HPV vaccine cutting cervical cancer by nearly 90%
- Published

The human papillomavirus, or HPV, vaccine is cutting cases of cervical cancer by nearly 90%, the first real-world data shows.
Cancer Research UK described the findings as "historic", and said it showed the vaccine was saving lives.
Nearly all cervical cancers are caused by viruses, and the hope is vaccination could almost eliminate the disease.
The researchers said the success meant those who were vaccinated may need far fewer cervical smear tests too.
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women around the world, killing more than 300,000 each year.
Almost nine-in-10 deaths are in low and middle income countries where there is little access to cervical cancer screening. The hope is vaccination will have an even bigger impact in those countries than wealthier nations such as the UK.
More than 100 countries have starting using the vaccine as part of World Health Organization plans to get close to eliminating cervical cancer., external.
In the UK, girls are offered the vaccine between the ages of 11 and 13, depending on where they live. The vaccine has also been offered to boys since 2019.
The HPV vaccine can only prevent an infection, it cannot rid the body of the virus once it has been caught. The viruses are so widespread that immunisation has to be aimed at children before they become sexually active.
The study, published in the Lancet, looked at what happened after the vaccine was introduced for girls in England in 2008.
Those pupils are now adults in their 20s. The study showed a reduction in both pre-cancerous growths and an 87% reduction in cervical cancer.
"The impact has been huge," said Prof Peter Sasieni, one of the researchers at King's College London.
The reductions were less dramatic when older teenagers were immunised as part of a catch-up campaign. This is because fewer older teenagers decided to have the jab and they may already have been sexually active.
Overall, the study estimated the HPV programme has prevented about 450 cancers and 17,200 pre-cancers.
Prof Sasieni said that was "just the tip of the iceberg" because those vaccinated were still young to be getting cancer, so the numbers would only grow with time.

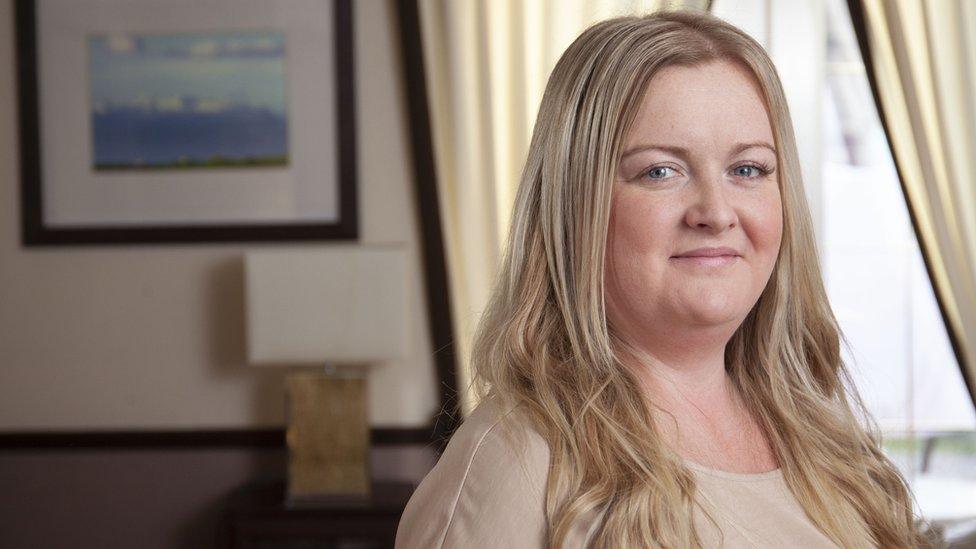
'I told them to save me for my children'
Laura Flaherty was diagnosed with cervical cancer after a routine smear test: "It came out of nowhere, I had no symptoms"
Laura Flaherty was diagnosed with cervical cancer this year at the age of 29 after putting off a routine smear test.
"The HPV vaccine hadn't been rolled out when I was at school," she says.
"I was diagnosed after a routine smear test. I'd put it off for four months - and while it wouldn't have made a difference to my diagnosis - it just shows how important it is to keep up to date with your smears.
"I was told I had abnormal cells and tested positive for HPV and further investigation revealed I had stage one cervical cancer, which resulted in a hysterectomy.
"I was sat in a room and told: 'I'm really sorry, it's cancer'. I had two small children and I said 'I need you to save me, they need looking after'.
"I went for my smear test in February this year and was given the all clear in August. I just always feel so lucky to be here."

At the moment, women are invited for a smear test every three to five years to screen for cervical cancer.
But Prof Sasieni said there "definitely" needed to be a rethink after these results.
He told me: "It should be a wake-up call to policy-makers, women will read this and think 'why should I go for screening?'
"I would hope we'd come back with a new screening programme, two to three times a lifetime and continue screening women who have not been vaccinated."
This is not the final say on the HPV vaccination. There are still questions about how long protection lasts and whether there needs to be a mid-life booster.
There are also more than 100 types of human papillomavirus.
The UK started using a vaccine that protected against two of them and is about to introduce one that protects against nine viruses, including the main causes of genital warts.
The cancer-causing versions lead to dangerous changes to the DNA of infected cells that transform them into cancer.
This can happen in any infected tissue. The viruses can be spread through vaginal, oral and anal sex, so are also linked to anus, penis and some head and neck cancers.
However, 99% of cervical cancers are caused by human papillomaviruses.
Dr Vanessa Saliba, a consultant epidemiologist for the UK Health Security Agency, said the findings were "remarkable" and showed the vaccine "saves lives by dramatically reducing cervical cancer rates among women".
Michelle Mitchell, the chief executive at Cancer Research UK, said: "It's a historic moment to see the first study showing that the HPV vaccine has and will continue to protect thousands of women from developing cervical cancer."
Follow James on Twitter, external
Why are girls from ethnic minority backgrounds less likely to have the HPV vaccine?

THE FLUX IS COMING: Terrifying forces are stirring all across the universe, can the Doctor save us?
WHAT TO COOK FOR DIWALI: Delicious dishes to get you in the Diwali spirit!

Related topics
- Published4 November 2021

- Published9 July 2019
- Published13 September 2021

- Published11 October 2021

- Published13 September 2018
