Boeing grounds entire 737 Max crash aircraft fleet
- Published
Trump: Boeing 737 Max planes grounded
Boeing has grounded its entire global fleet of 737 Max aircraft after investigators uncovered new evidence at the scene of the fatal Ethiopian Airlines crash.
The US plane-maker said it would suspend all 371 of the aircraft.
The Federal Aviation Administration said fresh evidence as well as newly refined satellite data prompted the decision to temporarily ban the jets.
The FAA had previously held out while many countries banned the aircraft.
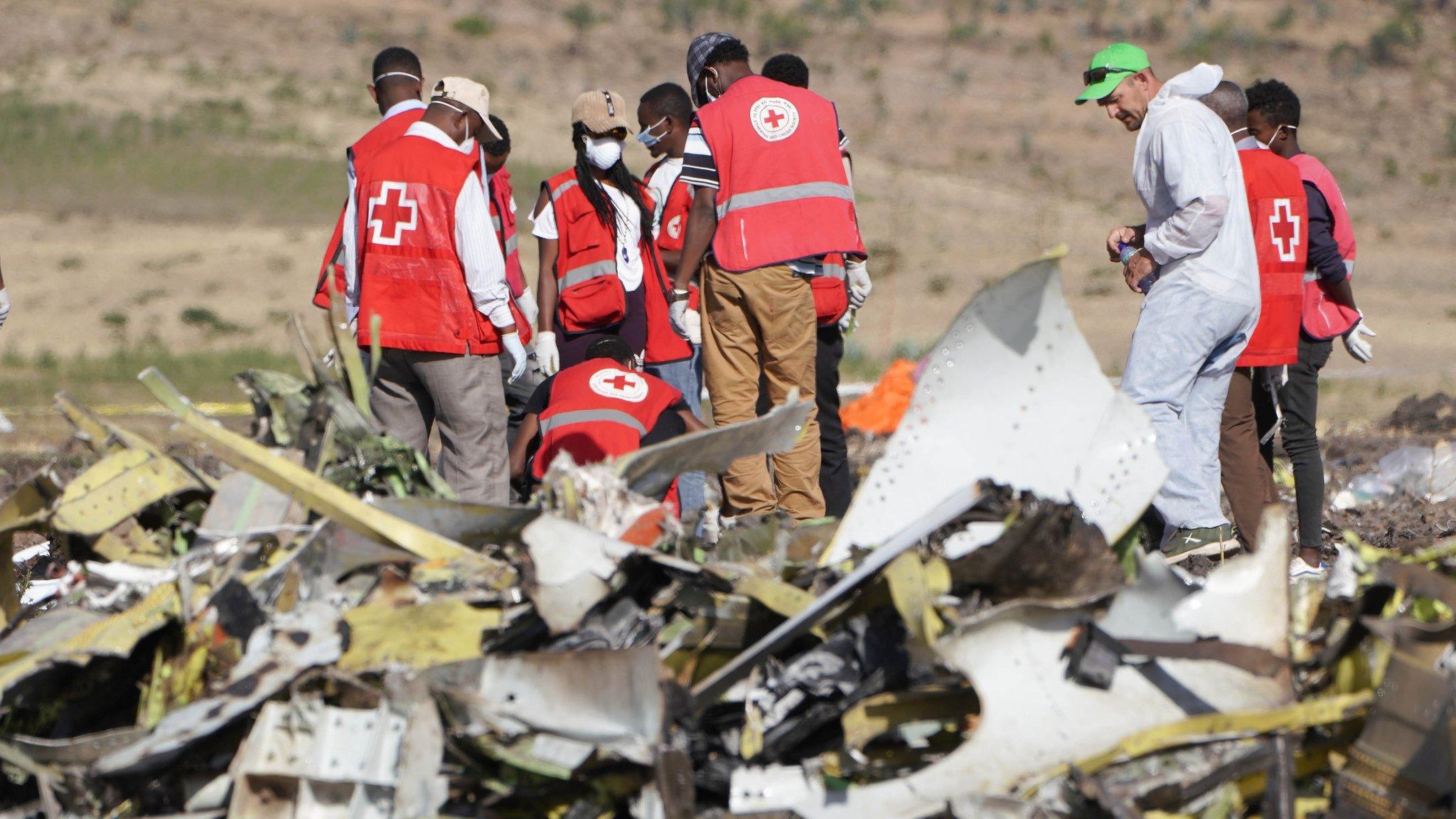
All 157 passengers and crew died in Sunday's crash. Ethiopian Airlines said on Thursday that the black box flight recorders from the aircraft have been flown to Paris for analysis.
"An Ethiopian delegation led by Accident Investigation Bureau has flown the Flight Data Recorder and Cockpit Voice Recorder to Paris, France for investigation," the airline wrote on Twitter.
What has the FAA discovered?
The FAA has a team investigating the disaster at the Ethiopian Airlines crash site working with the National Transportation Safety Board.
Dan Elwell, acting administrator at the FAA, said on Wednesday: "It became clear to all parties that the track of the Ethiopian Airlines [flight] was very close and behaved very similarly to the Lion Air flight."
He added that "the evidence we found on the ground made it even more likely the flight path was very close to Lion Air's".

Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

President Donald Trump initially announced that the FAA would be making an emergency order following "new information and physical evidence that we've received from the site and from other locations and through a couple of other complaints".
The US and Brazil became the latest countries to suspend the Boeing 737 Max from flying after nations including the UK, China, India and Australia all grounded the aircraft.
Until Wednesday, the FAA position was that a review had showed "no systemic performance issues" and that there was no basis for grounding the aircraft.
Earlier in the day, Canada grounded the planes after its transport minister Marc Garneau said he had received new evidence about the crash.
He said that satellite data showed possible similarities between flight patterns of Boeing 737 Max planes operating in Canada and the Ethiopian Airlines plane that crashed.
What has Boeing said?
Boeing, the US plane manufacturer, said that it "continues to have full confidence in the safety of the 737 Max".
However, it added that after consultation with the FAA and the National Transportation Safety Board it had decided to ground the flights "out of an abundance of caution and in order to reassure the flying public of the aircraft's safety".
Dennis Muilenburg, president, chief executive and chairman of Boeing, said: "We are doing everything we can to understand the cause of the accidents in partnership with the investigators, deploy safety enhancements and help ensure this does not happen again."
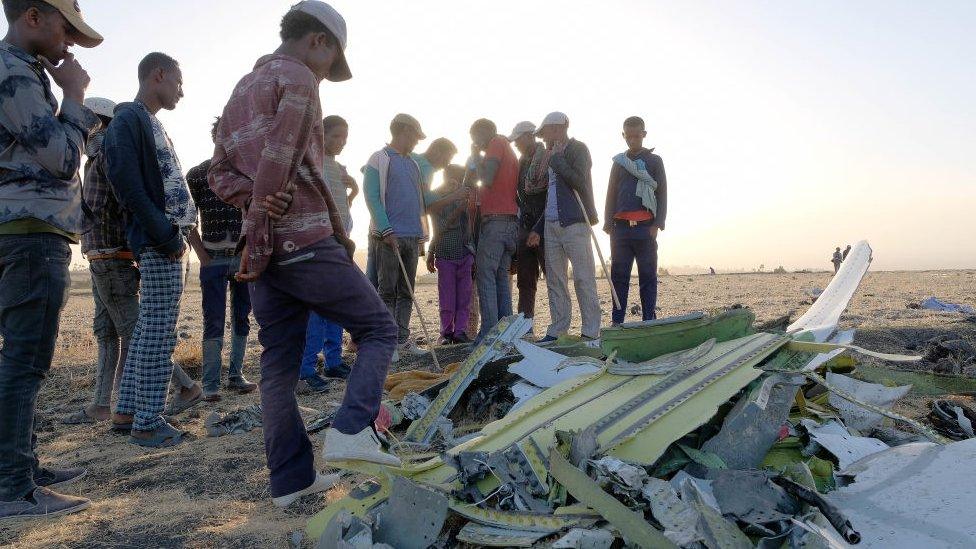

People gather at the Ethiopian Airline crash site
Sara Nelson, president of the Association of Flight Attendants-CWA, said: "Lives must come first always. But a brand is at stake as well. And that brand is not just Boeing. It's America. What America means in international aviation and by extension in the larger world more generally—that we set the standard for safety, competence, and honesty in governance of aviation."
Shares in Boeing ticked higher to $377 each following the announcement.
However, the company's market value has dropped by nearly $26bn since the crash in Ethiopia at the weekend.
What will happen to airline customers?
Southwest Airlines said it had immediately removed all 34 of the planes from scheduled service.
Although it has the biggest fleet of Boeing 737 Max 8 planes in the world, Southwest Airlines said they account "for less than 5% of our daily flights".
It said it is offering "flexible rebooking policies" which means that any customer booked on a cancelled Max 8 flight can rebook on alternate flights "without any additional fees or fare differences within 14 days of their original date of travel".



American Airlines said 24 of its aircraft would be affected by the suspension, adding: "Our teams will be working to rebook customers as quickly as possible, and we apologise for any inconvenience."
United Airlines said that its Max aircraft account for roughly 40 flights a day.
It said: "Through a combination of spare aircraft and rebooking customers, we do not anticipate a significant operational impact as a result of this order."

Analysis: Theo Leggett, BBC international business correspondent
With other aviation authorities around the world deciding to ground the 737 Max, the FAA - which provides the safety certification for the new aircraft - was under intense pressure to fall into line.
What's interesting here, though, is what the FAA has actually said.

While the UK's Civil Aviation Authority, for example, said its actions were simply precautionary, the FAA has gone further.
The US regulator, which is actually involved in the investigation, says it has made its decision as a result of new evidence collected at the site and analysed today - as well as satellite data.
That will have set alarm bells ringing at Boeing's headquarters in Chicago.
Since the accident, analysts have focused on similarities between Sunday's tragedy, and another crash involving a 737 Max off Indonesia last October.
Has the FAA found evidence that suggests those similarities were more than just superficial?
And does that mean Boeing's MCAS anti-stall system, already implicated in the Indonesia crash, may also have played a role in the latest disaster?

What have pilots said about the 737 Max 8?
Pilots in the US had complained late last year about problems controlling the Boeing 737 Max 8 during take-off.
They reported difficulties similar to those that contributed to the fatal Lion Air crash in Indonesia in October.
The Ethiopian Airlines plane crashed minutes into its flight.
Flightradar24, an air traffic monitor, said the plane's "vertical speed was unstable after take-off".

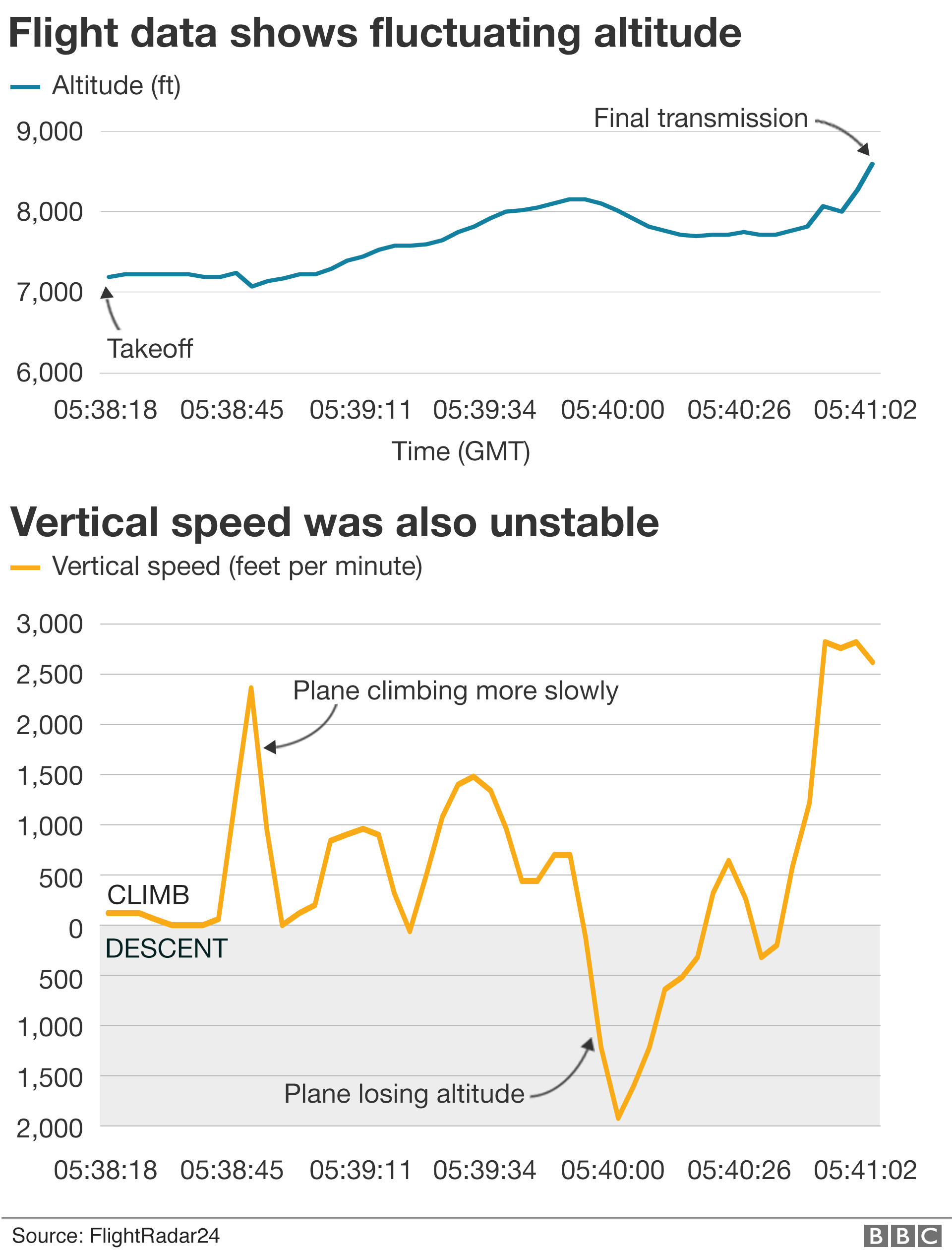

Documents reveal that pilots flying last November reported engaging autopilot only for the aircraft's nose to pitch lower, prompting the warning system to exclaim: "Don't sink! Don't sink!"
Two US pilots reported separate incidents involving the 737 Max's automatic anti-stalling system in November.
The feature, which was new to the 737 Max family, is designed to keep the plane from stalling.
The system prevents the aircraft from pointing upwards at too high an angle, where it could lose its lift.
However, according to filings with the US Aviation Safety Reporting System, which pilots use to disclose information anonymously, it appeared to force the nose down.
In both cases, pilots were forced to intervene to stop the plane from descending.
After the Lion Air crash, Boeing issued a bulletin on what to do regarding erroneous readings from the sensor, which sends out information about what angle a plane is flying at.
- Published5 April 2019

- Published14 March 2019

- Published13 March 2019

- Published13 March 2019

- Published12 March 2019
