Crippling viral infections 'cause asthma'
- Published
How could a virus increase the risk of asthma?
Viral infections in newborns "cripple" part of the immune system and increase the risk of asthma later in life, US researchers studying mice have said.
They showed infections by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) stripped immune cells of their ability to calm down inflammation in the lung's airways.
They say their findings, published in the journal Nature Medicine, external, will help develop ways of preventing asthma.
The charity Asthma UK said the study had "really exciting" potential.
When something irritates the airways of a patient with asthma, the airways become tightened, inflamed and produce too much sticky mucus. All of this can make breathing difficult.
Previous studies have shown a link between repeated lung infections with RSV and developing asthma later in life.
One Swedish study showed, external showed 39% of infants taken to hospital with RSV had asthma when they were 18. However, only 9% of infants who were not ill developed asthma.
How the virus might be able to do this was, however, unknown. Now a team of researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine believe they have an explanation.
Their experiments on mice showed the virus impaired the ability of a specific part of the immune system, called regulatory T cells, to calm inflammation.
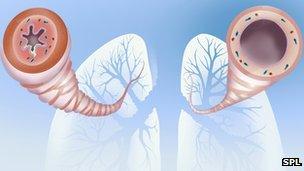
The tightened airway of an asthma patient (left) and a healthy airway
Inflammation is an important part of dealing with an infection. However, for asthma patients, chemicals in air which come from ordinary things like dust mites, pets and mould can trigger an inappropriate inflammatory response.
Infection with RSV led to a "complete loss of suppressive function" of the regulatory T cells, after which the mice developed asthma-like symptoms," researchers Prof Anuradha Ray and Prof Prabir Ray told the BBC.
Early window
They said there might be a window in early life when the cells were vulnerable to being "crippled".
They think the finding could help scientists devise treatments which prevent some people developing asthma.
"We feel that both prophylactic and therapeutic approaches can be developed.
"This is especially desirable in infants who have a strong family history of asthma."
Malayka Rahman, from Asthma UK, said: "This research provides vital information on how viruses interact with our immune cells and why this might lead to an increased risk of asthma.
"What's really exciting is the potential of these findings to translate into new treatments for asthma in the future."
- Published1 May 2012
- Published20 January 2012
- Published21 July 2012
- Published1 February 2012
- Published8 June 2011