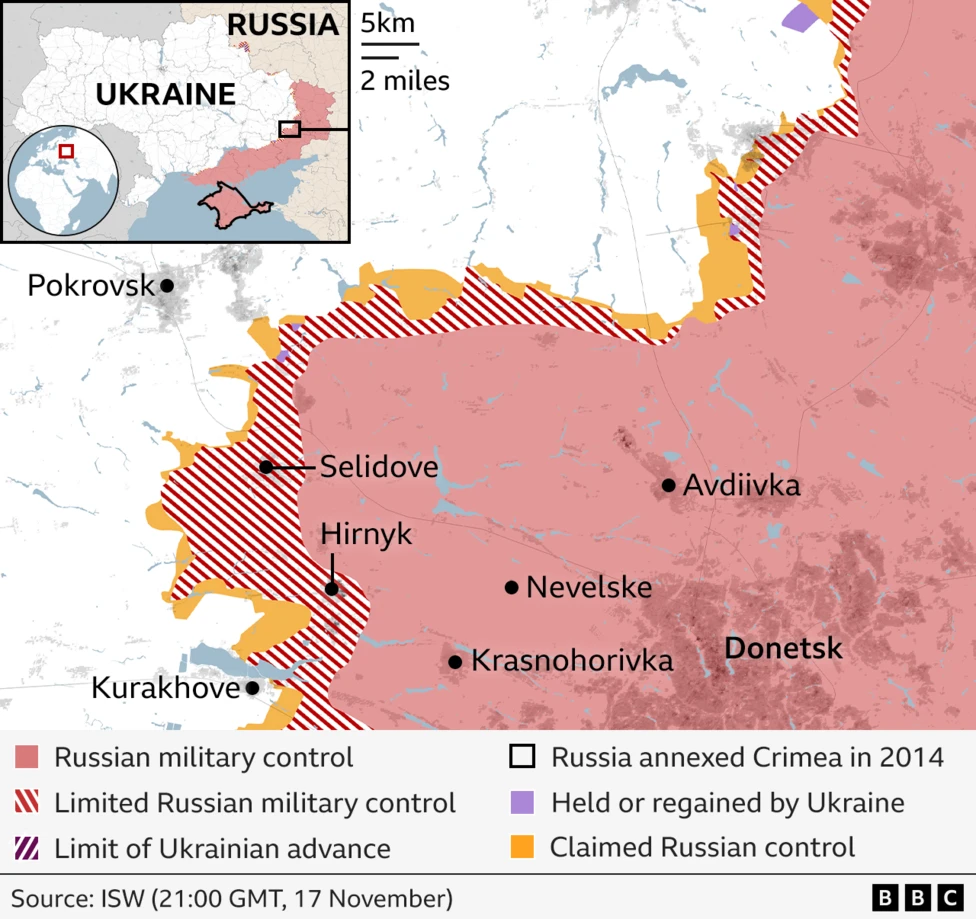
The ISW suggests that Russian forces have steadily advanced in eastern Ukraine.
Kupiansk and areas to the east of the Oskil river were liberated in the Kharkiv offensive of 2022, but Russia has progressively retaken the latter area. In a recent intelligence update, the UK's Ministry of Defence said Russian forces were trying to breach the north-eastern outskirts of the city.
Footage posted on 13 November and verified by the BBC is consistent with this analysis. The video shows a convoy of Russian armour being repelled after making it to within 4km of the key bridge at Kupiansk, the last major road crossing in the area.
While these reports do not necessarily translate to control of an area, it is indicative of how stretched Ukraine’s defensive line has become.
Elsewhere, since retaking the city of Vuhledar in October - an elevated position which sits above key supply lines and which Moscow spent two years fighting for - Russia has thrown resources at Kurakhove.
Ukraine’s forces defending the city have so far repelled attacks to the south and east. But the front line creeps ever closer, with Russia also threatening to encircle defenders from the north and west.
Col Yevgeny Sasyko, a former head of strategic communications with Ukraine’s general staff, said Russia places “powerful jaws” around the flanks of a city that slowly “grind though” defences until they collapse.
Footage from the city verified by the BBC showed massive destruction, with residential buildings heavily damaged.
The ISW concludes Moscow now holds a total of 110,649 sq km in Ukraine. For comparison, Ukrainian forces seized just over 1,171 sq km in the first month of its incursion into Kursk - though Russian forces have now retaken nearly half of that territory.
Despite its territorial gains, Russia's advance has come at a huge cost.
An analysis carried out by BBC Russian confirmed that at least 78,329 troops have been killed since Russia launched its full-scale invasion in February 2022, with Moscow’s losses from September to November this year more than one-and-a-half times greater than the same period in 2023.
The losses are compounded by the “meat grinder” approach said to be favoured by Russian commanders - describing the waves of recruits thrown towards Ukrainian positions in a bid to exhaust troops.
Despite the Russian advances, some experts have noted that the actual speed of the offensive is still slow. David Handelman, a military analyst, suggested Ukrainian troops in the east were slowly withdrawing to preserve manpower and resources, rather than suffering from a broader collapse.
The Kursk gambit
Ukraine launched its shock incursion into Russia’s Kursk region in August. It is unclear why Russia took so long to respond to the operation, which saw Kyiv’s troops quickly gain control over a number of border communities.
Dr Miron suggested that while the Kremlin would suffer a domestic political cost for as long as the incursion continued, Russia’s general staff had been keen to keep Ukraine’s forces tied down in Kursk as its forces made gains elsewhere along the front line.
But Moscow is now clearly intent on reclaiming the territory lost on its own soil. Some 50,000 troops have been deployed to the region.
Verified videos from the Kursk region show fierce fighting is taking place - and that Russia is suffering considerable losses in terms of manpower and equipment. But the data clearly shows Ukraine’s control of the region is shrinking.
Since the start of October, Russian counter-attacks have regained some 593 sq km worth of territory in the border region, ISW figures showed.
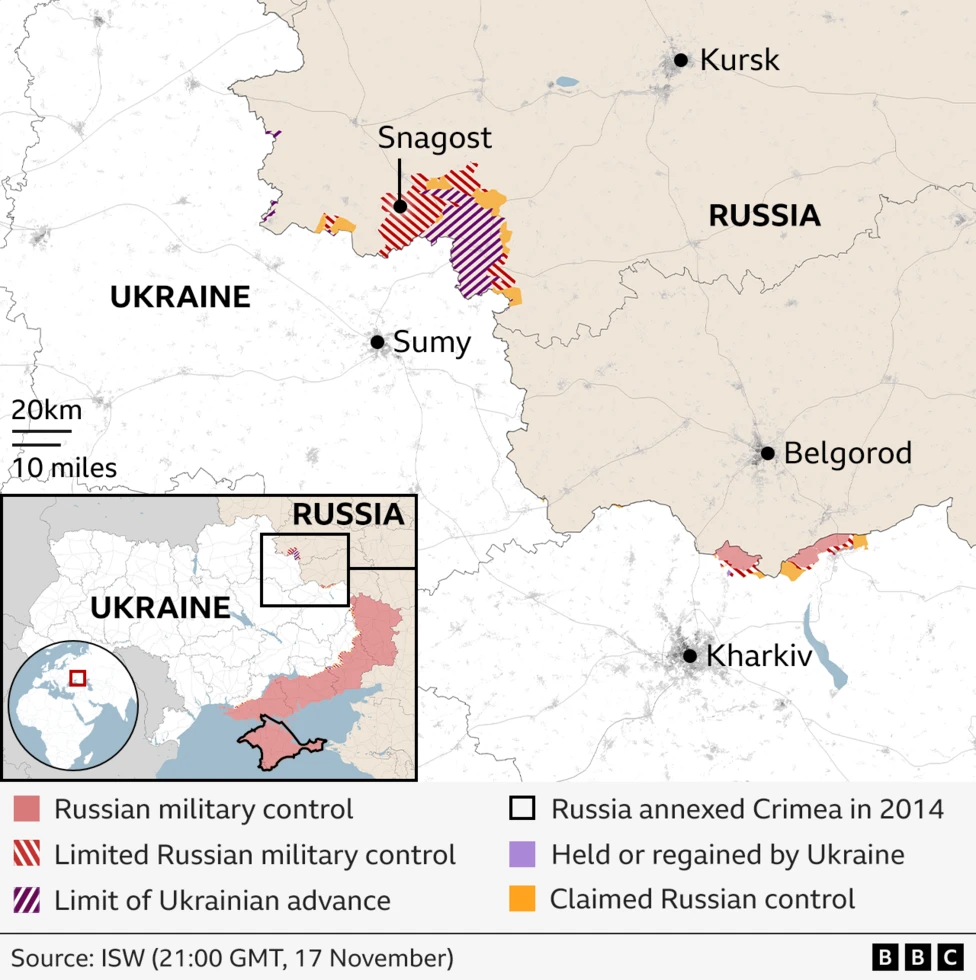
In Kursk, the ISW suggests Russia has steadily won back territory.
The Kursk incursion was initially a major boon for Ukraine in terms of morale at a time of serious setbacks, and the audacity of the operation was a reminder of its ability to surprise and harm its enemy.
But Dr Miron said while the Kursk incursion was a moment of “tactical brilliance” it has also been a “strategic catastrophe” for Ukraine.
“The whole idea was to maybe gain some political leverage in potential negotiations, but militarily to draw the Russian forces away from the Donbas in order to liberate Kursk. And what we're seeing instead is that Ukrainian units are tied down there.”
Some of Kyiv’s most experienced and effective units are known to be fighting in Kursk. Mechanised units equipped with state-of-the-art Western armour are also involved in the offensive.
Ukrainian leaders had hinted that they hoped the incursion would force Moscow to redirect some of its forces from eastern Ukraine, slowing the Russian advance there. Instead, experts say most reinforcements were moved to Kursk from parts in Ukraine where the fighting is not as intense.
“According to Ukrainian soldiers from different parts of the front, the Russian troops reinforcing Kursk were mainly pulled from Kherson and Zaporizhzhia,” Yurri Clavilier, a land analyst with the International Institute for Strategic Studies, told the BBC.
“The fighting there is not as intense as it is in the East. Some Russian units attacking Kharkiv were also redirected to Kursk as Ukraine managed to stall the Russian onslaught there,” he added.
The importance of territory to both sides is the strength it lends to their position in any potential negotiations. Although no peace negotiations have been discussed, US President-elect Trump has claimed he could end the war within 24 hours, without saying exactly how.
Fears persist in Ukraine that Trump could cut military aid as a means to force Kyiv to the table. President Volodymyr Zelensky told Fox News on Tuesday "I think we will lose [the war]" if cuts are pushed through.
"We have our production, but it's not enough to prevail and I think it's not enough to survive," he said.
On Tuesday, Ukraine fired US-supplied long-range missiles into Russia for the first time - a day after Washington gave it permission to do so. It is thought that the decision was made in part to help Ukraine hold on to part of the Kursk region, to help use as a bargaining chip in future negotiations.
Dr Miron told the BBC that Russia’s advance has handed them a stronger negotiating position as Trump’s new foreign policy team prepare to take office.
“What they're controlling right now, it does give them a certain advantage,” she said. “If it came to negotiations, I'm sure that as the Russian side has been stressing, ‘we will do it based on the battlefield configuration’.
“From a Russian perspective, they have much better cards than the Ukrainians.”

Related topics
- Published20 November 2024

- Published24 December 2024