Fuel poverty to rise to 8.5m, report warns
- Published
- comments
Fuel poverty in England is likely to worsen, despite measures to try to eradicate it, a government-commissioned report has warned.
Some 7.8 million people could not afford their energy bills in 2009, its author, Prof John Hills said. This is due to rise to 8.5 million by 2016.
Campaigners have called for more money to be invested in cutting bills.
The government has said it is committed to tackling the problem which has been linked to 2,700 deaths a year.
"Fuel poverty is a serious national problem and this government remains committed to doing all it can to tackle it and make sure that the help available reaches those who need it most," said the Secretary of State for Energy and Climate Change, Ed Davey.
The previous government had said it was committed to eradicating the problem, "as far as reasonably practical", by 2016.
Prof Hills' interim report last year said almost 3,000 people died each year from problems linked to fuel poverty such as respiratory or cardiovascular disease. It said the problem was getting worse as energy costs rose.
But he said the difficulties went beyond health to education and climate change.
"It is also bad for families with older children, if they can't afford to keep a room warm enough for them to get on quietly with their homework," Prof Hills told the BBC.
"People who find their homes hard to heat are pumping out carbon into the atmosphere which is blocking some of the efforts to reduce carbon emissions."
Green deal
Prof Hills' report redefines fuel poverty to focus on households which are both on low income and have relatively high bills.
The new definition includes many lower-income households with relatively high heating and cooking costs which may have been ignored in the past.

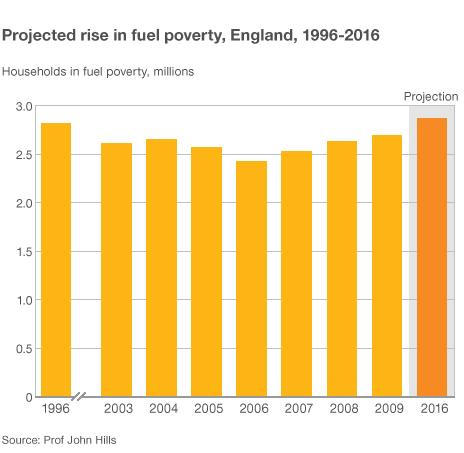
Fuel poverty is expected to rise over the next four years
"When one focuses on the core of the problem in the way I propose, the outlook is profoundly disappointing," said Prof Hills.
"With the scale of the problem heading to be nearly three times higher in 2016 - the date legislation set for its elimination - than in 2003."
The government has said it will publish its own new definition in the summer.
Regressive
He called for action to insulate the poorest homes, but warned current government measures would have mixed results.
The Energy Company Obligation (ECO) allows firms to levy a flat charge on bills to subsidise insulation.
But with only a quarter of the money specifically targeted at low-income homes, Prof Hills warns it may be "regressive", driving extra homes into fuel poverty.
The government's own Fuel Poverty Advisory Group (FPAG) has called on it to use projected revenues from a minimum price on carbon and carbon trading to tackle fuel poverty.
The government said it is already tackling the problem through a range of other measures, including the Warm Homes Discount, which offers help with bills to low-income households.
New approach
"The number of fuel-poor households helped by government-backed schemes is likely to more than halve over the next three years, despite fuel poverty levels having almost tripled in five years," said Derek Lickorish, chairman of the FPAG.
The new definition is designed to exclude households who are relatively wealthy and have high bills, or who are living on low incomes but have relatively low bills.
By this definition, the report finds 7.8 million people were fuel-poor in 2009, across 2.7 million households, more than previously thought.
Under the previous definition, which focused on households spending 10% of their income on bills, four million households were in fuel poverty but with 7.6 million inhabitants.
Poverty gap
In addition to examining the extent of fuel poverty, the report also includes a measure of its severity.
The fuel poverty gap shows the amount by which bills would need to be cut, in order for fuel-poverty households to be able to afford to heat their homes.
The report found that in 2009, this figure was £414 per household. By 2016, the report warns, it may be £600.
Campaigners have welcomed the report and also called for a programme of home insulation.
"The time has come for the government to step up and invest to help the fuel-poor households through a major expenditure and an extensive insulation programme," said Michelle Mitchell, director general at Age UK.