Coronavirus: What's the evidence Europe is having a 'second wave'?
- Published

UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson has warned there are signs of a "second wave" of coronavirus cases in Europe, but what's the evidence for that?
Talk of a second wave is the stuff of nightmares, conjuring up images of another deadly surge of infections.
This is what happened with Spanish Flu after the First World War when a second wave proved deadlier than the first.
But the truth is many experts try to avoid the phrase altogether.
Margaret Harris, from the World Health Organization, has made clear that what we have seen is "one big wave" that is making its way across the globe.
Some countries, such as South Korea and Singapore, have been better than others at flattening it from the start by stopping the virus spreading by using comprehensive testing and tracing regimes.
But others - and the UK, France, Spain and Italy are examples of this - have just managed to flatten it partway through the wave by introducing lockdowns.
This was because they did not have such sophisticated infectious disease systems in place to control the virus.
Thanks to investment, they are in a much stronger position now and have been able to release lockdown, while still trying to suppress the virus wave through testing and tracing.
But there are signs cases are picking up, especially in Spain.
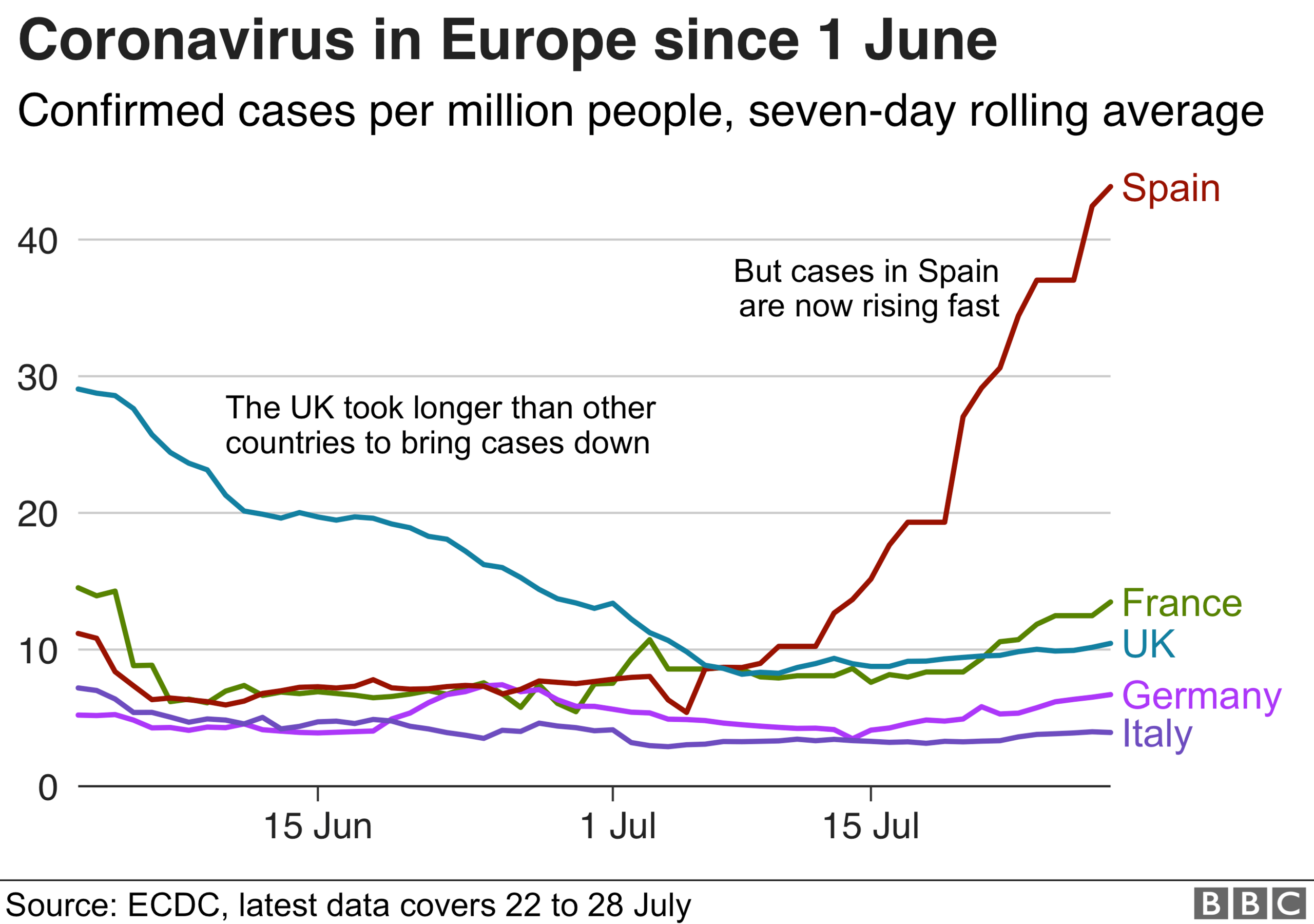
But rather than this being a second wave - or the start of one - perhaps we are better off thinking of these as the existing wave bursting through the defences.
Prof Paul Hunter, a Covid expert at Norwich Medical School, says for it to be a second wave the virus would have to have gone away completely, so he prefers to call it a "resurgence".
And really it should come as no surprise that this happens in highly-populated areas like Western Europe.
Containing the virus relies on good systems for detecting cases and for the public to play its part by social distancing, and engaging with the test and trace systems.
Clearly any weakness leaves countries susceptible, particularly to this virus which can be transmitted even if people are not displaying symptoms.
However, while cases may be going up, it is worth noting they are nowhere near the levels seen during the peak of the pandemic.
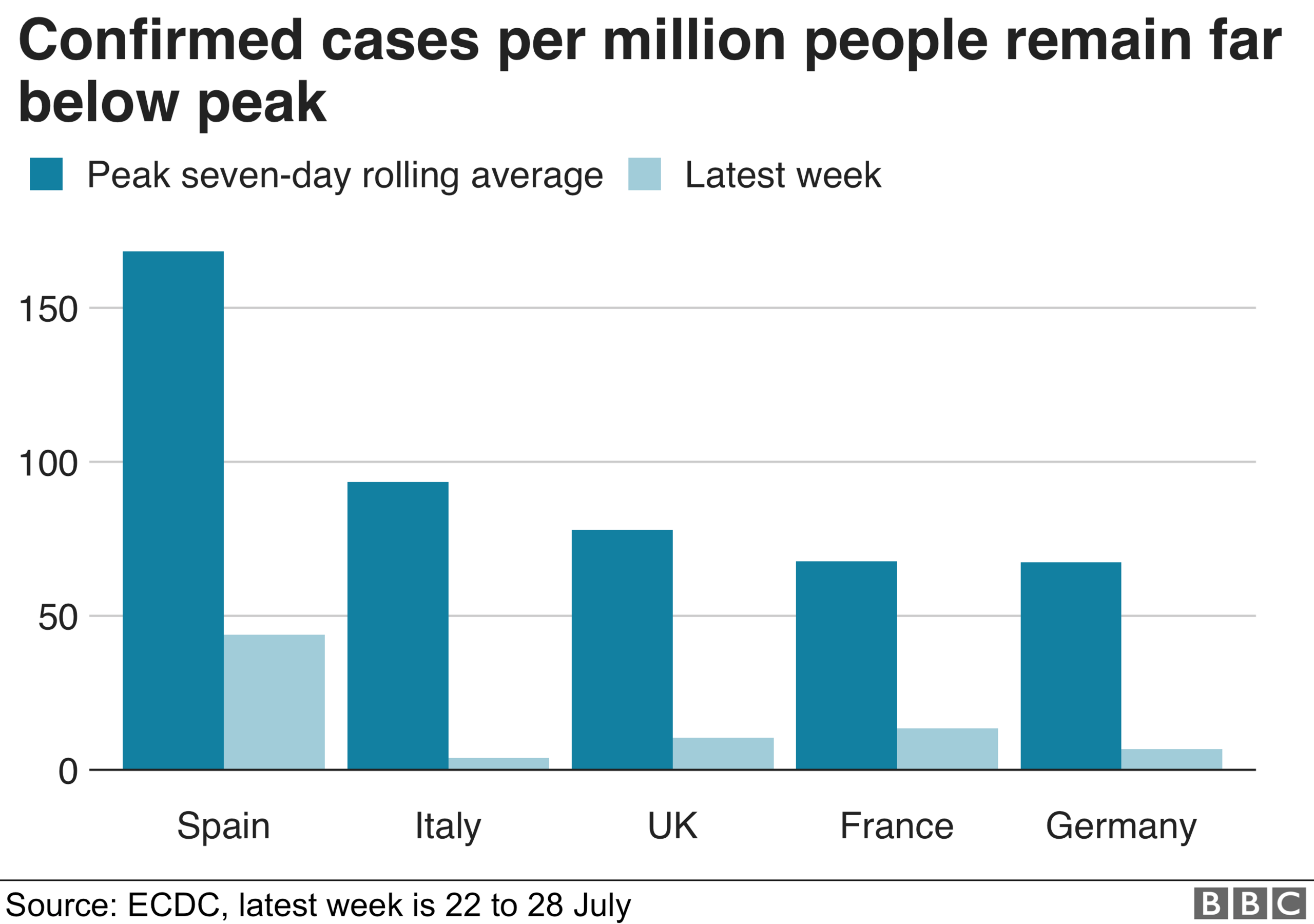
And bear in mind that the peaks seen in the charts above for all the countries - bar maybe Germany which had widespread testing in place quickly - are a gross underestimate of the true scale of infections.
That's because there was not widespread testing available at the time.
In the UK alone it is estimated that there were 100,000 cases a day at the peak - 20 times more than the testing in place at the time suggested.
The greater access to testing there is, the more likely you are to pick up mild infections.
If you only test patients in hospital - as was largely the case in the UK until late April - you are going to miss a lot of cases.
What is also clear is that infection levels vary greatly within countries.
There are areas where the virus is virtually non-existent, while in others it is lurking menacingly.
In the UK there have been flare-ups in Leicester and - to a lesser extent - Blackburn with Darwen and Oldham.
A similar picture emerges when you look at the data for Spain.

Even Germany is not immune to this, with local lockdowns announced in recent weeks.
There are many reasons why this is happening.
There are signs young people are spreading it in certain areas.
Certainly, the young are less likely to get extremely sick, which could make them more relaxed about the need for social distancing.
But it could also be true that the virus has always been circulating in these groups, it is just that more widespread testing is picking it up.
There also seems to be a link to deprivation - where people live in close proximity the likelihood of transmission increases.
What factors determine a potential second wave of Covid-19 infections?
Whatever the reasons behind the local flare-ups, what is certain is that they will continue for the foreseeable future.
Prof Keith Neal, an expert in infectious diseases from University of Nottingham, says these spikes will become a way of life, but they are in "no way" a second wave.
He says countries across Europe are "learning to live" with the virus by taking precautions such as social distancing and wearing masks.
He believes that if people remain vigilant, coupled with the improved treatments that are being found and greater testing, the scale of deaths seen during the peaks will hopefully not be repeated.
There is a good chance, it seems, that what will be seen are the ripples from the first wave rather than a big second wave.
Follow Nick on Twitter, external

A SIMPLE GUIDE: How do I protect myself?
AVOIDING CONTACT: The rules on self-isolation and exercise
HOPE AND LOSS: Your coronavirus stories
LOOK-UP TOOL: Check cases in your area

- Published28 July 2020

