Music royalties reach a record high - but a storm is coming
- Published

Ed Sheeran and Mabel were among the British singer-songwriters who scored major hits in 2019
Musicians and songwriters in the UK received a record amount of money last year, but the loss of live music poses a major threat to income in 2020.
The warning was issued by PRS for Music, the body that makes sure 145,000 songwriters, composers and publishers in the UK are paid when their music is played or performed around the world.
The organisation collected a record £810m last year, a rise of 8.7%.
But it said Covid-19 would result in an "inevitable decline" in 2020 and 2021.
"Even though we had a record-breaking year, we know very well that we're in unprecedented, unpredictable times," chief executive Andrea Martin told the BBC.
Revenues from "live music and public performance will be hit" not just in 2020 but in 2021, as international payments often take time to trickle down, she said.
"There will be a downfall," she added. "But by how much and by what per cent... your guess is just as good as mine."
The situation will hit smaller acts, many of whom were already struggling before the pandemic, the hardest.
'Catastrophic blow'
PRS processed 18.8 trillion "performances" of music last year, including streams, downloads, radio and TV broadcasts, and music played in pubs, clubs, hairdressers and concert venues.
UK songwriters contributed to many of the year's most-played hits, including like Someone You Loved by Lewis Capaldi, Old Town Road by Lil Nas X and Don't Call Me Up by Mabel.
Live music generated £54m in royalties, up £15m since 2018. Revenues were boosted by major tours from the Spice Girls, Sir Elton John, Ed Sheeran and the return of Glastonbury after a fallow year in 2018.
But with an entire summer of festivals cancelled and dozens of major tours postponed until 2021, that figure will be impossible to recreate in next year's results.
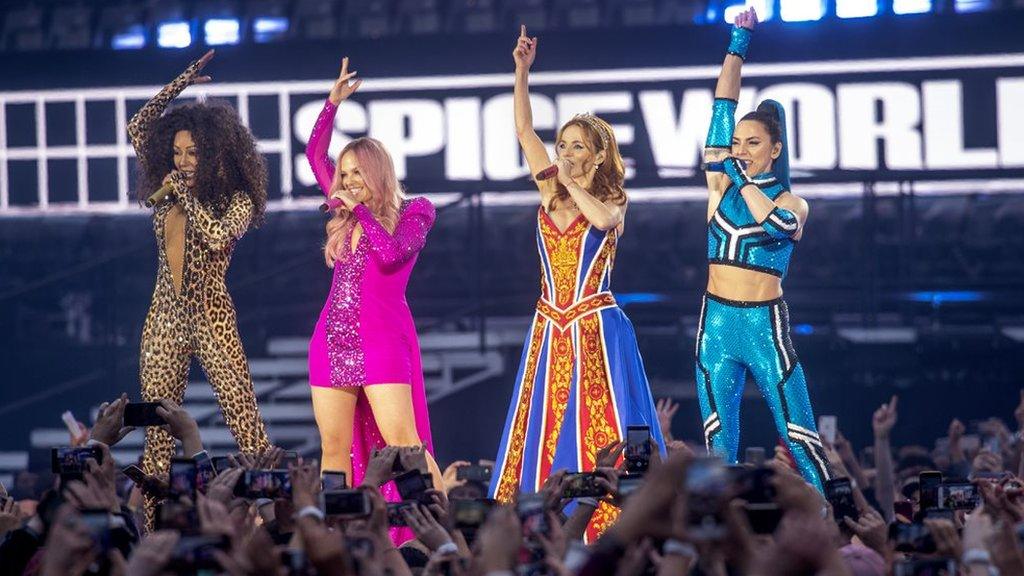

The Spice Girls' reunion tour grossed £78m last year, but this summer's stadium concerts have been cancelled
Last week, UK Music revealed the contribution of live music to the UK economy is set to drop in 2020 from an estimated £1.1bn to £200m, describing it as a "catastrophic" blow to the industry.
Meanwhile, the Ivors Academy of songwriters and composers said it anticipated a loss of £25,000 per member over a six-month period.
The lockdown also means songwriters will lose out on royalties gathered when their music is played in shops, cinemas, pubs, clubs and restaurants. In 2019, that figure was £168.2m.
There is some good news, however. Royalties from music streaming rose 22.1% to £155m, while the money generated from music on video-on-demand services like Amazon and Netflix increased 47.5% to £17.7m.
Early figures suggest more people have taken out streaming subscriptions during the lockdown, which may provide a small counterweight to the loss of live music.
But many musicians have noted that the money they receive from the likes of Spotify, Apple Music and Amazon is not enough to sustain a career.
Tom Gray from indie band Gomez recently shared a chart, originally compiled by The Trichordist, showing how many streams artists require to make a living in the UK.
On YouTube, a song would have to be played 7,267 times to generate £8.72 - or one hour of minimum wage. On Spotify, the figure was 3,114 streams, and on Apple Music 1,615 streams.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

That has led to a campaign, #BrokenRecord, seeking a more equitable system of distributing streaming money.
Spearheaded by the Ivors Academy and the Musicians' Union, it is calling for a new system, where your subscription fee is distributed to the artists you actually listen to - rather than going into a central pot, where money is split between the most-streamed songs on a percentage basis.
"This is what the consumer wants," said Graham Davies of the Ivors Academy, external, who is calling for a government-backed review.
"They want their £9.99 a month to be paid to the artists, performers, songwriters and composers of the music they love."
In the meantime, the PRS Emergency Relief Fund has raised more than £2.1m to help members who have lost income as a result of Covid-19. Martin says 1,600 songwriters have applied for assistance in the last week alone.
Another £5m fund, set up by the charity Help Musicians, ran out of cash within a week after being launched in March.
Trade body UK Music has subsequently called on the government to set up a new taskforce to revive the music industry as it navigates the pandemic.

Follow us on Facebook, external, or on Twitter @BBCNewsEnts, external. If you have a story suggestion email entertainment.news@bbc.co.uk, external.
- Published1 January 2020
