UK coronavirus infections may be 'stabilising'
- Published
- comments

The increase in coronavirus infections appears to be slowing around the UK, latest data from the Office for National Statistics, external show.
Although the number of people with Covid continues to rise, the growth is levelling off.
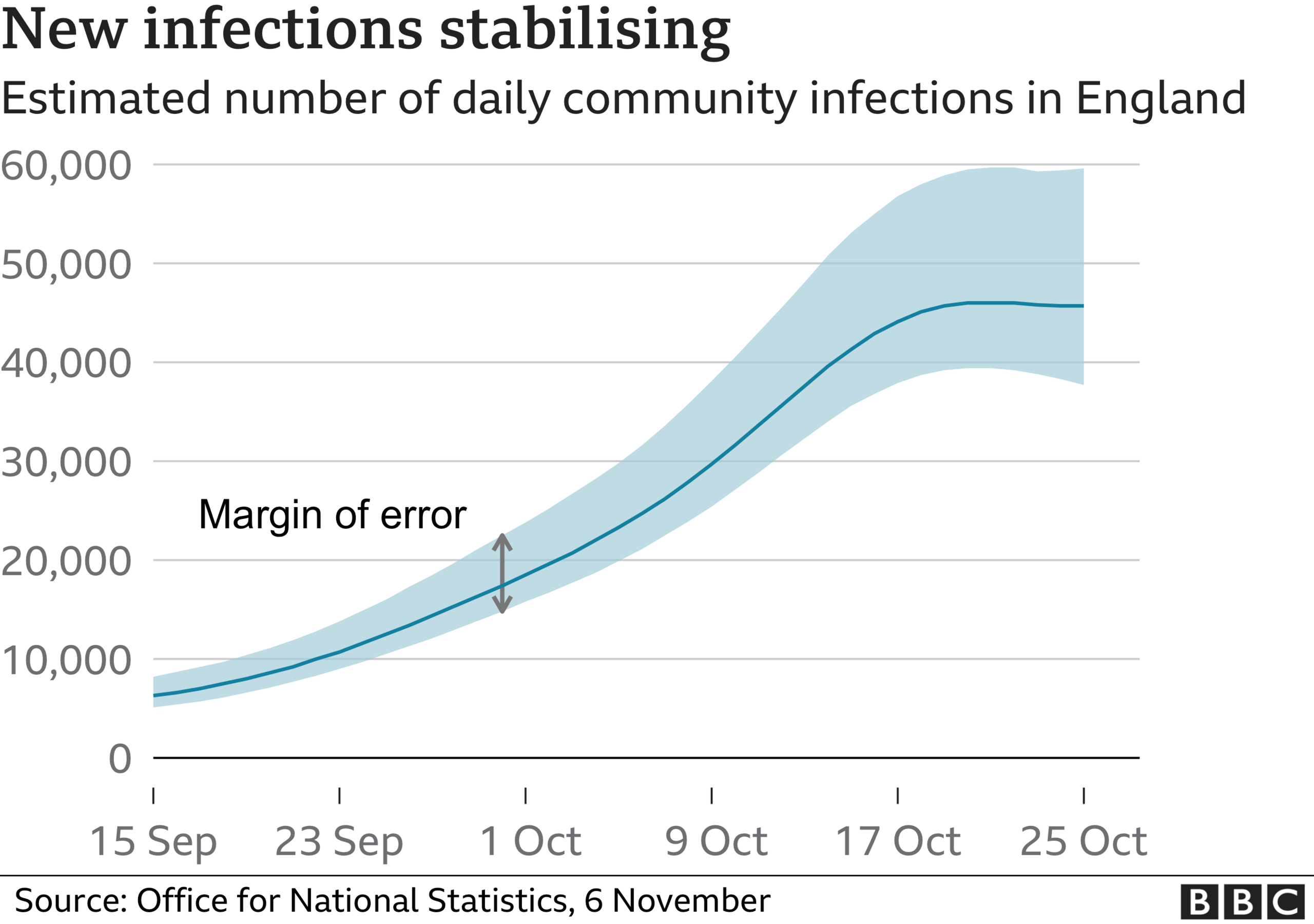
In the week to 30 October, ONS says new daily infections in England stabilised at around 50,000.
That means around one person in every 90 in England has Covid. In Wales and Scotland the figure is slightly lower.
There, one in 110 people are testing positive for the virus.
In Northern Ireland it is one in 75 - and it is too soon to say if rates are levelling off there, say experts.
The ONS data looks at Covid-19 infections in the community, and does not include cases in hospitals, care homes or other institutional settings.
It shows:
There have been increases in infection rates in every region in England apart from the North East over the last two weeks
The North West and Yorkshire and the Humber continue to have the highest infection rates
With much of the UK in lockdown, experts hope the number of new infections can reduce in coming weeks.
In Liverpool, city-wide mass testing for Covid has begun.
Everyone living or working in the region will be offered repeat tests, whether or not they have symptoms, as part of a two-week pilot.

TESTING: What tests are available?
GLOBAL TRACKER: Where are the virus hotspots?
YOUR QUESTIONS: We answer your queries

Meanwhile, data from the Covid Symptom Study app, external - based on a million people logging symptoms and 13,000 recent swab test results - suggests 42,049 people are developing Covid symptoms every day in the UK.
The R number remains the same as last week, at between 1.1 and 1.3, which means that on average every 10 people infected will infect between 11 and 13 other people and the outbreak is growing.
Ruth Studley from the ONS said: "At a national level we are seeing infections slow across England and Wales but they are still increasing.
"The level of infection in young adults and older teenagers appears to have levelled off recently. However, they continue to be the most likely to be infected despite increases in all other age groups."
Prof James Naismith from Oxford University said the findings were "encouraging" and suggested that the spread of the virus was slowing.
"This is evidence that the social restrictions prior to lockdown have had a real impact.
"Should next week's data show a similar stabilisation or reduction, then we can be confident that the second wave has for now stabilised. The national lockdown will not begin to show up in ONS figures for another two weeks, but we would expect it to bring a rapid decrease in the number of new infections.
"If we can contain the virus until the new year, mass testing, vaccines and new medicines will transform our outlook."
A Birmingham hospital has postponed all its non-emergency procedures because of an increase in the number of Covid-19 patients.
Queen Elizabeth Hospital is currently treating 389 patients who have tested positive, with 36 in its Intensive Care Unit (ICU). That compares with 60 in-patients a month ago, and just five in ICU.

THE NAKED SCIENTISTS: Why are people catching coronavirus on purpose?
EAT WELL FOR LESS: The team are in Bromley with a family who desperately want to change

- Published6 November 2020

- Published6 November 2020