Hiroshima and Nagasaki: 75th anniversary of atomic bombings
- Published
It is 75 years since the US dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August, leading to the end of World War Two.
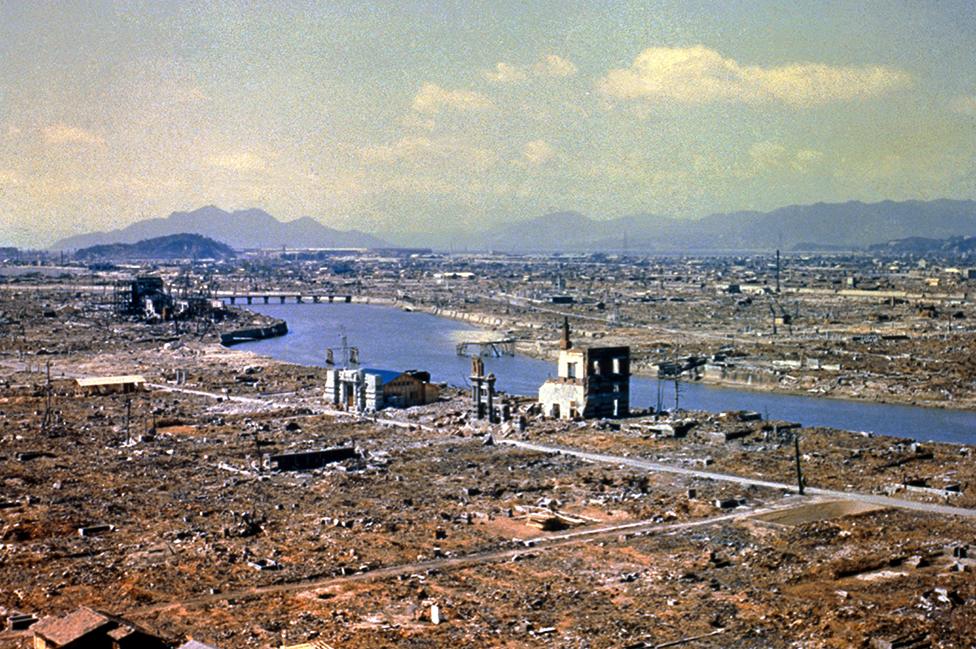

The devastated city of Hiroshima after the atomic bomb blast
The article contains graphic images and details some people may find upsetting.
The recorded death tolls are estimates, but it is thought that about 140,000 of Hiroshima's 350,000 population were killed in the blast, and that at least 74,000 people died in Nagasaki.
The nuclear radiation released by the bombs caused thousands more people to die from radiation sickness in the weeks, months and years that followed.
Those who survived the bombings are known as "hibakusha". Survivors faced a horrifying aftermath in the cities, including psychological trauma.
The bombings brought about an abrupt end to the war in Asia, with Japan surrendering unconditionally to the Allies on 14 August 1945.
But critics have said that Japan was already on the brink of surrender.
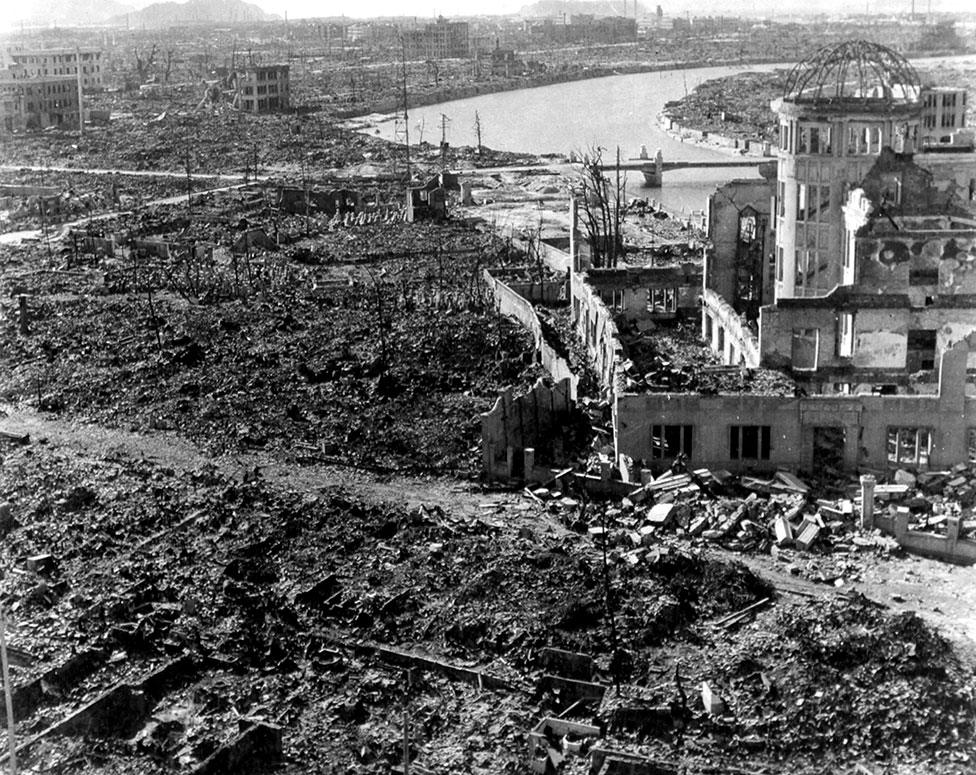

It is estimated that about 140,000 of Hiroshima's 350,000 population were killed by the atomic bomb
Following the end of the fighting in Europe on 7 May 1945, the Allies told Japan to surrender by 28 July, but the deadline passed without them doing so.
An estimated 71,000 soldiers from Britain and the Commonwealth were killed in the war against Japan, including more than 12,000 prisoners of war who died in Japanese captivity.
On 6 August 1945 at 08:15 Japanese time, an American B-29 bomber plane named Enola Gay dropped an atomic bomb on Hiroshima.
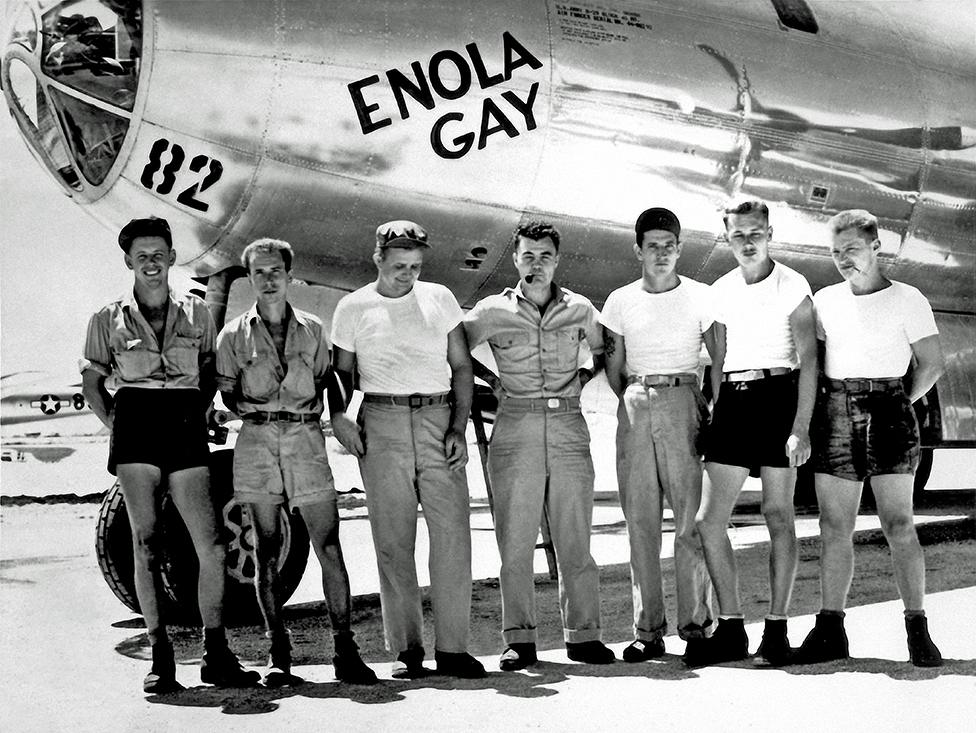

The crew of Enola Gay, which dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima
It was the first time an atomic bomb had ever been used in a war.
The Hiroshima bomb, known as "Little Boy", contained the equivalent of between 12,000 and 15,000 tons of TNT and devastated an area of 13sq km (5sq miles).
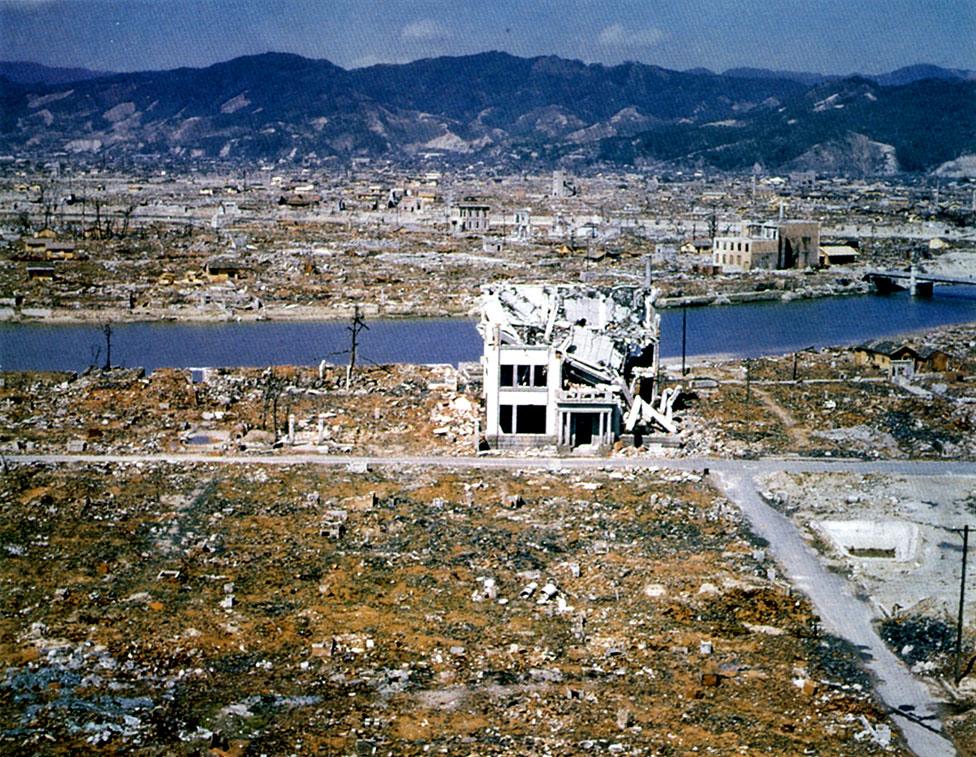

More than 60% of the buildings in Hiroshima were destroyed
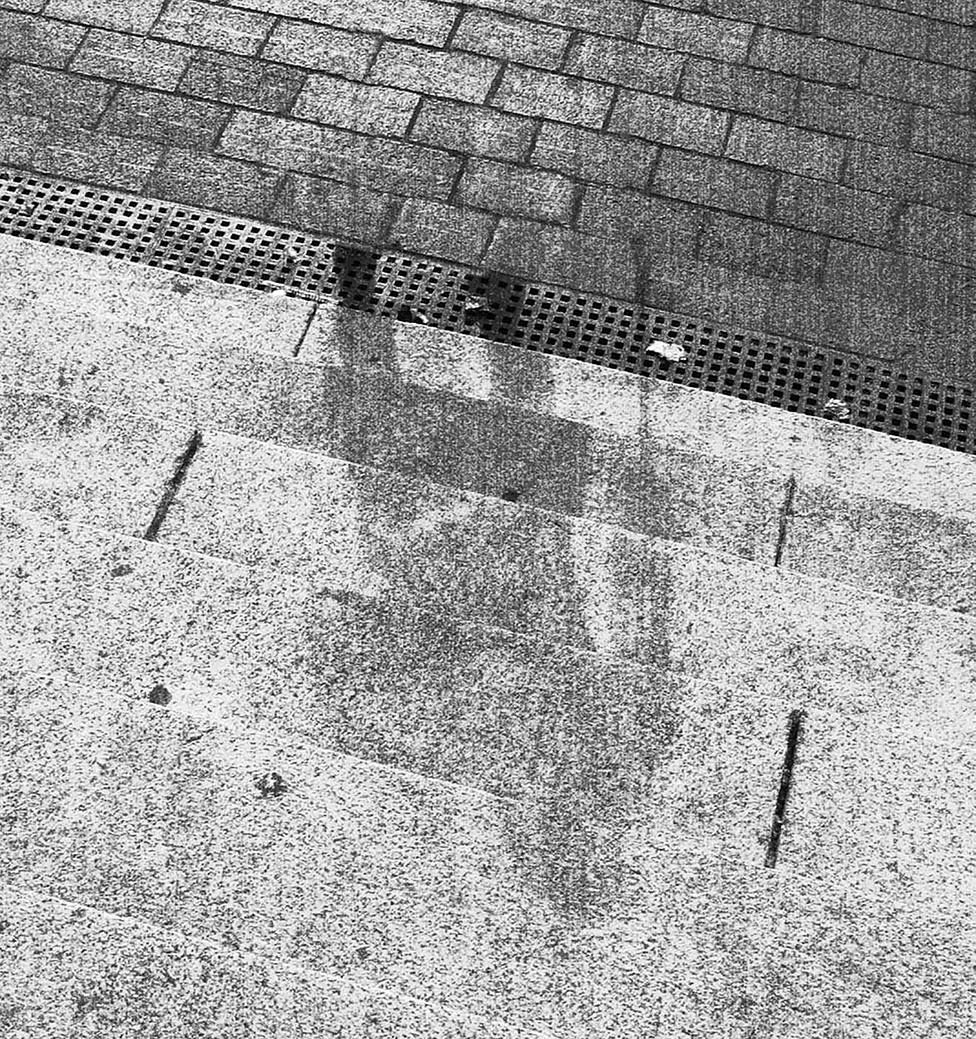


A shadow of a victim of the Hiroshima atomic bomb seen on stone steps

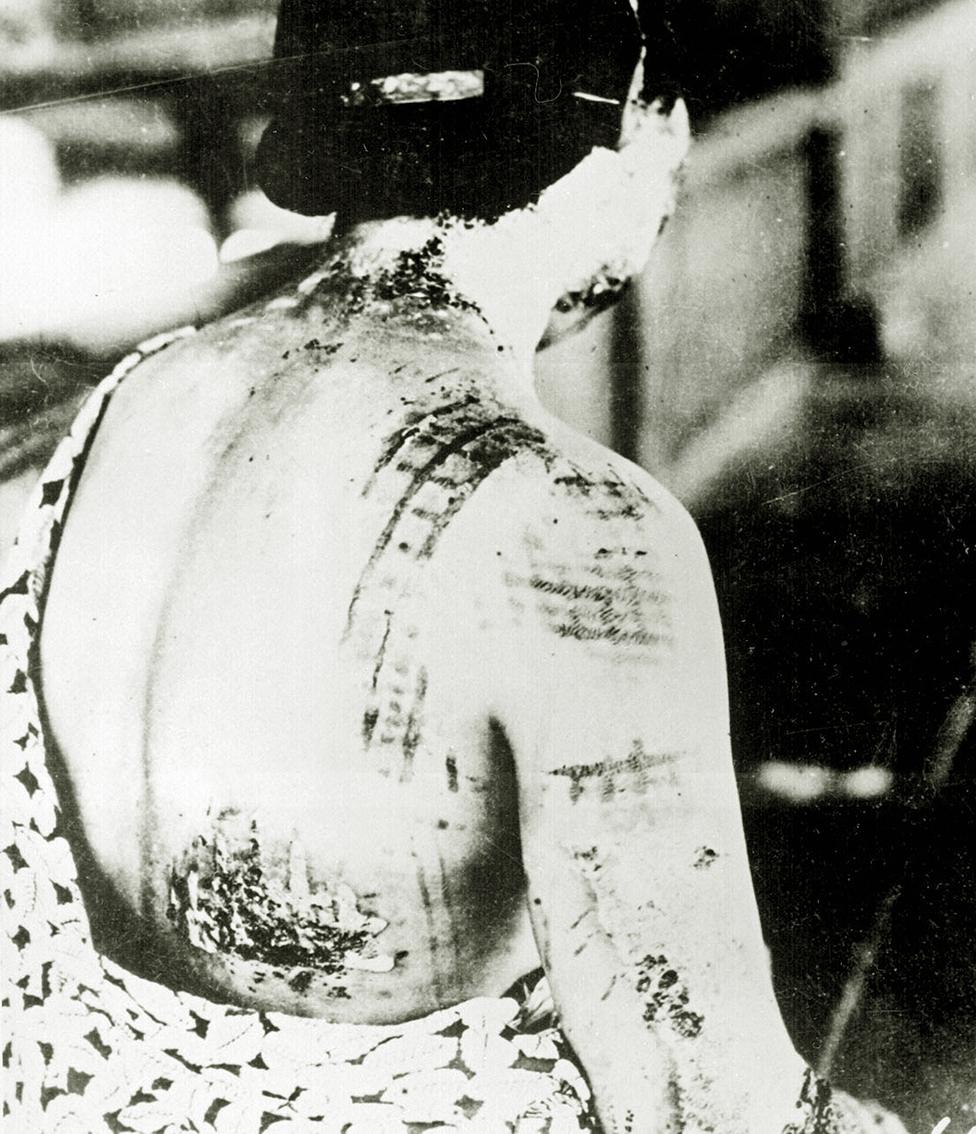
A woman shows her injuries in Hiroshima; her skin was burned in a pattern corresponding to the dark portions of a kimono worn at the time of the explosion

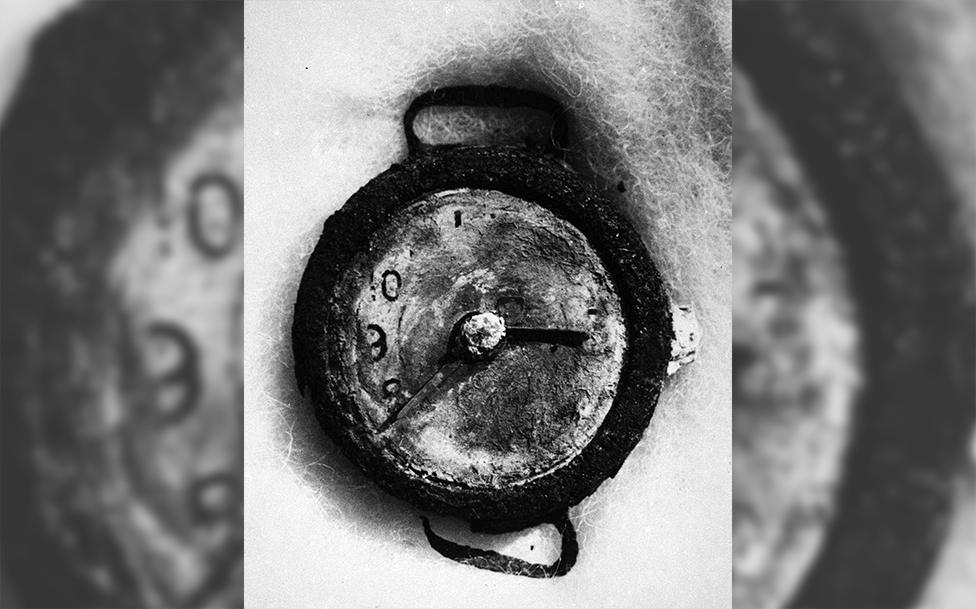
A watch from the wreckage of Hiroshima, which stopped at 08:15


A composite image shows aerial views of Hiroshima before the atomic bomb (bottom left) and after (top right)
However, Japan did not surrender.
Three days later, the Americans dropped another atomic bomb on the city of Nagasaki at 11:02 Japanese time.
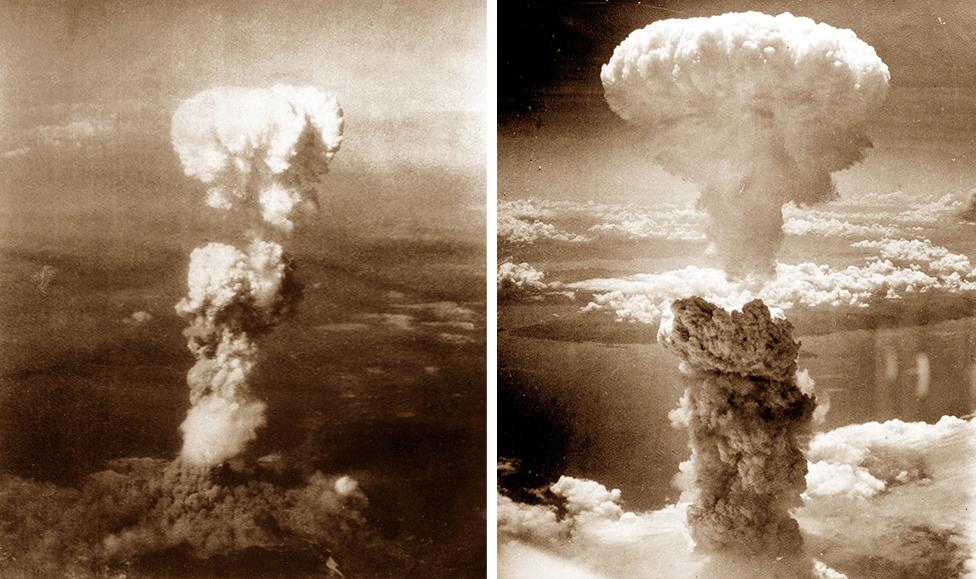

The atomic bomb mushroom clouds over Hiroshima (left) and Nagasaki (right)
Reiko Hada was nine years old when the bomb exploded in Nagasaki.
In an interview with photojournalist Lee Karen Stow, she described her experience: "I made it to the entrance of my house, and I think I even took a step inside, then it happened all of a sudden.
"A blazing light shot across my eyes. The colours were yellow, khaki and orange, all mixed together.
"I didn't even have time to wonder what it was... In no time, everything went completely white.
"It felt as if I had been left all alone. The next moment there was a loud roar. Then I blacked out."
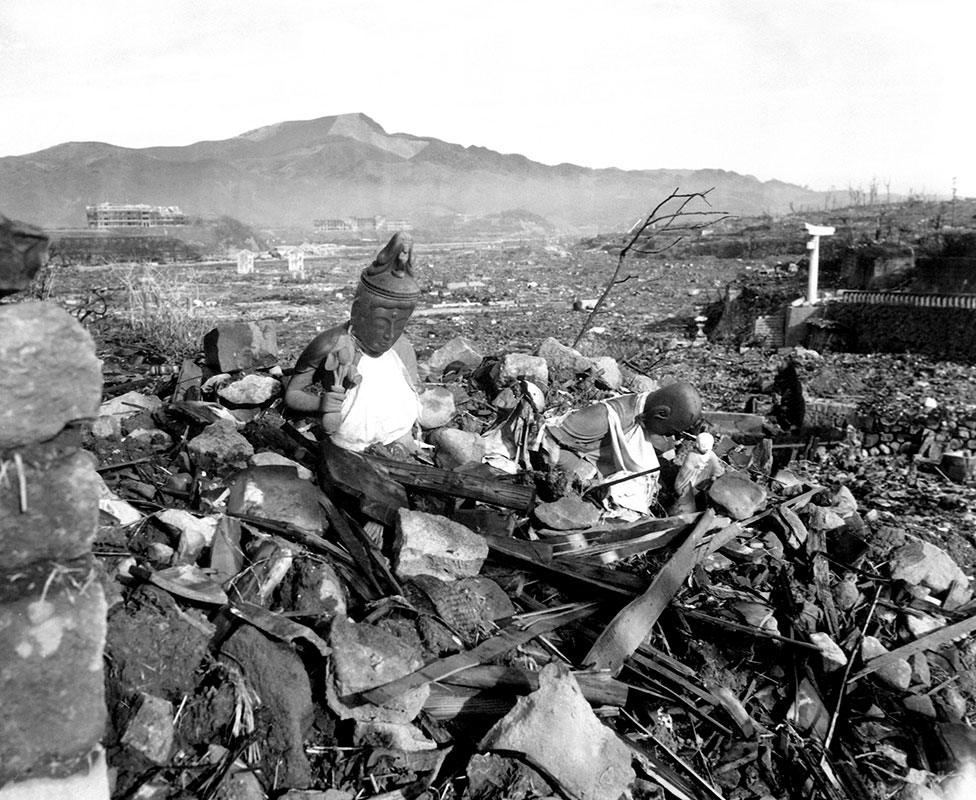

The ruined buildings of Nagasaki after the atomic bomb
Hada witnessed some of the catastrophic injuries from the atomic bomb.
"Many fled over Mount Konpira to our community. People with their eyes popped out, their hair dishevelled, almost all naked, badly burned with their skin hanging down.
"My mother grabbed towels and sheets at home and, with other women in the community, led the fleeing people to the auditorium of a nearby commercial college where they could lie down.
"They asked for water. I was asked to give them water, so I found a chipped bowl and went to the nearby river and scooped water to let them drink.
"After drinking a sip of water, they died. People died one after another.
"It was impossible to know who those people were. They didn't die like human beings."
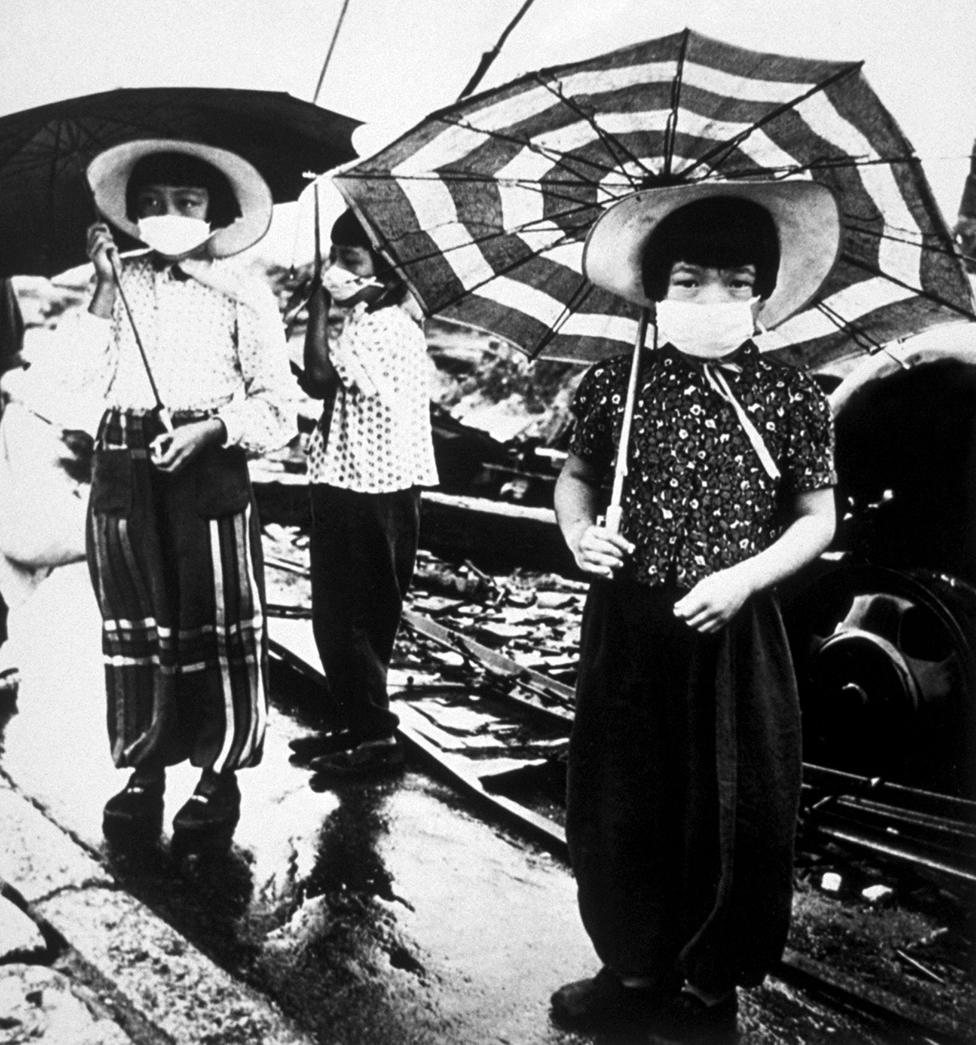

Children in Hiroshima wear masks to protect themselves from air pollution amid the ruined city in October 1945
Japan surrendered unconditionally on 14 August.
On the same day, US President Harry Truman gave an address to a crowd gathered outside the White House in which he said: "This is the day we have been waiting for since Pearl Harbor. This is the day when fascism finally dies, as we always knew it would."
The following day, Japan's Emperor Hirohito was heard on the radio for the first time ever in a broadcast in which he blamed the use of "a new and most cruel bomb" for Japan's unconditional surrender.
He added: "Should we continue to fight, it would not only result in the ultimate collapse and obliteration of the Japanese nation, but would lead also to the total extinction of human civilisation."
British Prime Minister Clement Atlee said: "The last of our enemies is laid low."
He added that special thanks went to the US "without whose prodigious efforts the war in the East would still have many years to run".
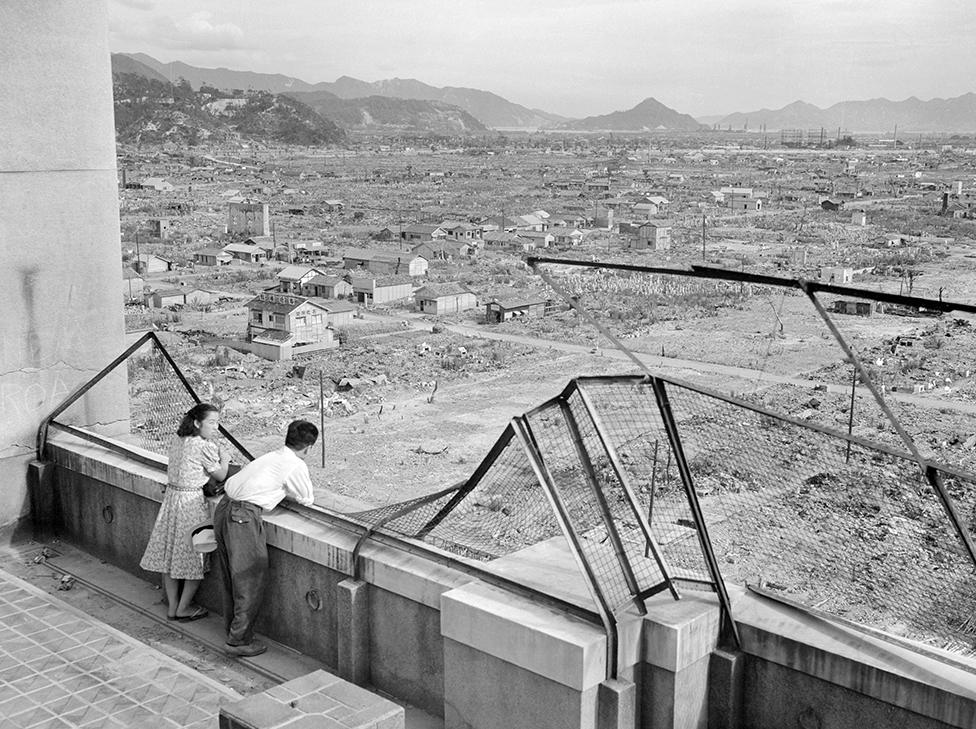

Hiroshima a year after the atomic bomb, showing government-supplied wooden buildings built on the flattened city
After the surrender of Japan, two days of national holiday were announced for celebrations in the UK, the US and Australia.
Millions of people from the Allied countries took part in parades and street parties on Victory over Japan (VJ) Day on 15 August.
In London, the Royal Family greeted cheering crowds from the balcony of Buckingham Palace.
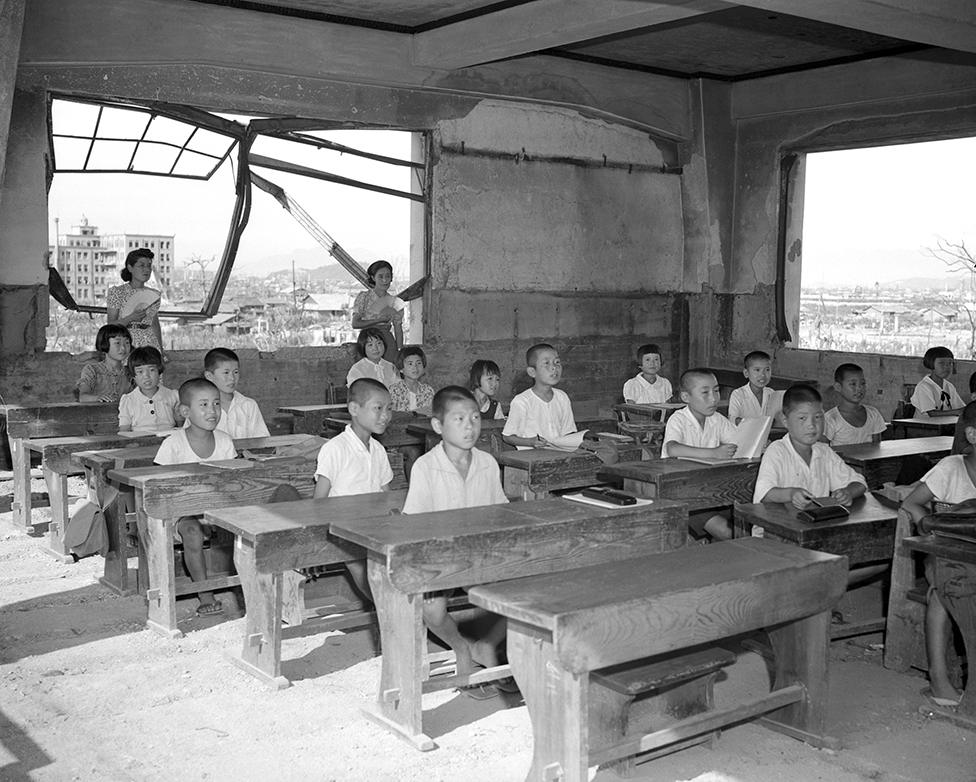

A lesson takes place in a bomb-damaged classroom in Hiroshima in 1946, whilst thousands of bodies were still buried under the ruins
The official surrender documents were signed by Japan on 2 September aboard the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay.
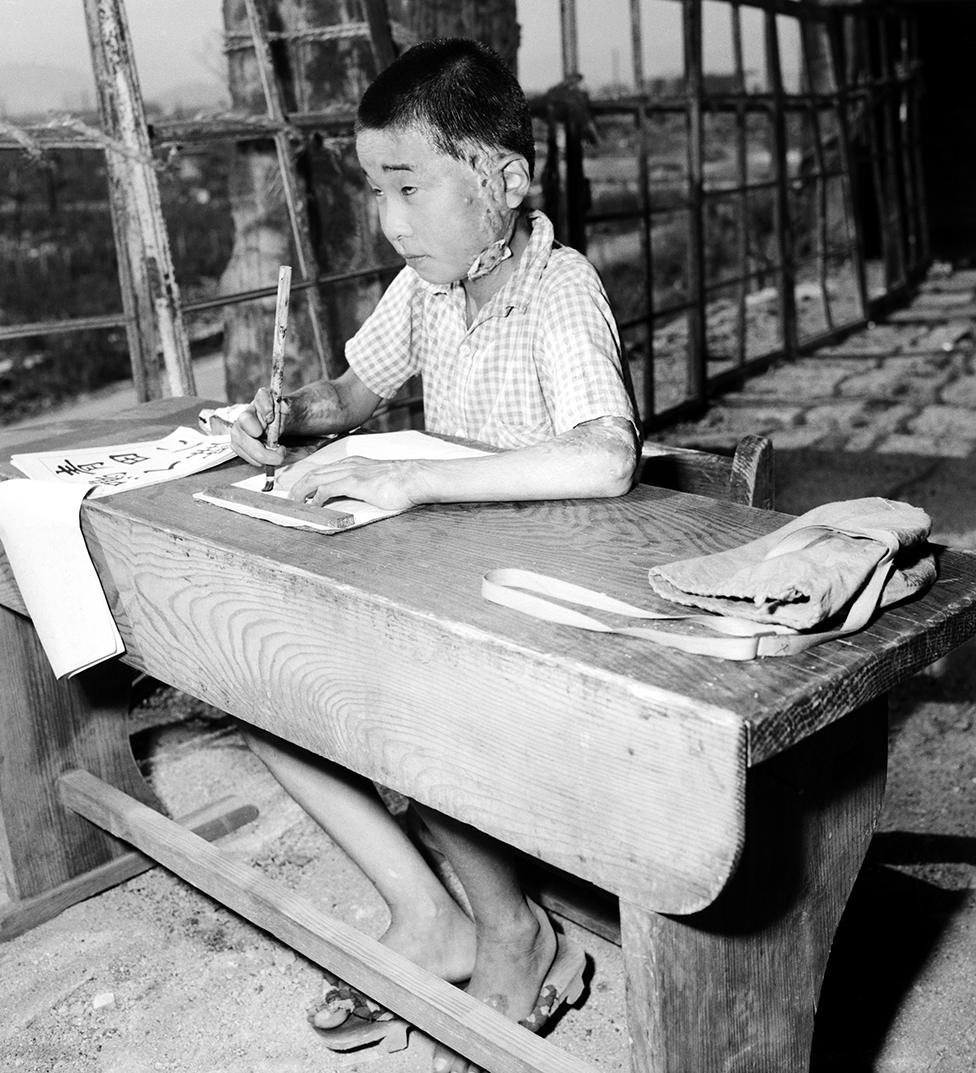

A schoolchild scarred by the Hiroshima atomic bomb attends a lesson in 1946
The Atomic Bomb Dome in Hiroshima, seen below in August 2020, was one of the few buildings to survive the bomb and has been preserved as a memorial.
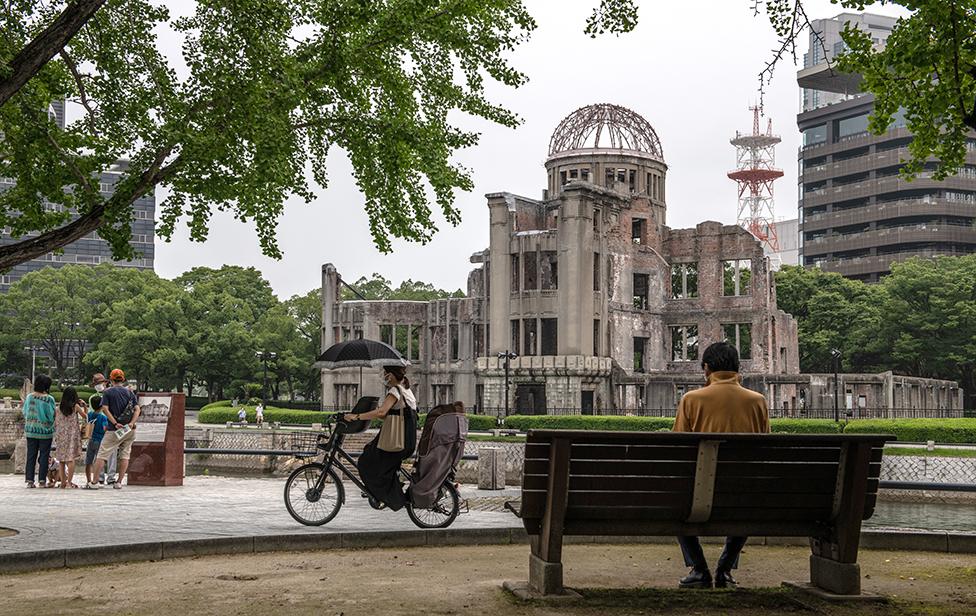

The dome is located in the city's Peace Memorial Park and has been named as a Unesco World Heritage site.
All photographs subject to copyright.