Coronavirus: UK pharmacies see sanitiser sales spike
- Published

Pharmacies say they have seen a spike in sales of hand sanitisers and more demand for face masks in the wake of the coronavirus outbreak.
While virologists say hand sanitising can help stop the virus, they say there is not much evidence that face masks help.
Hand washing with soap is still the best cleaning practice, says the NHS.
Nonetheless, some online shops show a shortage of sanitiser and some stores are saying they don't stock masks.
Boots has seen an increase in sales of its own brand anti-viral hand foam and hand sanitisers, the BBC understands, and while some lines are out of stock, others can still be bought.
Ian Anderson, director of marketing at Nice Pak International, one of the world's biggest manufacturers of hand wipes, including the Sani Hands brand, said his firm's sales are up.
"At the moment we are trying to work out how best we can respond to that and in terms of supply chain management making sure we can access sufficient raw materials to keep pace with it - we are identifying how we can keep up with demand," he told the BBC. The firm has two factories in the UK and one in Germany.
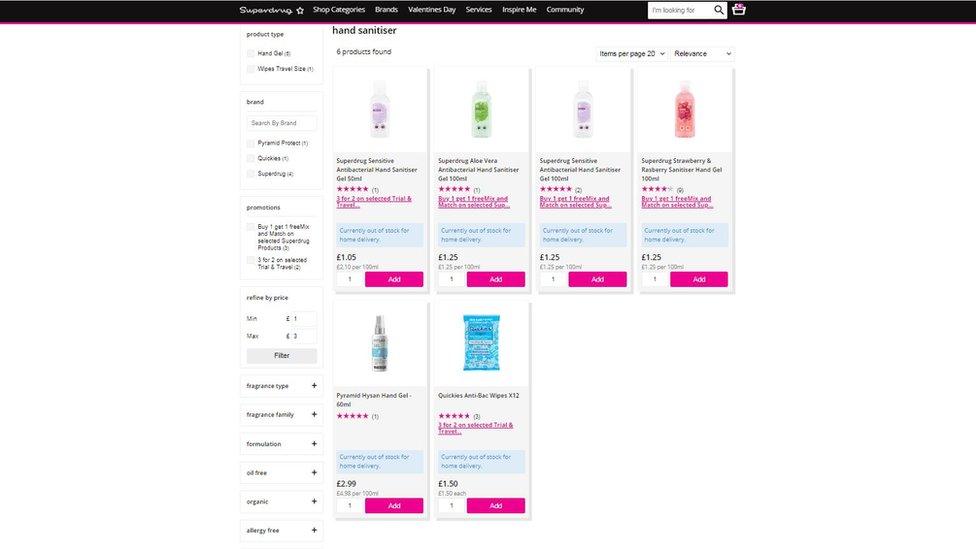
Superdrug's website says hand sanitisers are not available for home delivery
Dorset-based medical supplies firm MediSupplies, external told customers on its website: "Due to the current high volume of face masks orders, we are unable to offer any face masks at this time." It advised customers to wash their hands and consider disinfectant wipes, sprays and gloves.
The Tesco and Morrisons websites are showing that some cleansing gels are out of stock.
The supermarkets declined to comment on sales.
"We know that in a hospital setting surgical masks are very effective and that's because the people using them are trained in their use," said Jonathan Ball, professor of virology at the University of Nottingham.
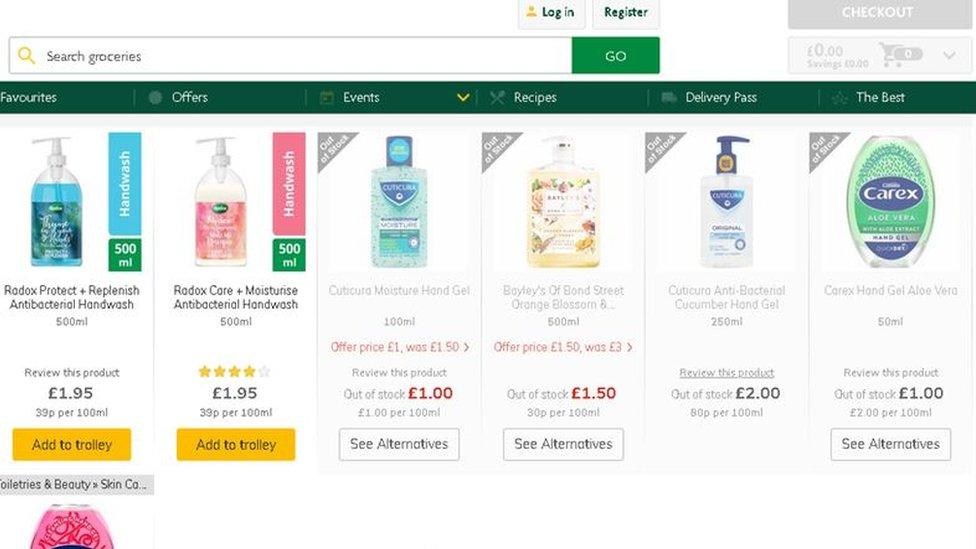
Morrisons website showed not all hand sanitisers were in stock
The mask must be properly fitted for it to filter all incoming air, he said. Users must also avoid cross contamination when taking it off, not wear them for too long and not meddle with them.
In a hospital, a doctor or nurse treating an infected patient might wear a gown, gloves, goggles and a mask, changing all of these once their time with the patient is over, he said. This isn't practical outside a hospital.
In the wider world "the consensus is it doesn't work," he said.
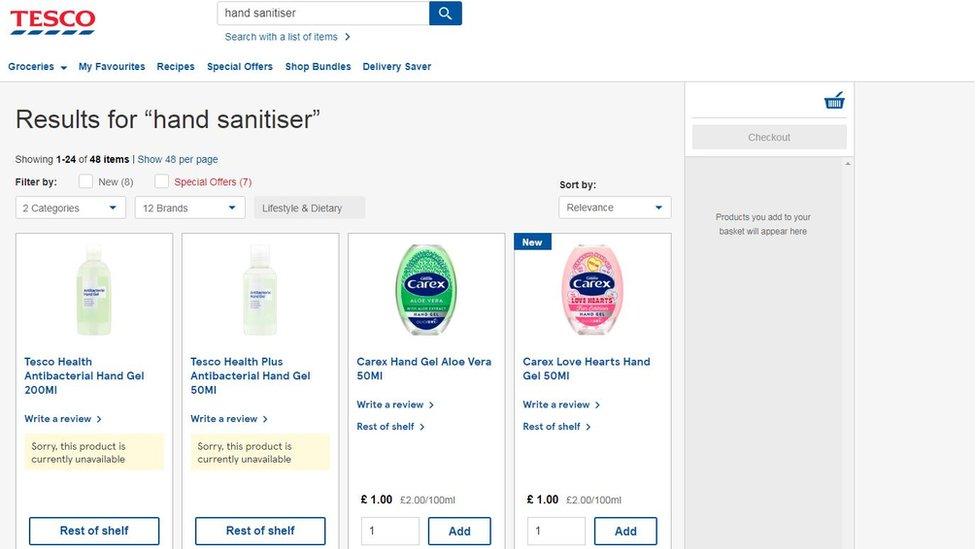
Tesco's website said two own brand products were not available
Instead, detergents, including soap, and disinfectants are "generally effective" against this kind of virus, he said.
Viruses similar to the structure of coronavirus are sensitive to alcohol and detergents, which can help break down their oily, fatty shells.
"Because sanitisers on the whole have alcohol, it does the same thing, breaks apart the virus particle," although there's evidence they are only effective when applied to a relatively clean surface, he warns. For muddy hands, soap and water are best.
The NHS says the best way to avoid catching viruses such as flu, external is to:
regularly wash your hands with warm water and soap
avoid touching your eyes and nose wherever possible
maintain a fit and healthy lifestyle

Walking into a central London Boots this afternoon, the hand sanitiser shelf only had a few bottles left. And customers were making a beeline for them.
People told me they had started to use these sorts of products more regularly, particularly after being on public transport.
One of the world's biggest manufacturers of antibacterial wet wipes, Nice Pack International, says they are concerned about keeping up with this surge in demand.
This spike in antibacterial product sales is however a rare positive business story in a nightmare scenario.
Many UK businesses will have a link to China, even if it is through a customer or trading partner's supply chain.
The ongoing quarantines and closures could mean that their ability to obtain or sell products is threatened.
And not knowing how long it will continue makes the situation even more difficult to manage.
According to George Magnus from Oxford University's China Centre, if it continues beyond mid-February, the hit to China's economic growth could be as much as 1 or 2 percentage points. And this will have an impact on global growth too.
Related topics
- Published16 March 2022

- Published30 January 2020
