Many English maternity units not meeting safety standards
- Published
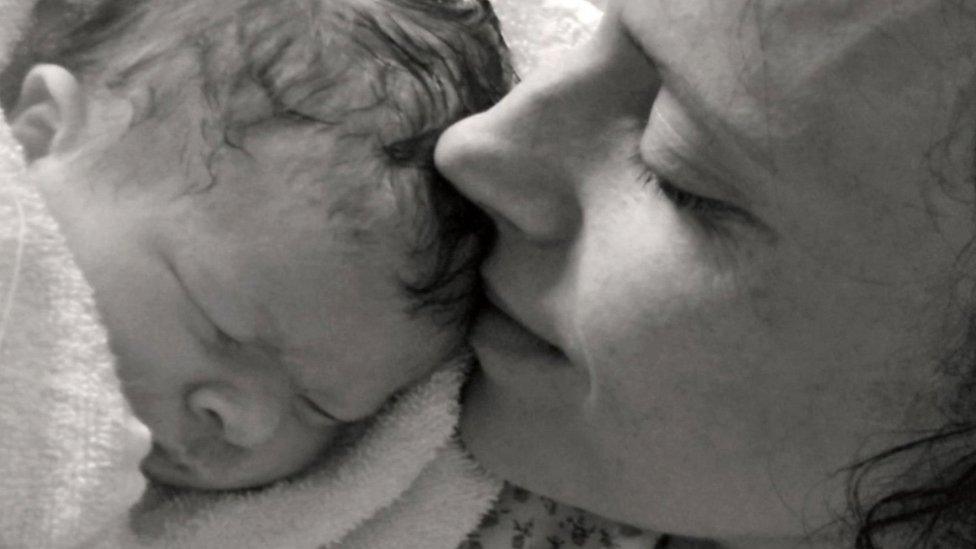
Laura Ellis, whose baby Theo died at a maternity unit: "There was just a catalogue of errors"
More than half of maternity units in England fail consistently to meet safety standards, BBC analysis of official statistics shows.
Health regulator the Care Quality Commission (CQC), external rates 7% of units as posing a high risk of avoidable harm. A further 48% require improvement.
The figures are slightly worse than a few years ago, despite several attempts to transform maternity care.
The regulator says the pace of improvement has been disappointing.
In most cases, pregnancy and birth are a positive and safe experience for women and their families, says the CQC. But when things do go wrong, it is important to understand what happened and whether the outcome could have been different.
Laura Ellis lost her newborn son.
She checked out the CQC rating of her local hospital, Frimley Park, when she was pregnant. Maternity services were good.
But Laura did not realise the unit had been told that it required improvement on safety.
She went into labour after an easy pregnancy, and got to the birth centre around 16:40.
But within an hour it became clear that the baby was breech, meaning that instead of being head-first in the womb, the legs or bottom were down, making delivery harder.
Laura remembers that there seemed to be a "complete sense of panic" in the room and that no-one seemed to have any idea what they should be doing.
Just after 18:00, the baby's legs and chest had been delivered and the midwife said she could feel a heartbeat.
But a few minutes later, a senior midwife tried to listen for it with a stethoscope - and could not hear anything.
Laura says she was told that the stethoscope was broken.
When her son, Theo, was fully delivered at 18:13, his heart had stopped beating.
Medical staff tried to resuscitate him. At one stage, the oxygen canister used on Theo ran out, before being replaced.
Laura and her husband James watched, slowly coming to the realisation that their son was probably not going to survive.
Doctors and midwives stopped resuscitation after 39 minutes.
Laura describes Theo as "the most perfect baby, just absolutely beautiful".
"It was just so hard. So hard to deal with. So hard to leave as well. How would you leave your baby in hospital when you should be taking them home?"
Frimley Park NHS Foundation Trust says it is extremely sorry for what happened.
It says it has made a number of changes since Theo died, including an emergency response if a baby is unexpectedly breech during advanced labour.

If you are affected by issues raised in this article help and support is available via the BBC Action Line.
If you or someone you know needs support for issues relating to bereavement and emotional distress, these organisations may be also able to help.

Lack of progress
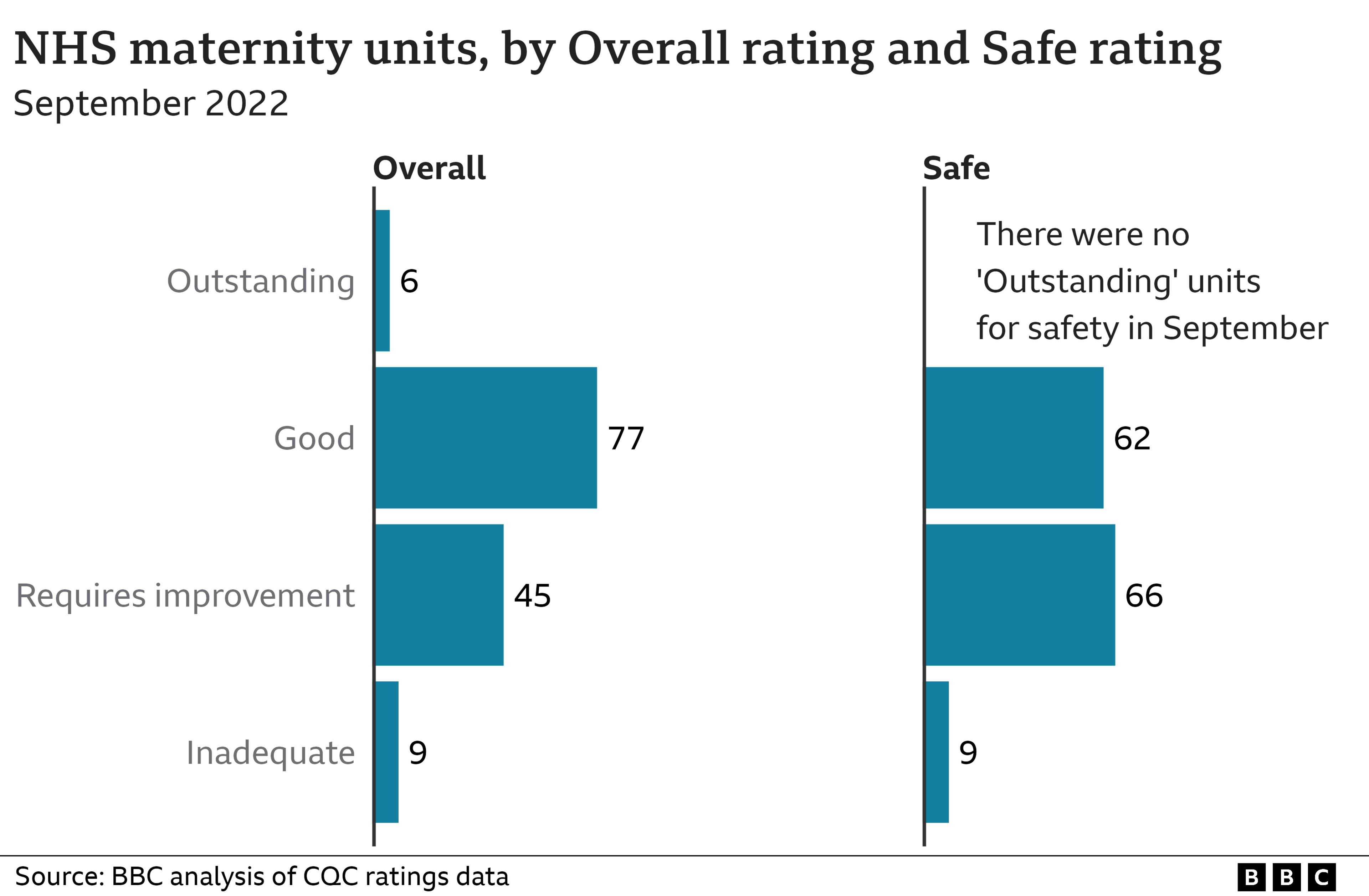
The BBC analysed the most recent CQC safety ratings, published in September 2022, for 137 maternity units in England and found:
Nine were given the lowest possible rating of inadequate for safety, meaning urgent action is required
66 required improvement to reduce risk to mothers and babies, and ensure legal requirements on safety are met
62 had a good rating for safety
None were given the top rating of outstanding that would mean a comprehensive safety system is in place
It is hard to give a direct comparison between the current ratings and older ones, because the CQC has changed its approach to inspections.
Also, during the pandemic it moved to a risk-based approach, looking at units it was more concerned about.
But in December 2016, 50% of maternity and gynaecology units had good safety ratings, compared to 45% now.
Victoria Vallance, the CQC's director of secondary care, says inspectors often find the same problems in the maternity services they visit, for example, not managing risk when women are deteriorating.
"We are worried. We are concerned," she said.
"We have not seen the pace of improvement consistently, nationally, that we would hope and expect to see across maternity services."
The CQC only inspects in England.
Northern Ireland's Regulation and Quality Improvement Authority has not inspected care in maternity units yet - but will in autumn next year.
NHS Wales says it has recognised the need for improvement in maternity services.
The Scottish government says it is transforming maternity services with its Best Start programme.
Safety scandals
There have been a series of serious safety scandals at maternity units in England.
Morecambe Bay, and Shrewsbury and Telford have been investigated. East Kent is expected to report back next - and another review has started into problems in Nottingham.
Royal College of Midwives chief executive Gill Walton says there is an "ongoing crisis in maternity services" and more funds are badly needed.
"Every time there's an inquiry, there's a flurry of 'we're going to do this, this and this. And then it falls off the agenda," she said.
The NHS in England needs 2,000 more midwives and almost 500 obstetricians.
But more than 500 midwives left the profession last year.
The government recently invested £127m to grow the NHS maternity workforce and improve neonatal care. This is on top of spending £95m a year to boost maternity staff numbers.
England's chief midwifery officer, Professor Jacqueline Dunkley-Bent, admits this is one of the most challenging times in her career.
"One of my key priorities is to ensure a safe and personal care for everybody using our NHS services in England regardless of postcode, socio-economic status, or colour of their skin," she said.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

How to explore the care in your area
After consultation with the CQC, the BBC analysed the overall and safe ratings for each unit that had a "Maternity" Service.
For anyone pregnant or planning to deliver at their local hospital it is important to look at the CQC's, external latest report into their local hospital, and check what it says about maternity care and safety. If anyone has any concerns they should talk to their GP, midwife or obstetrician.

Every year the NHS in England pays compensation claims when care goes wrong. Last year, there were 10,284 negligence claims. Of those, 12% - 1,243 - were for maternity.
But the money paid out for these claims is far, far more than any other medical specialty.
Maternity claims are expensive, partly because they tend to be an initial lump sum and then annual payments for the rest of the mum or baby's life.
The NHS expects that 60% of the money it will pay out for medical mistakes that happened last year will be maternity cases. That would be just under £8bn, forecast to be paid out over many years.
Another way to see that money is that it is over four times more than the annual salary of all midwives and maternity doctors and nurses.
Professor Dunkley-Bent says: "I'm keen that we reduce those claims.
"We want to ensure that our babies and mums are cared for safely, that they have safe and personal maternity care, which means that if we get it right first time, those claims will reduce.
"One baby dying is one to many. It's absolutely heart-wrenching."
The English picture is reflected across the UK.
Of all clinical negligence claims NHS Wales handled last year, 18% were about maternity care.
Northern Ireland's figures show 16%.
Scotland does not break down maternity claims alone, but says 18% of the compensation cases it looks at involve maternity and gynaecology.
Have you been affected by the issues raised in this story? Share your experiences by emailing haveyoursay@bbc.co.uk, external.
Please include a contact number if you are willing to speak to a BBC journalist. You can also get in touch in the following ways:
WhatsApp: +44 7756 165803
Tweet: @BBC_HaveYourSay, external
Please read our terms & conditions and privacy policy
If you are reading this page and can't see the form you will need to visit the mobile version of the BBC website to submit your question or comment or you can email us at HaveYourSay@bbc.co.uk, external. Please include your name, age and location with any submission.
Related topics
- Published23 February 2022

- Published30 March 2022
