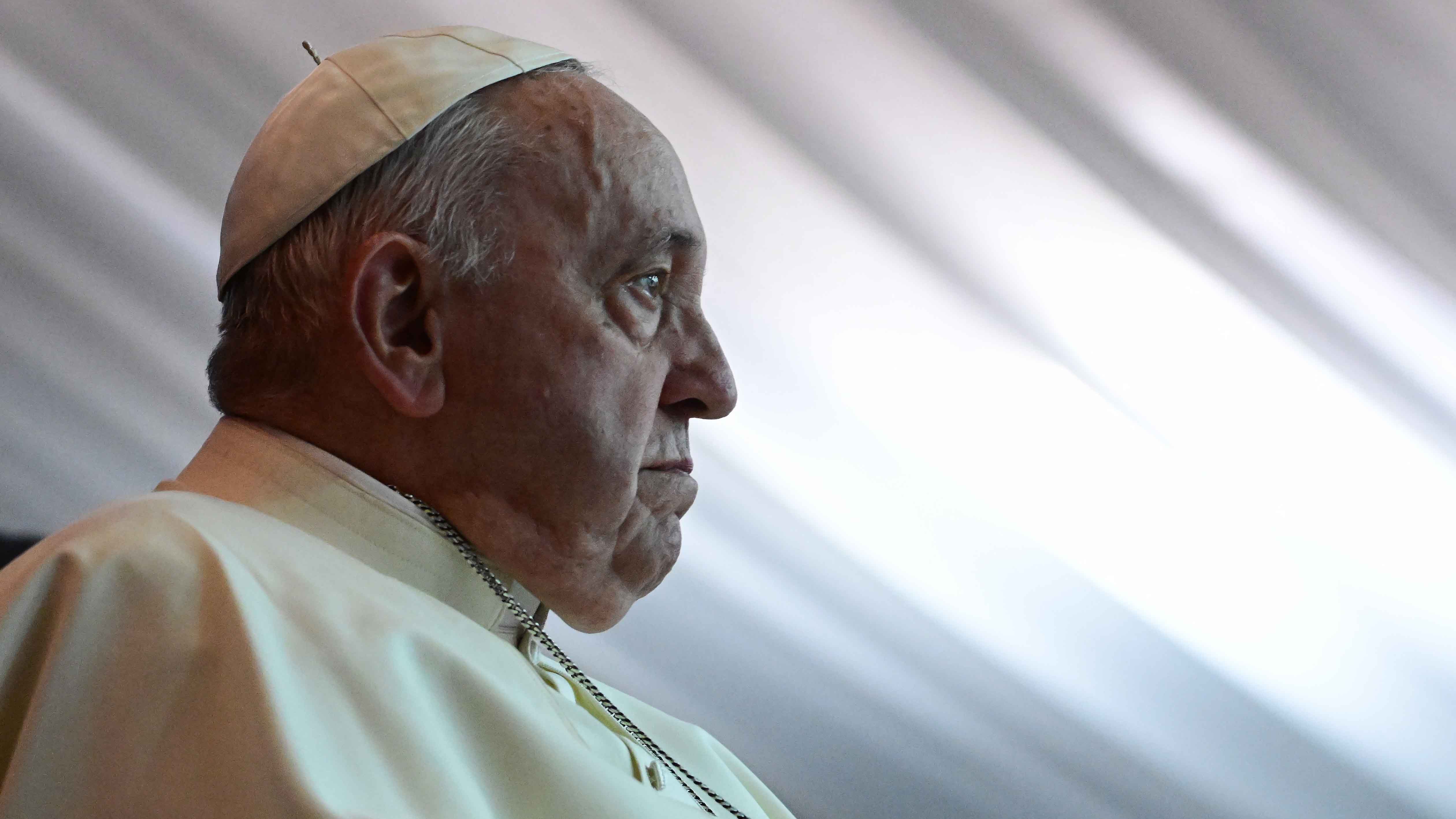
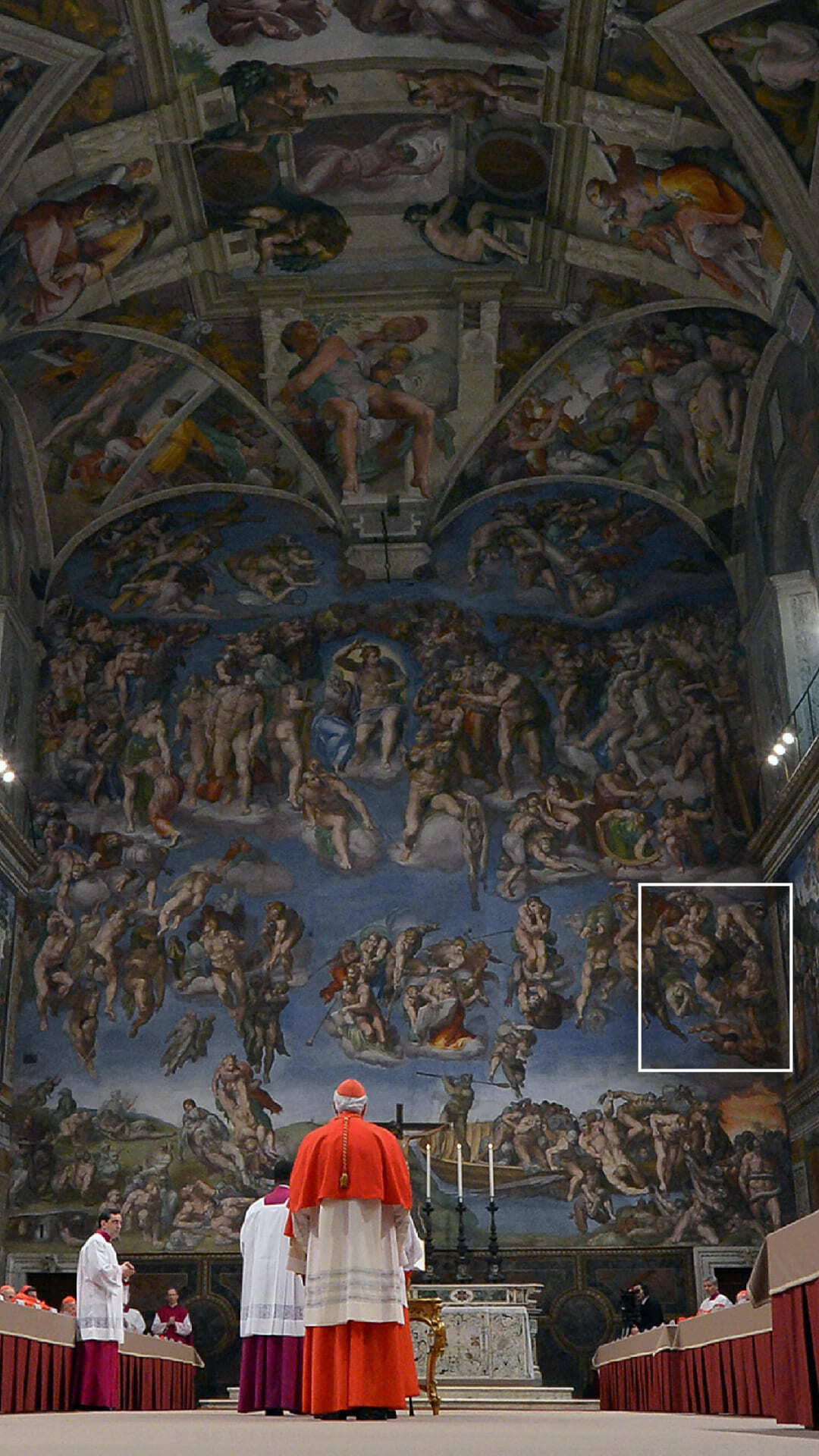
Leaders of the Catholic Church from around the world have gathered in the Vatican for the conclave, the confidential process through which a new pope will be chosen.
They are selecting the successor to Pope Francis, the Church's first Latin American pope who died on Easter Monday aged 88.
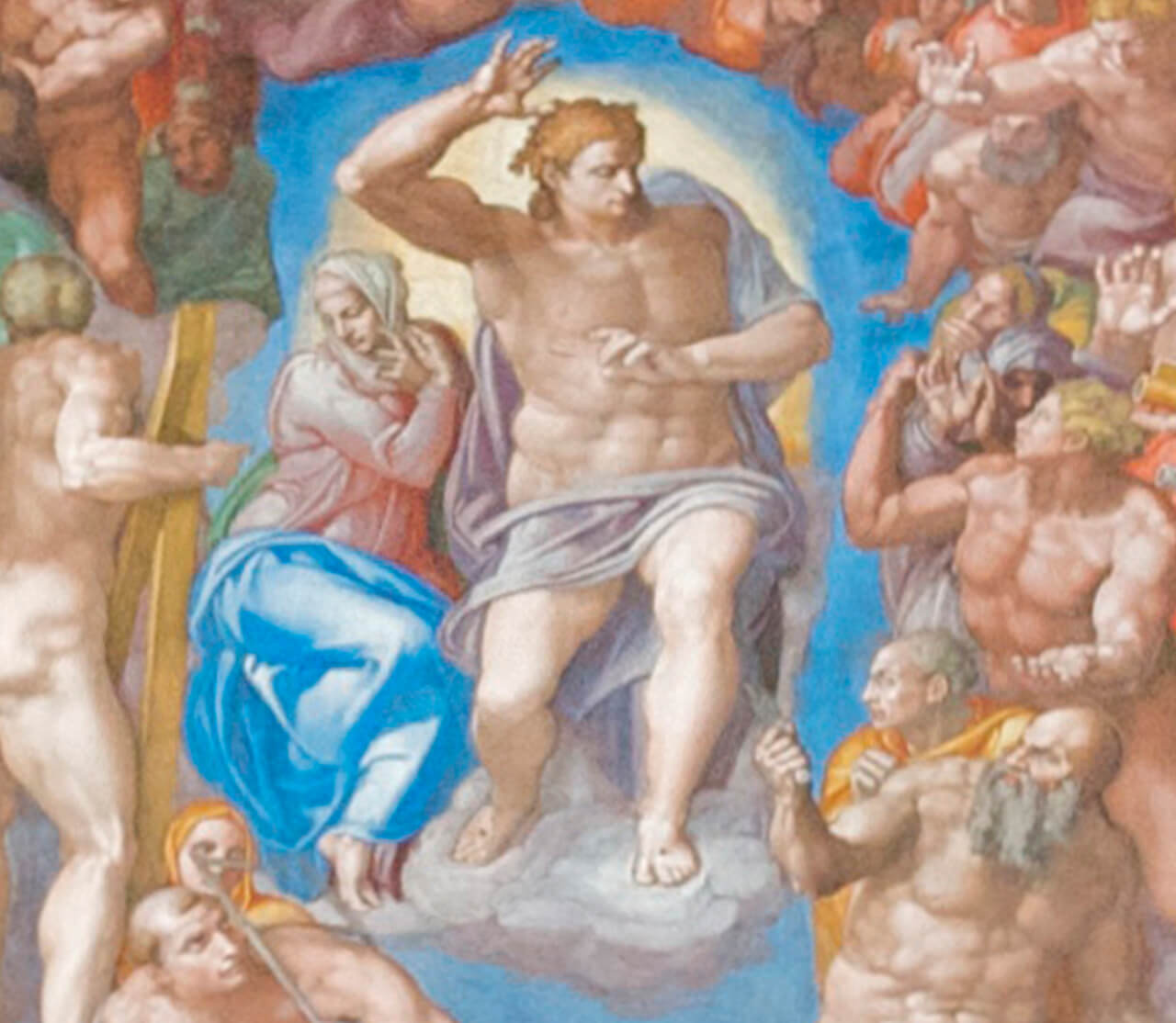
Throughout history, conclaves have brought moments of significant change for the Catholic Church, as each new pope leaves his own mark.
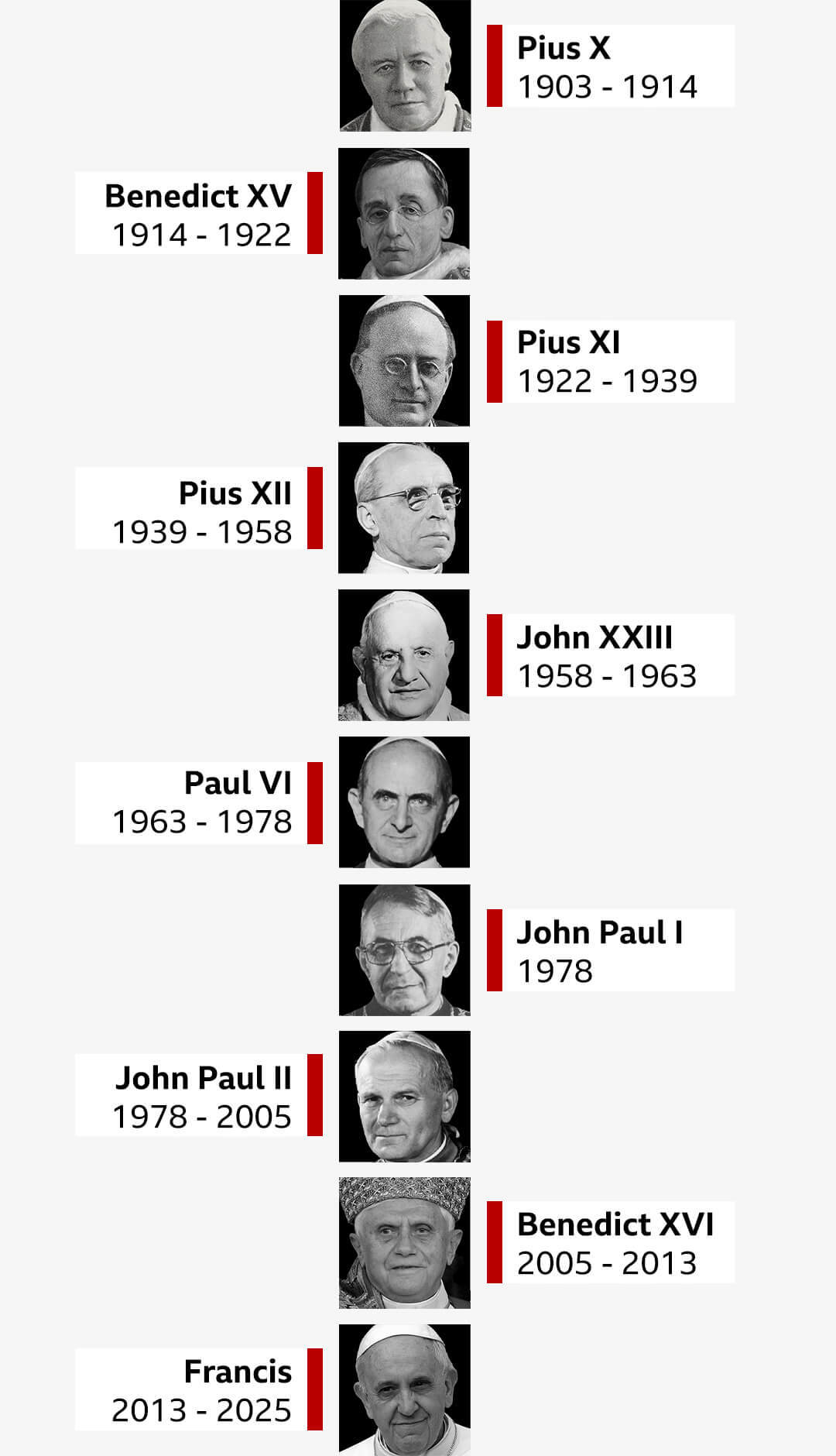
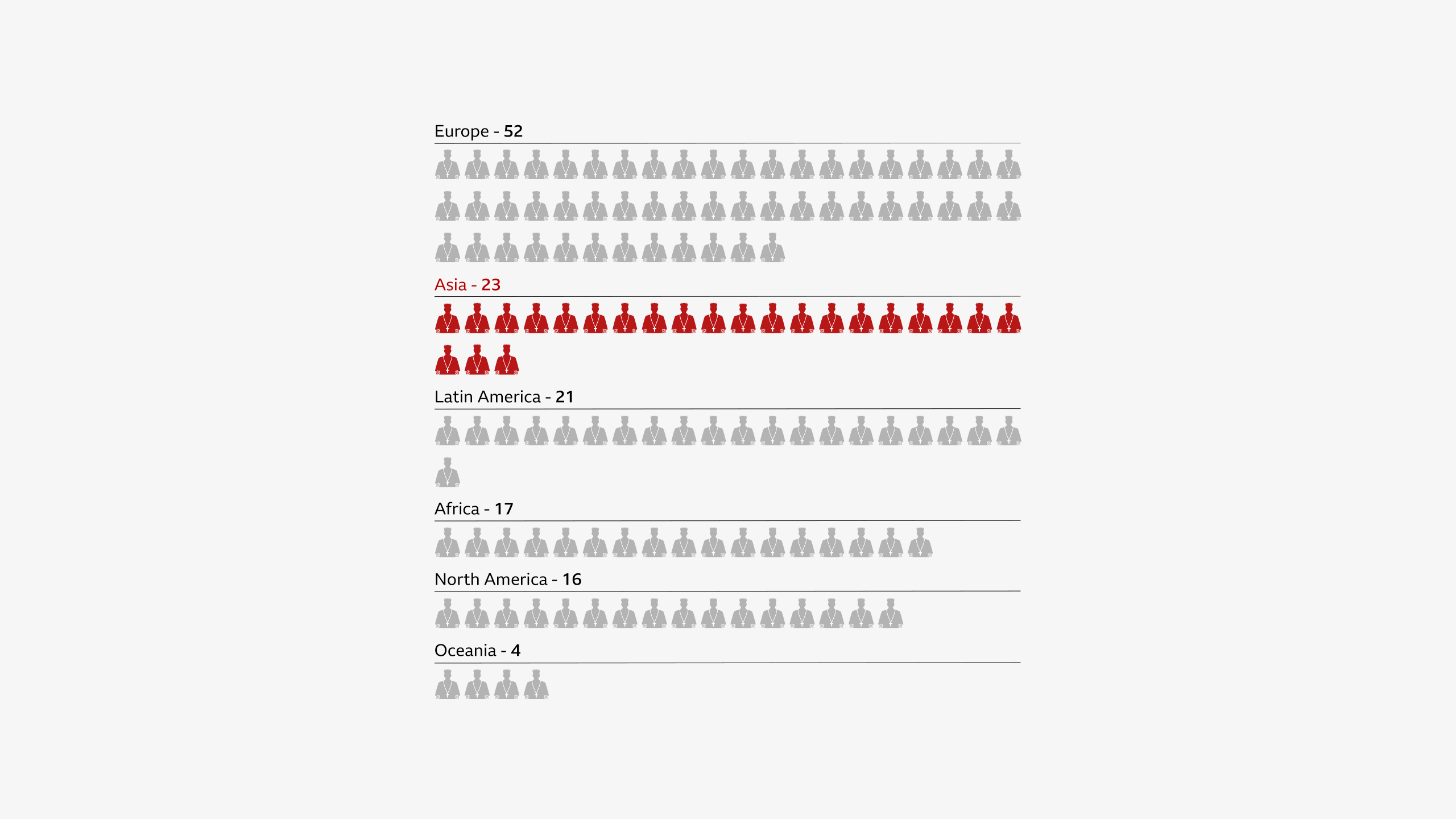
The last 10 popes of the Catholic Church
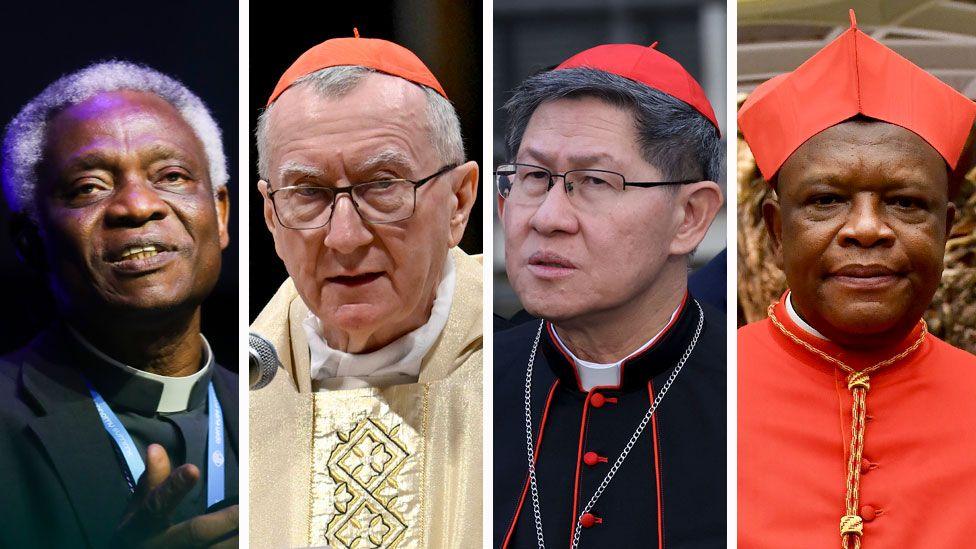
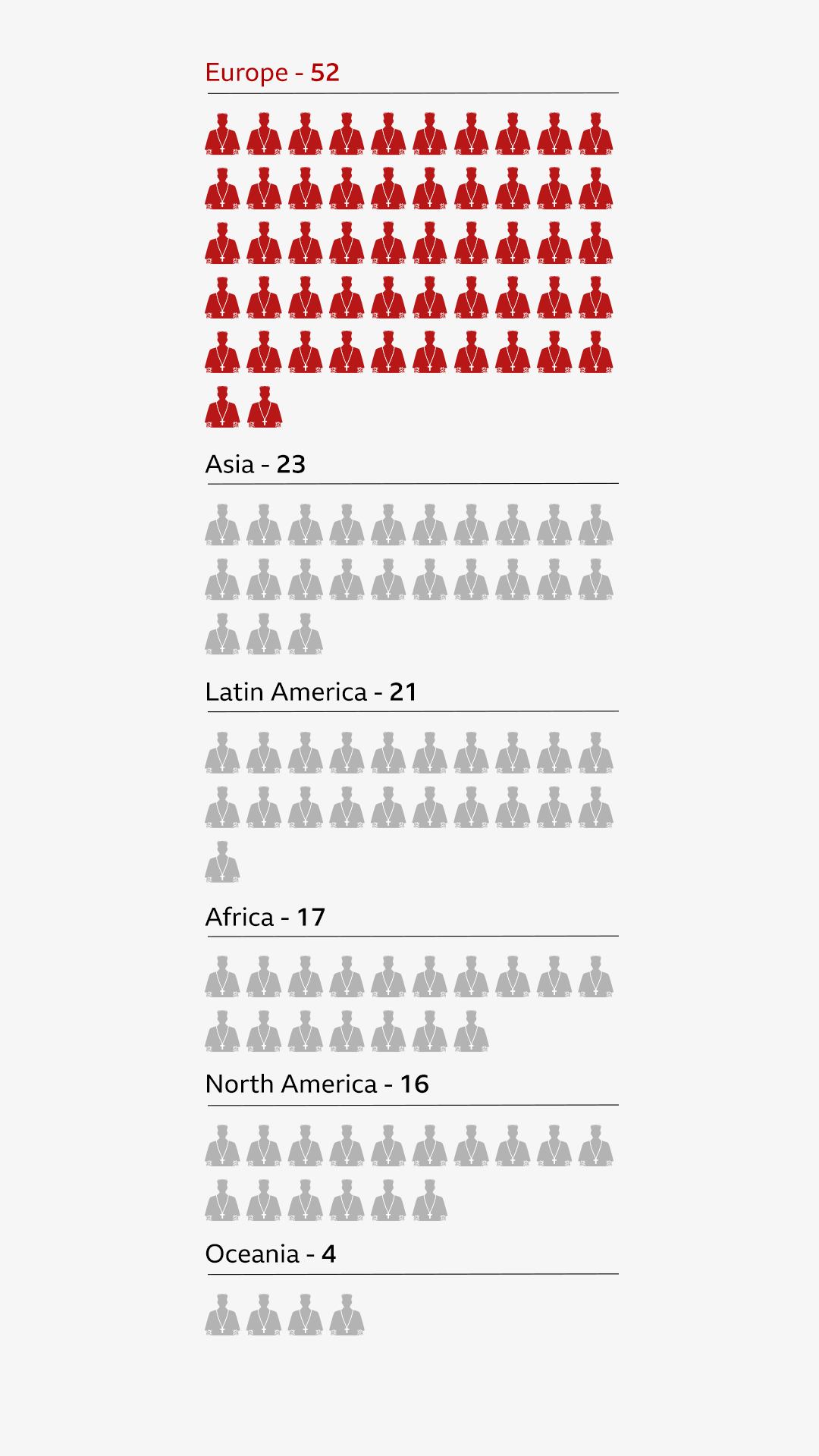
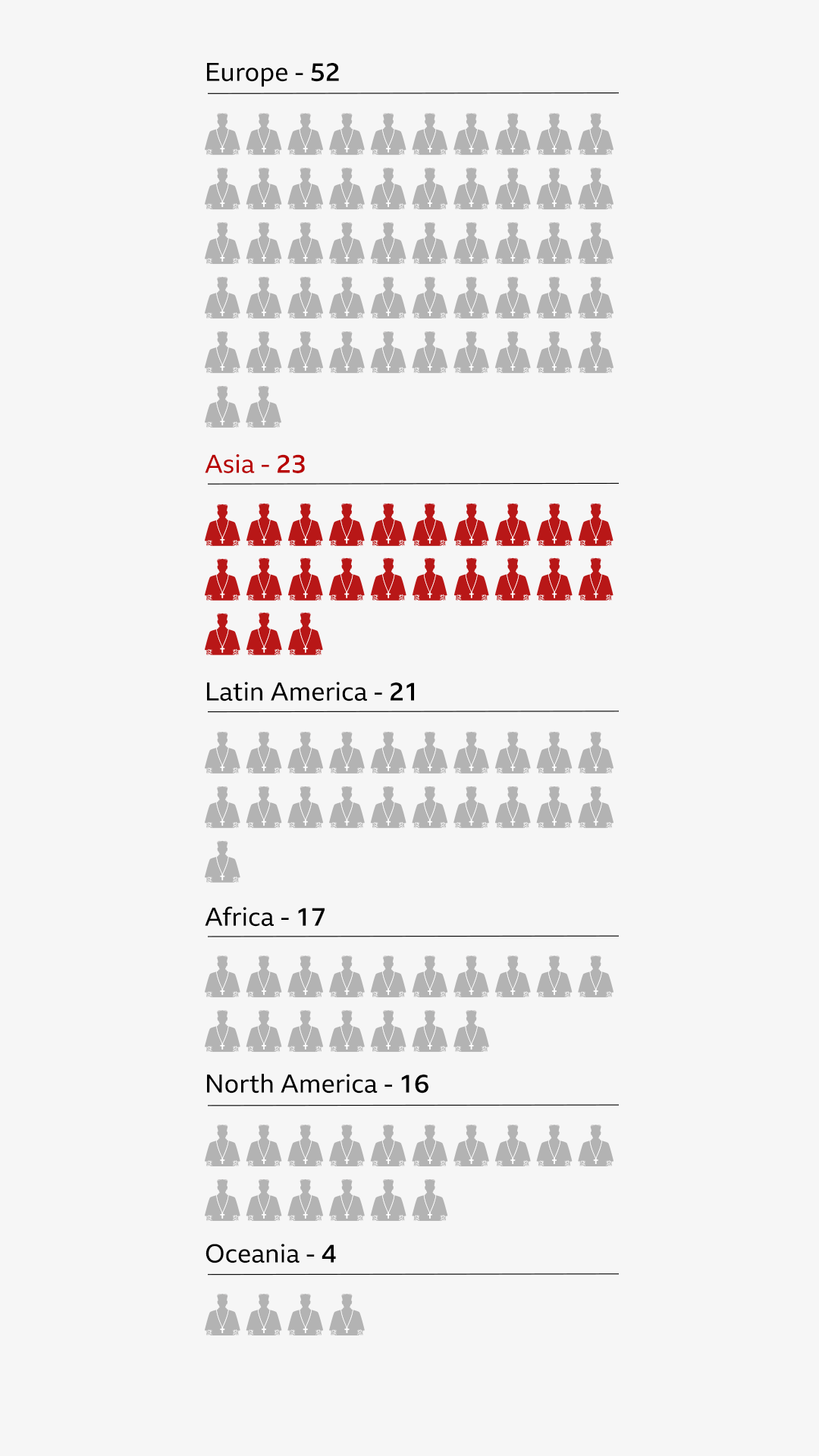
Only senior Catholic leaders known as cardinals - who must be under 80 - are eligible to vote, and the choice of a new pontiff is seen as both a duty and a spiritual responsibility.
Conclaves have been held for centuries, following strict rules designed to protect secrecy and prevent outside influence.
The word "conclave" comes from the Latin cum clave - meaning "with a key" - reflecting the tradition of locking the cardinals away.
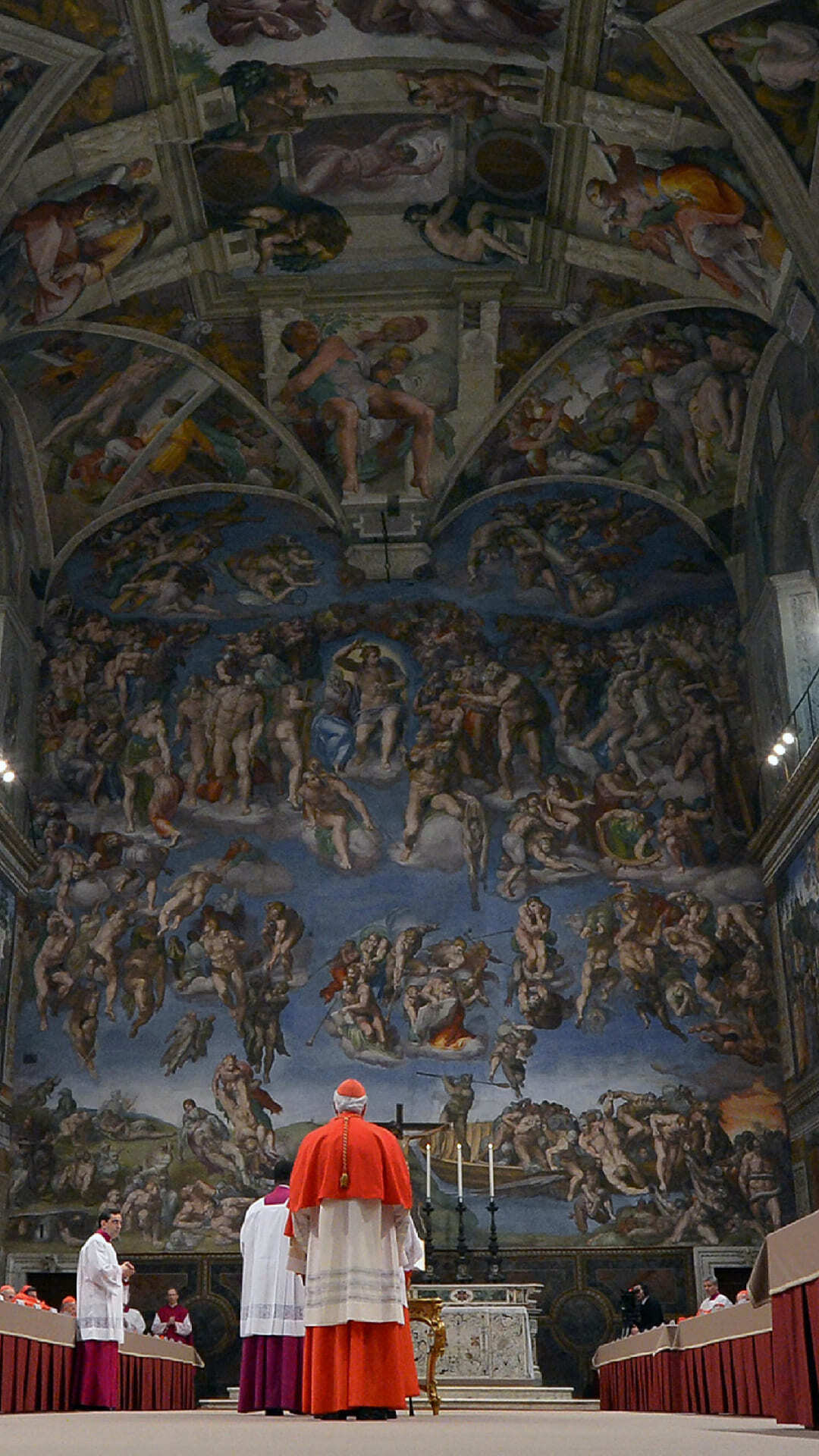
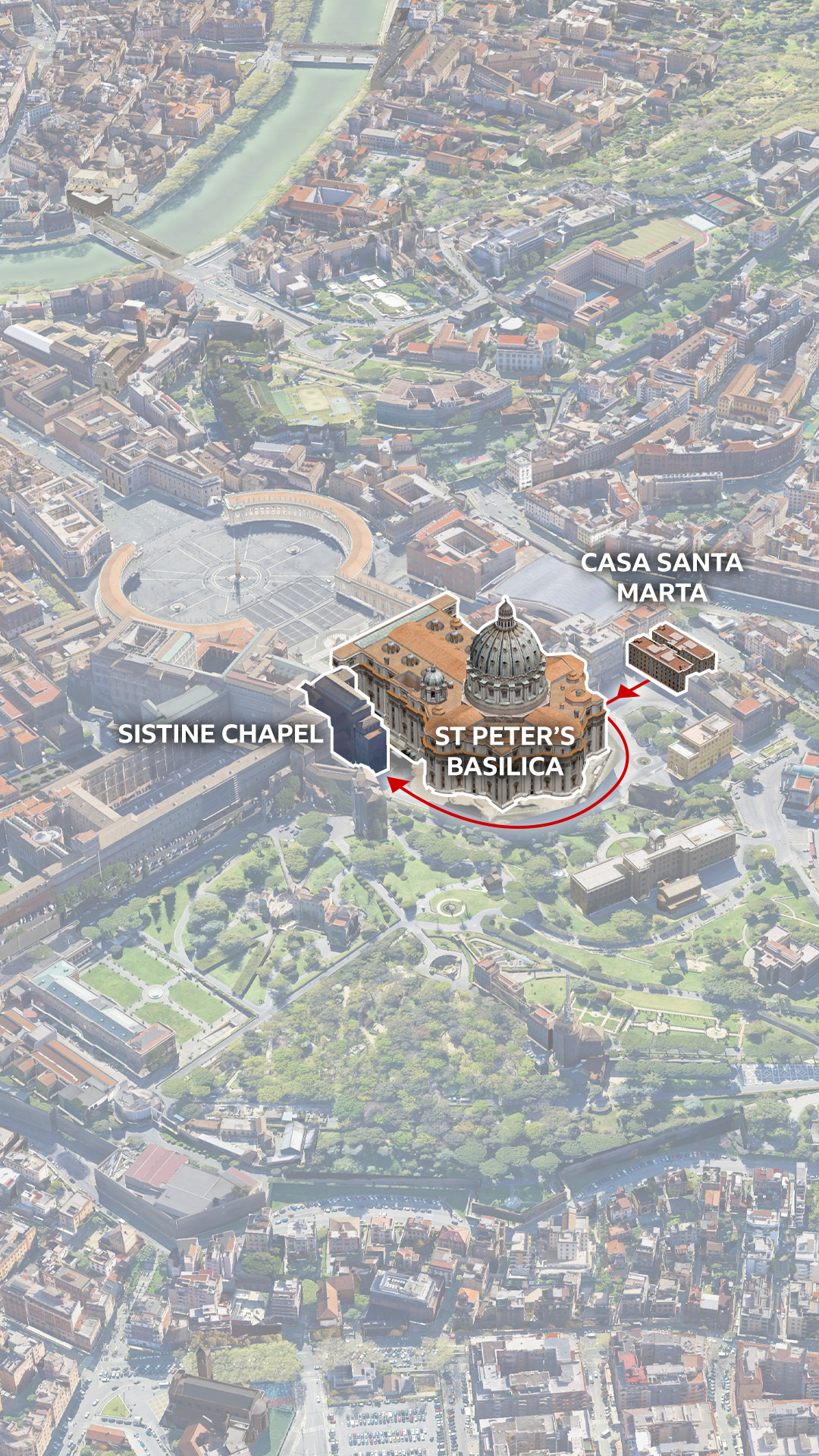
Since the 15th Century, elections have taken place inside the Sistine Chapel, beneath its famous Renaissance frescoes.
The last conclave, in 2013, elected Pope Francis after just five rounds of voting, making it one of the quicker decisions in modern times.
In earlier centuries, however, disagreements between factions sometimes caused conclaves to stretch on for months.
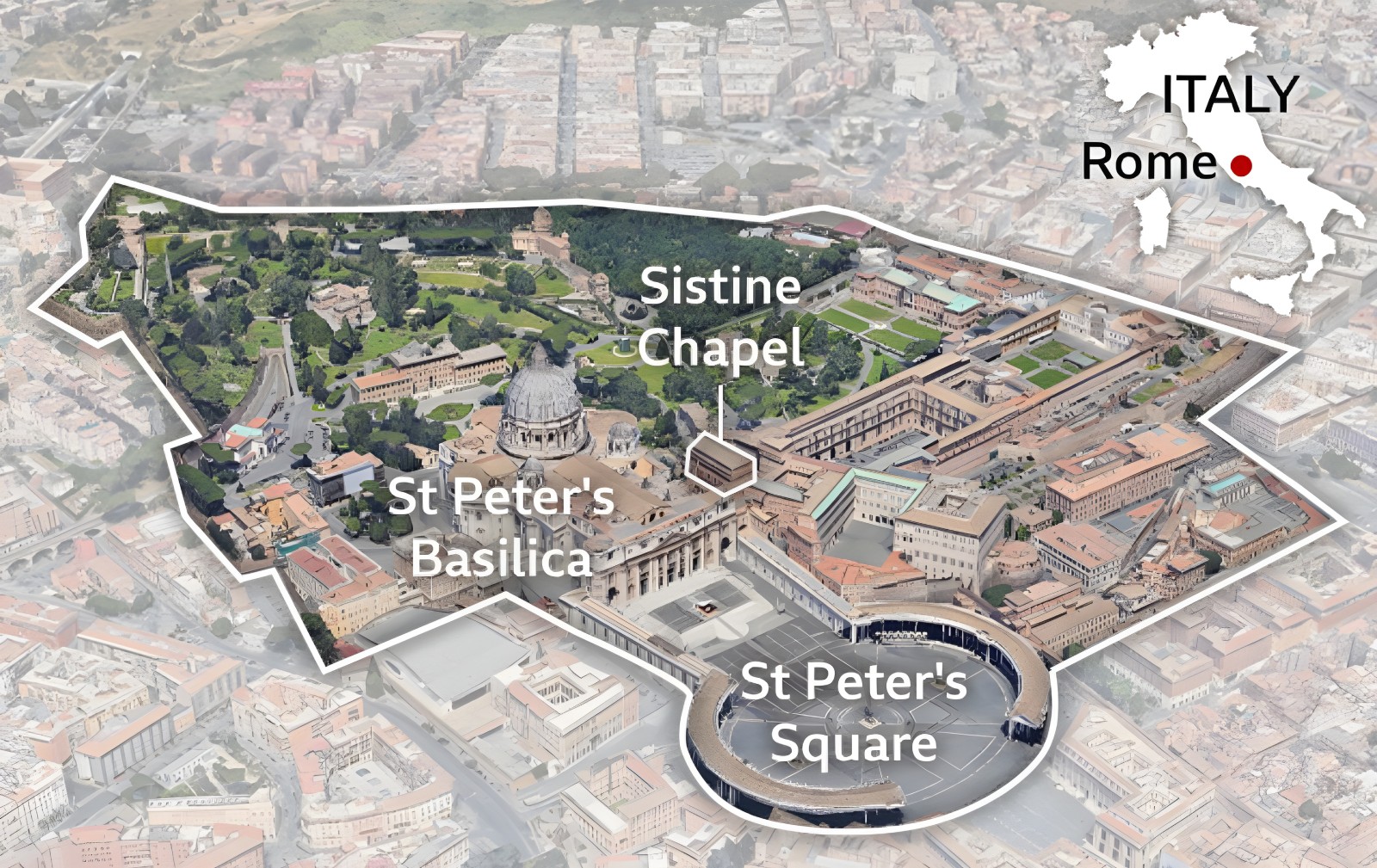
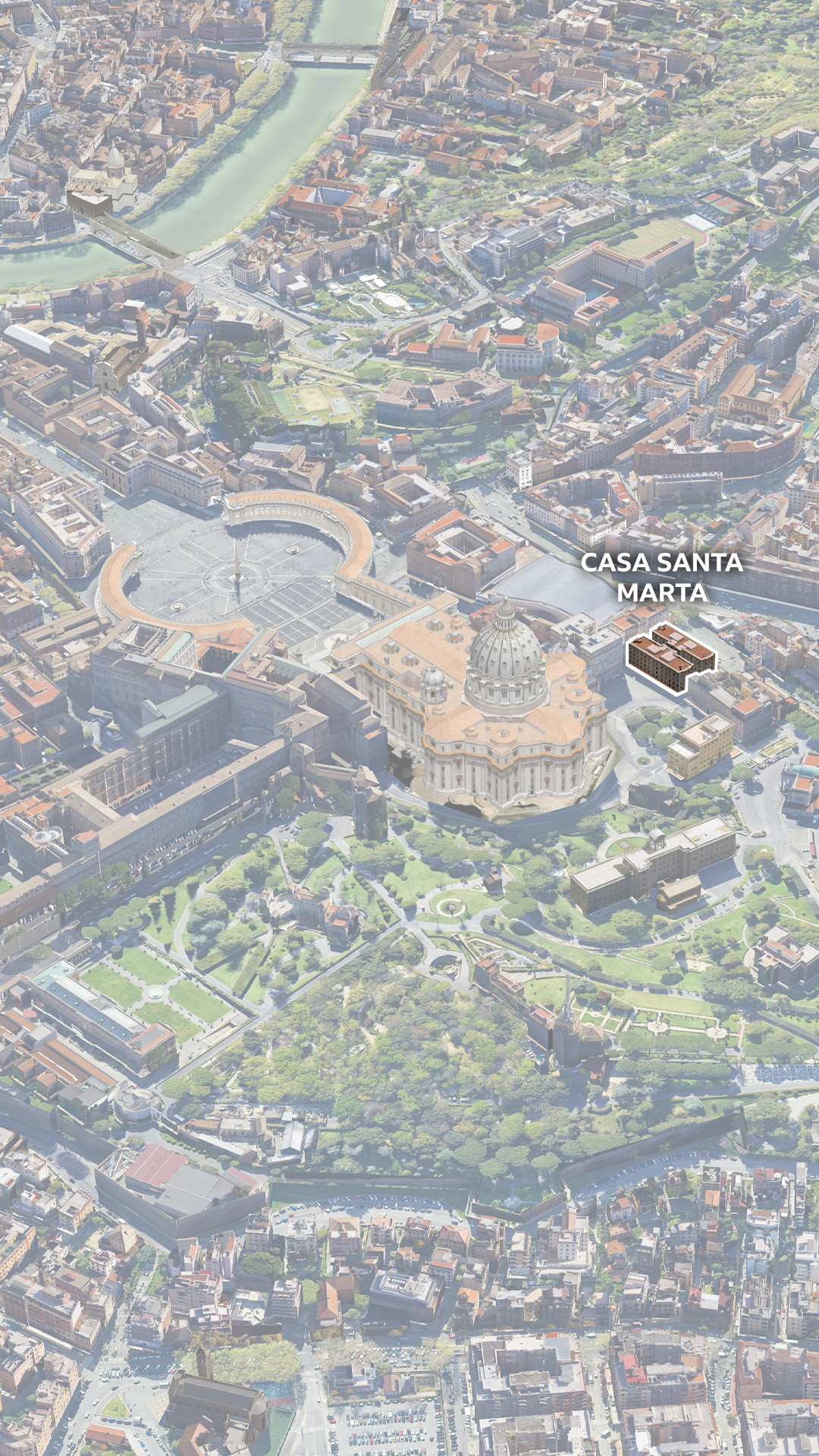
This time, cardinals have gathered in Vatican City, an independent state within the heart of Rome, to choose the 267th pope. St Peter, regarded as the first pope in Catholic tradition, was elected around the year 30AD.
Once a new pope is chosen, he will be asked if he accepts the role and the name he wishes to take.
The result will be announced with the appearance of white smoke rising above the Sistine Chapel, signalling that a new pope has been elected.
Until then, the Catholic Church remains in the Sede vacante period, awaiting its next leader.
What does the Pope do?
The Pope leads the Catholic Church and is celebrated as St Peter’s successor, giving him authority over its 1.4 billion followers. Catholics believe this connects him directly to Jesus Christ, making him a key source of spiritual guidance.
Alongside the Bible, his teachings help shape the Church’s beliefs and practices. Other Christian denominations, such as Protestants and Orthodox Christians, do not recognise his authority.
Choosing the pontiff



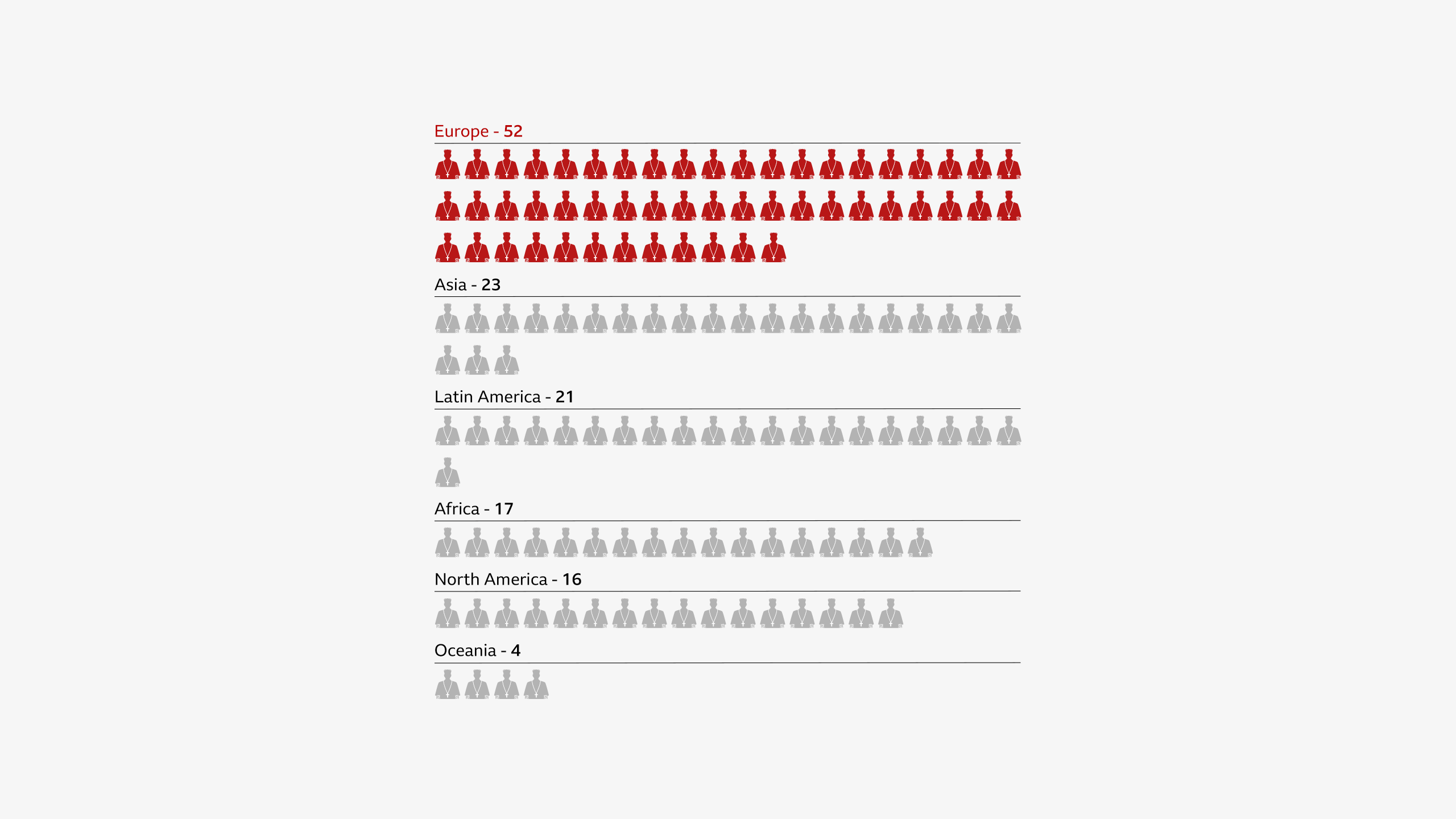
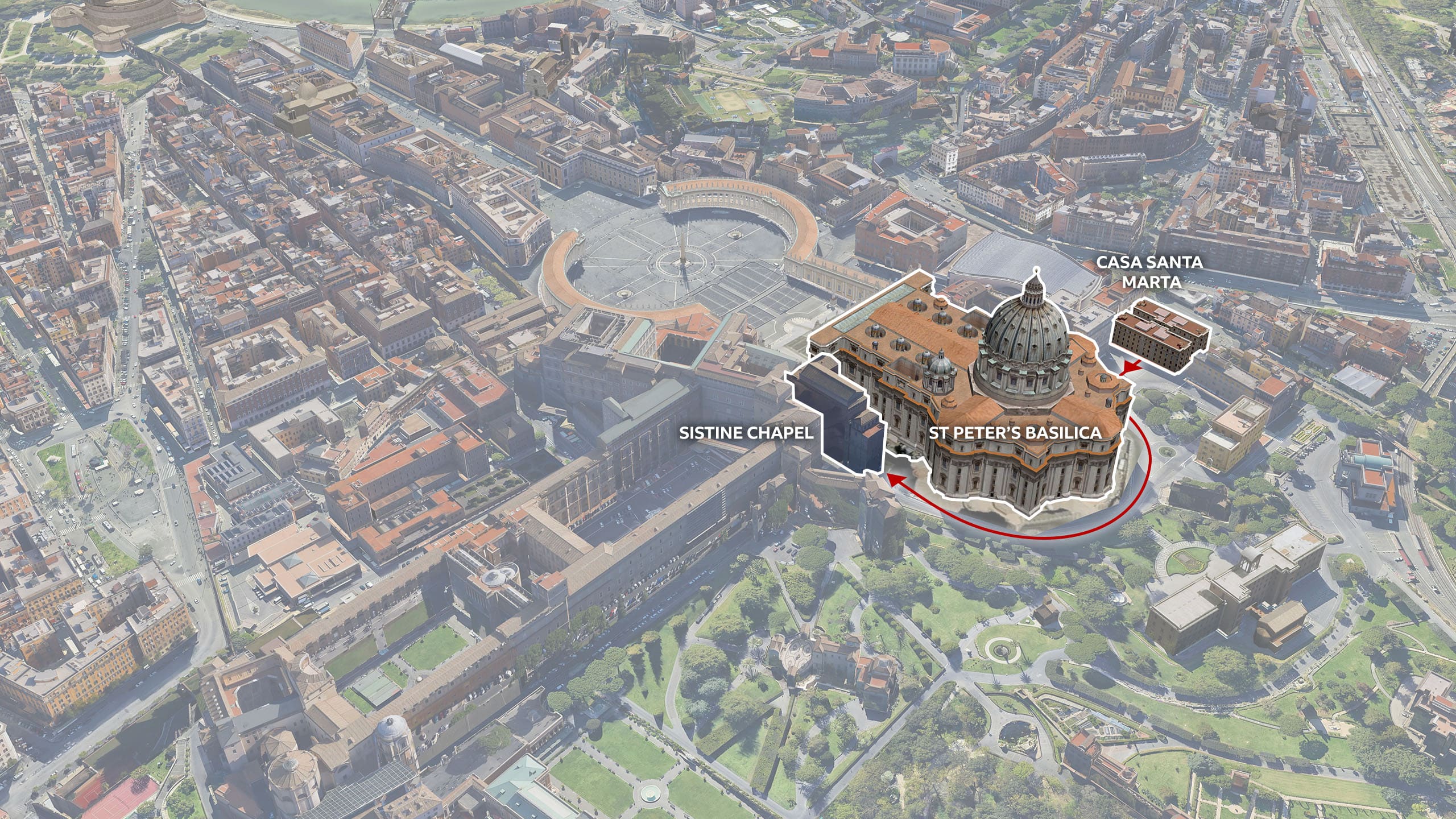
Following Francis' death, the dean of the College of Cardinals, Cardinal Giovanni Battista Re, summoned the cardinals to Rome.
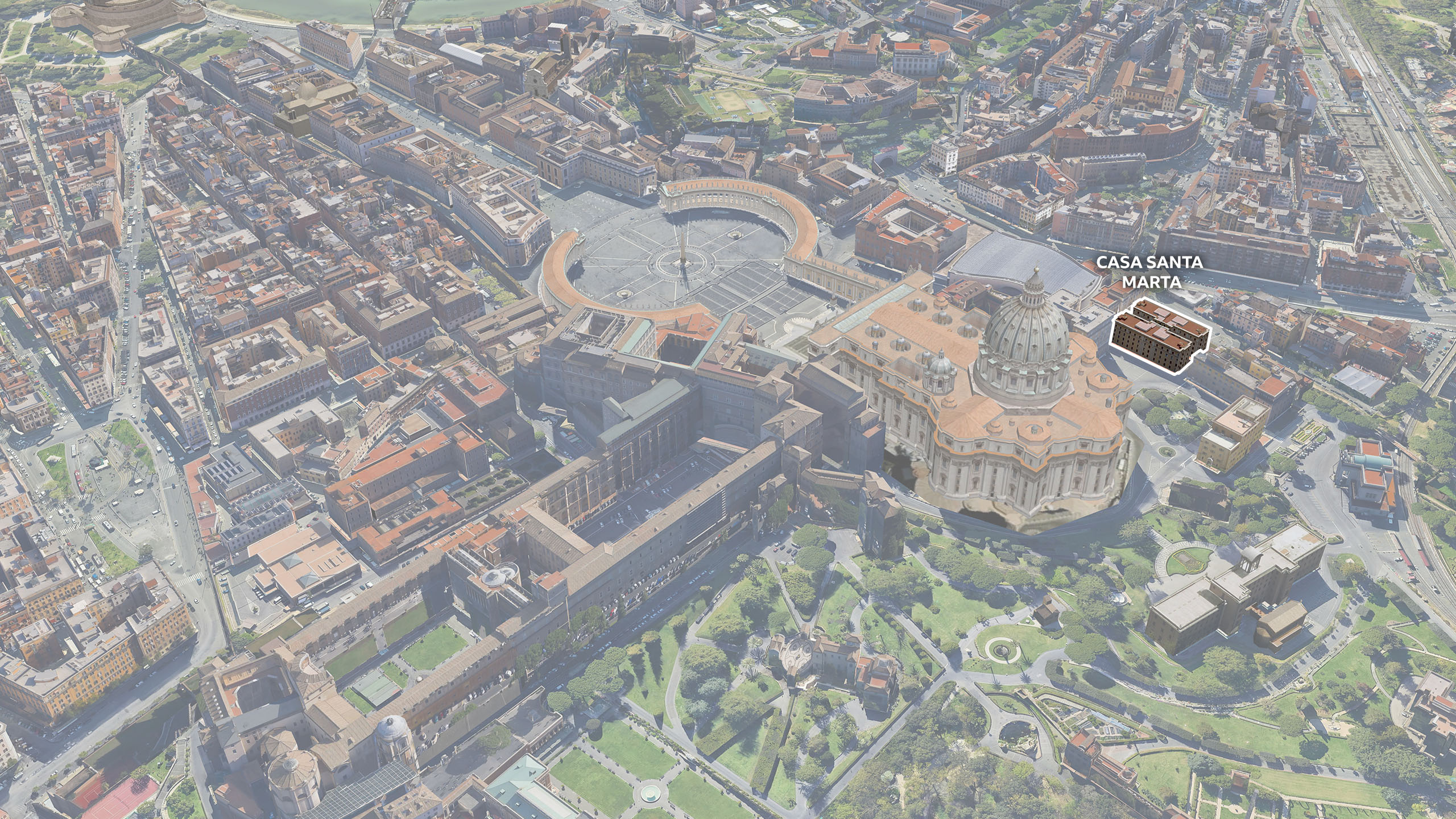

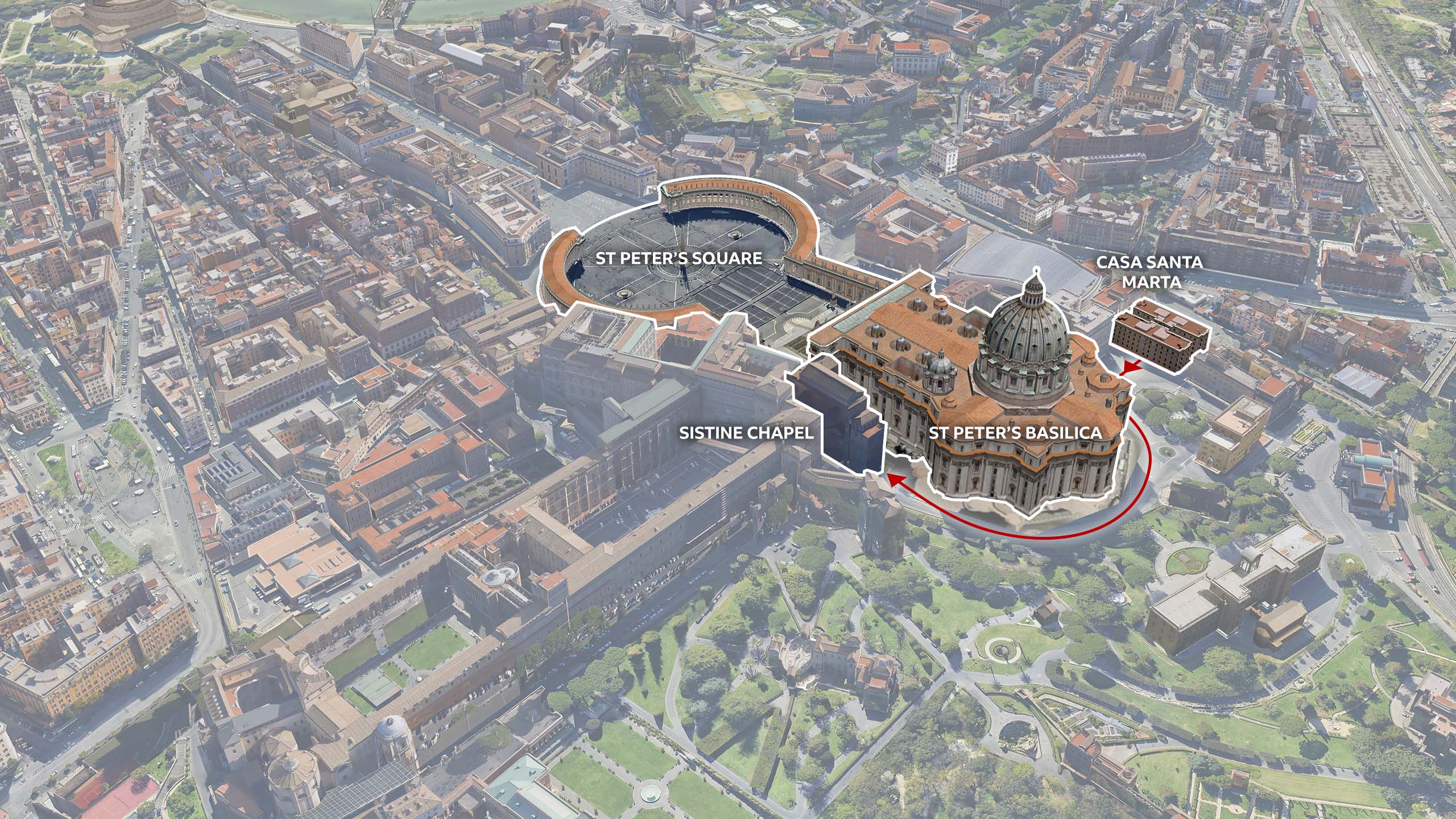
Inside the conclave
Papal conclaves are notoriously difficult to predict because the election process is shrouded in so much secrecy. Once they enter the Sistine Chapel, cardinals must have no communication with the outside world until a new pope is elected.
There is only one round of voting on the first afternoon of the conclave, but the cardinals vote up to four times every day afterwards.
A new pope requires a two-thirds majority - and that can take time.
Each cardinal casts his vote on a simple card that says, in Latin: "I elect as Supreme Pontiff" to which they add the name of their chosen candidate.
They walk in line, in order of seniority, and place their cards inside the large silver and guilded urn.
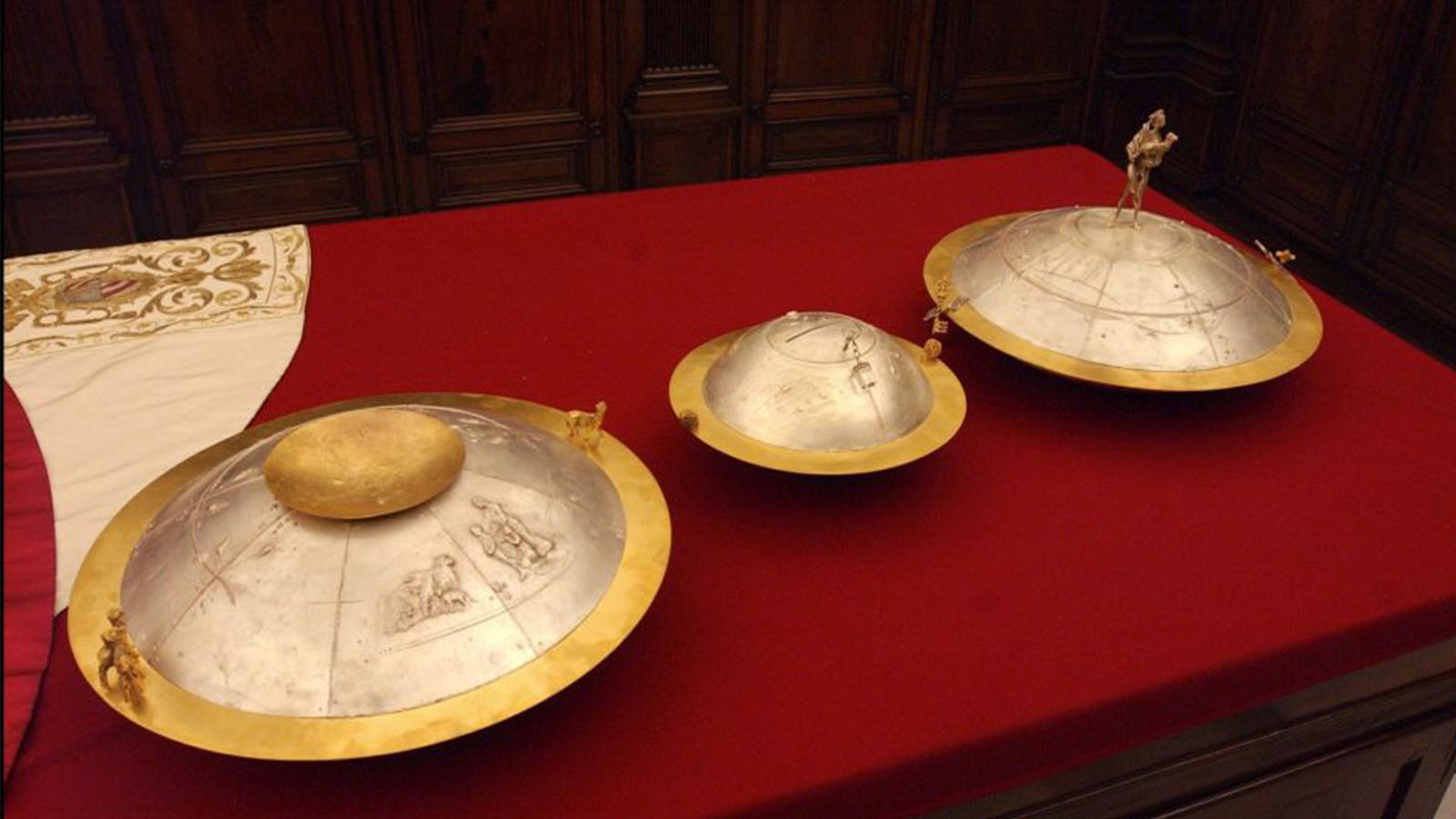

Three assistants to the camerlengo (the official managing Vatican affairs during a papal vacancy), known as the scrutineers, will then count the votes as they are read out loud. All the paper cards are then threaded together and burnt.
Outside the Sistine Chapel the world will be watching for the smoke from the chimney. If the smoke is black, there will be another round of voting. White smoke signals that a new pope has been chosen.

If the conclave completes its third day without reaching a decision, the cardinals may pause for a day of prayer.
From then on, they may take another break every seven rounds of voting.
If, after 33 rounds, no decision is still made, a run-off will happen between the two most voted candidates – though one of them will still require two-thirds of the vote to be elected pope.
The wait
“Unlike other world governments, these men are not aligned with any particular political parties so one never knows exactly what their priorities are, where they stand on controversial issues and what they will have top of mind when they cast their ballot. All of it adds up to a lot of intrigue and very little certainty,” says the BBC's Davide Ghiglione in Rome.
It’s not uncommon for conclaves to last a few days - the longest in history lasted two years and nine months, starting in 1268.
But after several rule changes to speed up the process over time, the average length of a conclave since the beginning of the 20th Century has been three days. The longest, in 1922, lasted five.
Both Pope Francis and his predecessor, Pope Benedict XVI, were elected after two days.
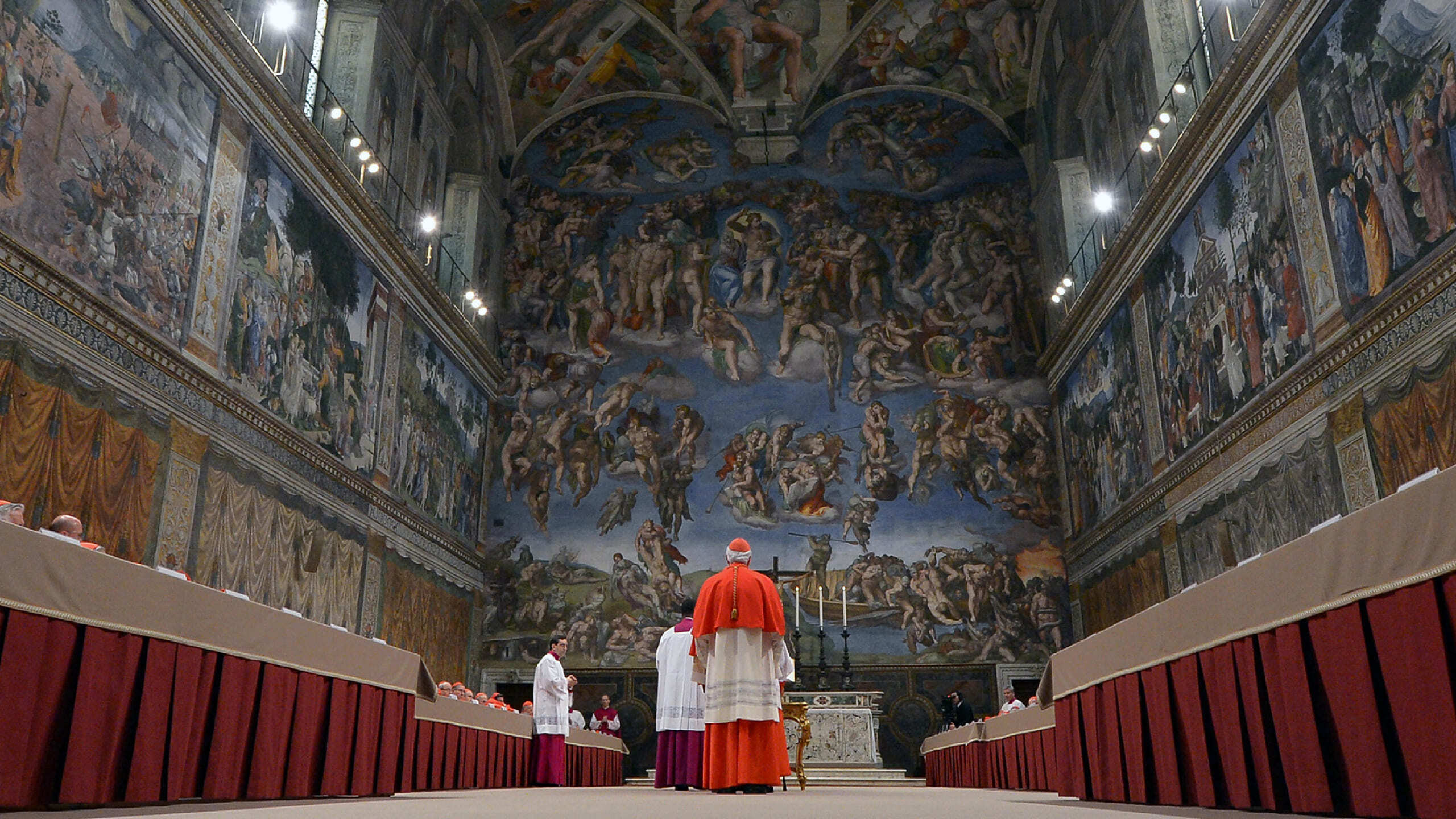
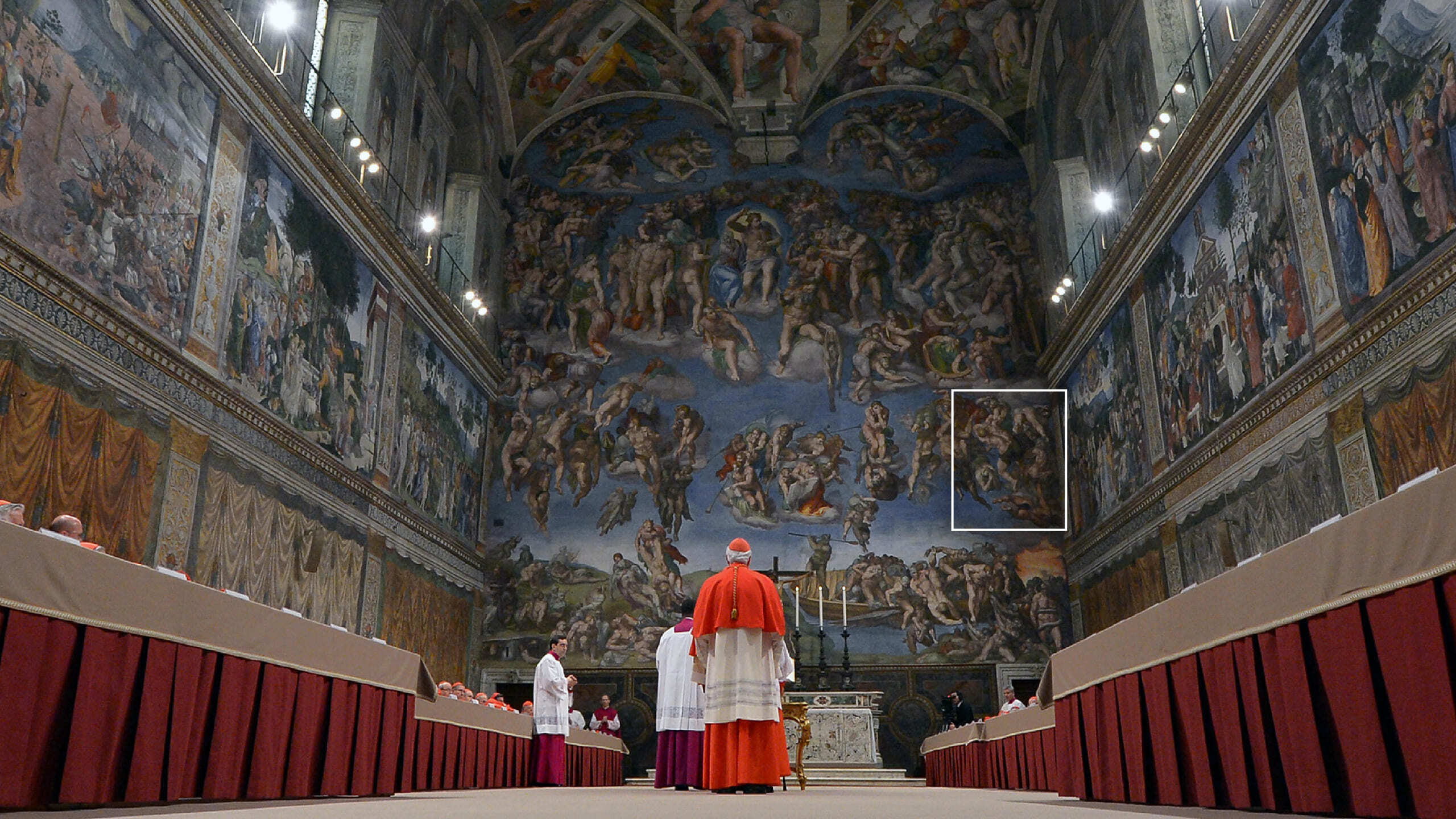





There are also two temporary structures joining the cardinals in the Sistine Chapel for the duration of the conclave.
Two furnaces have been installed at the back of the room to burn the ballots and create smoke for the chimney.
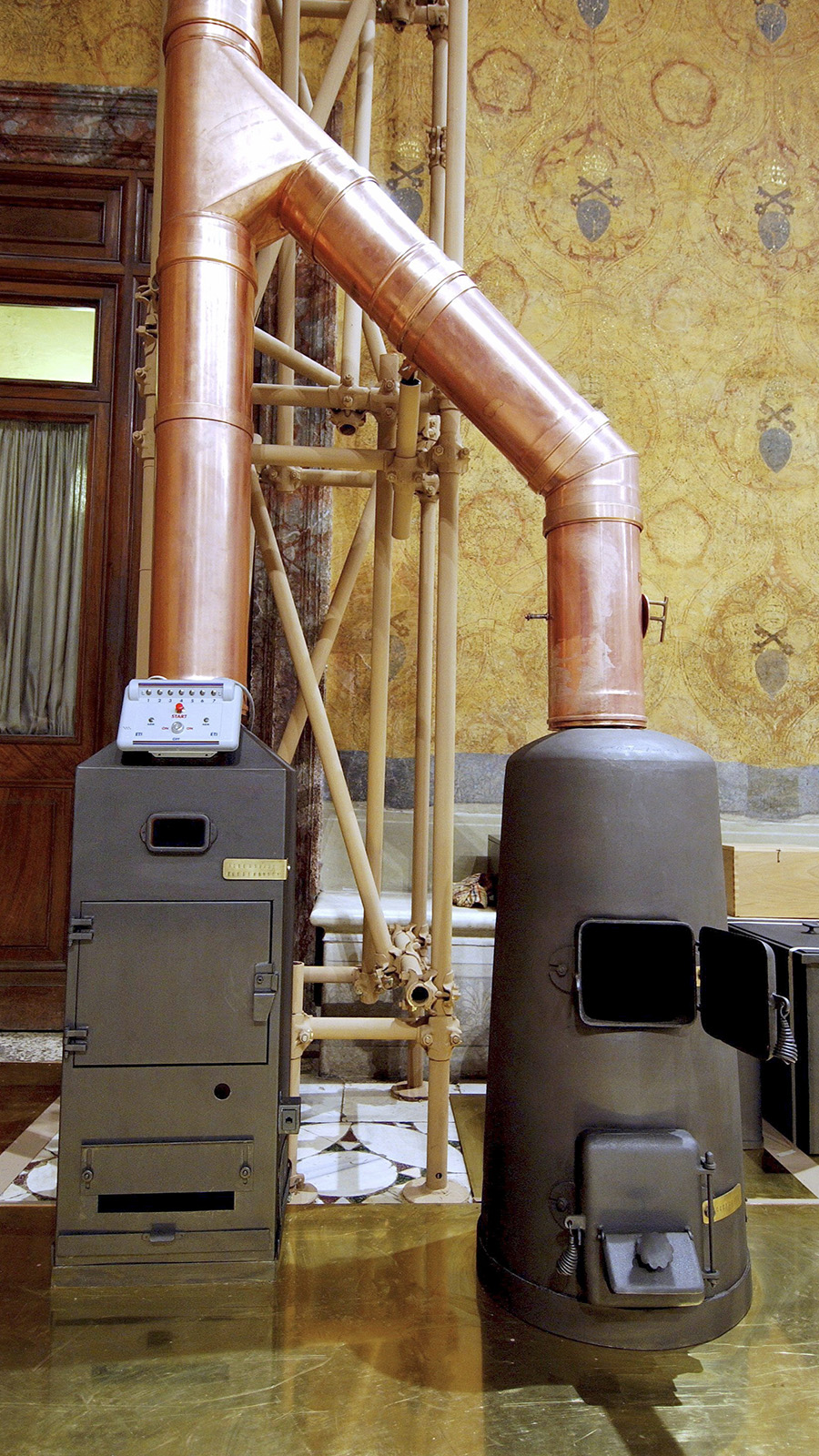

The one on the right is used for the burning of the ballot papers and the one on the left is used to generate additional smoke to signal which way the vote has gone.
Chemical compounds are mixed to make the smoke either black or white.
The release of white smoke is accompanied by pealing of bells – to avoid confusion for those waiting outside in the Square of St Peter.
What’s in a name?
Once a pope is elected, he has to formally accept the job in front of the College of Cardinals, and state his papal name.
In a press conference after his election, Pope Francis said his name honoured St Francis of Assisi, and that he was inspired by his Brazilian friend Cardinal Claudio Hummes.
The pontiff told reporters that when he was proclaimed, Hummes hugged and kissed him, saying: "Do not forget the poor."
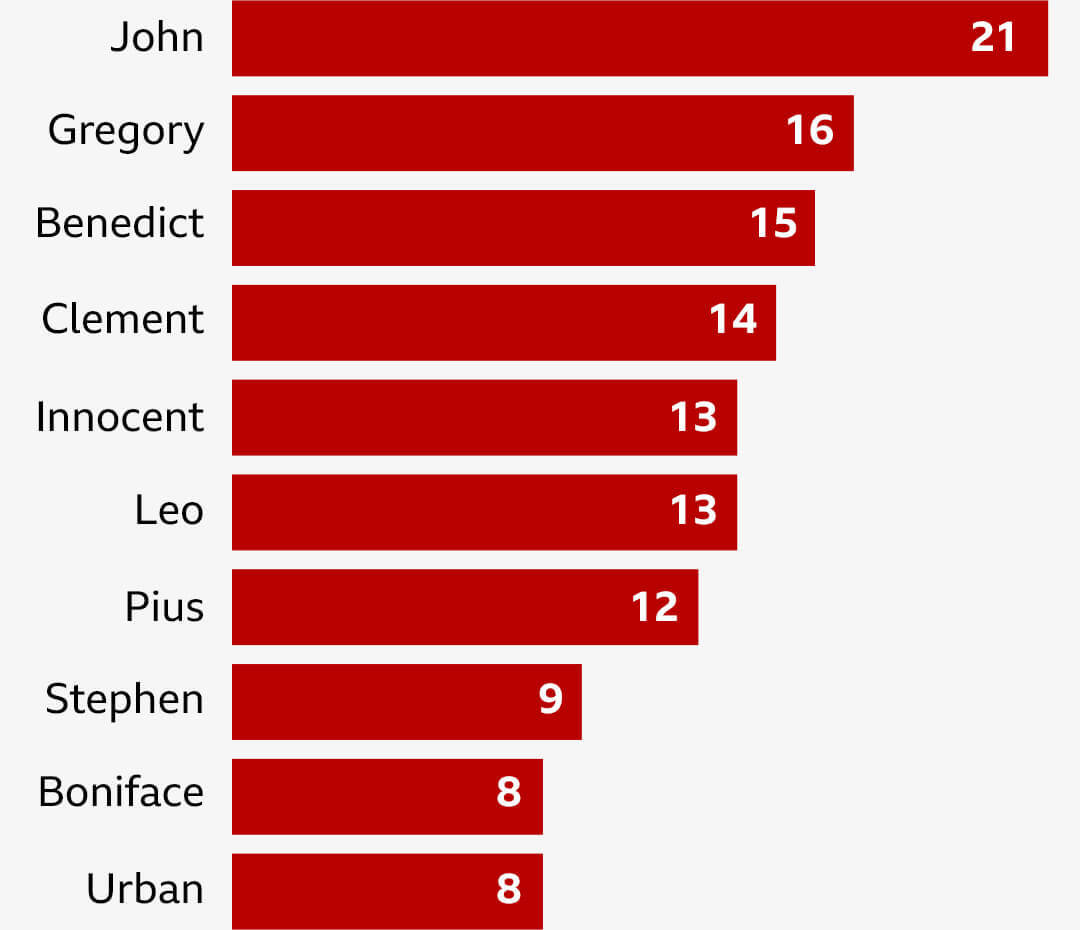
For more than 500 years, popes used their own names. This changed to symbolic names in order to simplify their given names or to refer to previous pontiffs.
That is why most popes in history have chosen the name John.
The 10 most popular Pope names
After stating his new name, the new pope is taken to the so-called "Room of Tears", an antechamber in the Sistine Chapel, where he first receives his papal robes and accessories like the white cassock, a cape called the mozzetta and a white skullcap called the zucchetto.
The room earns its nickname from accounts of previous popes who, overwhelmed by the weight of the moment, were moved to tears after their election.
What he chooses to wear from that selection in those first minutes is a personal decision - one that can signal how he sees the role he’s just accepted. Pope Francis notably declined to wear the elaborate red cope (a ceremonial cloak worn by clergy) with ermine, opting instead for a simple white cassock.

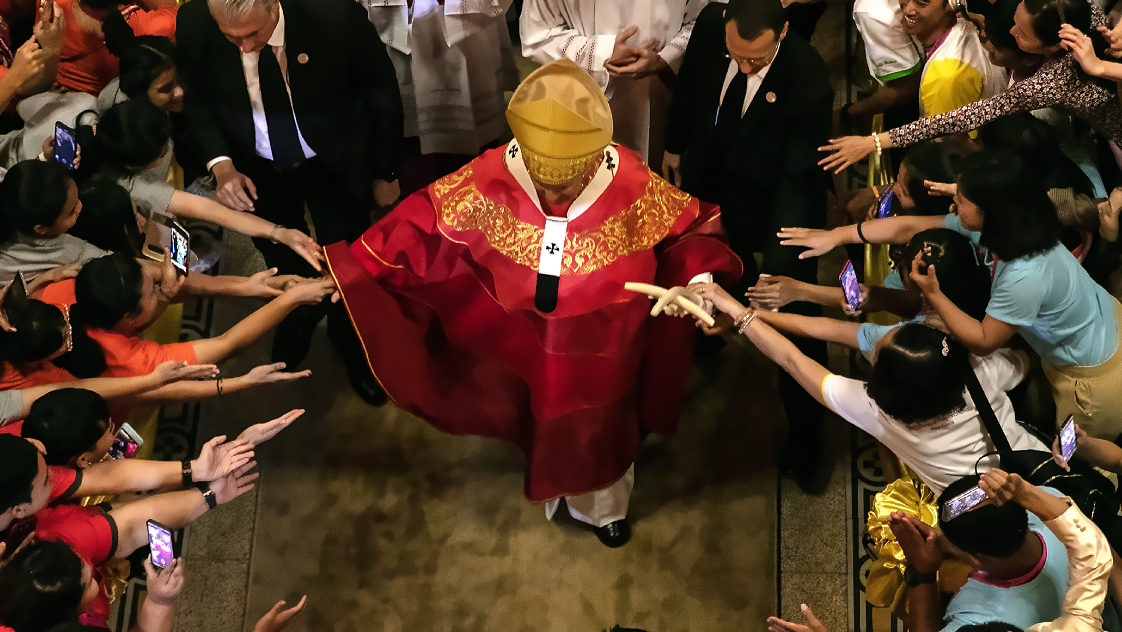
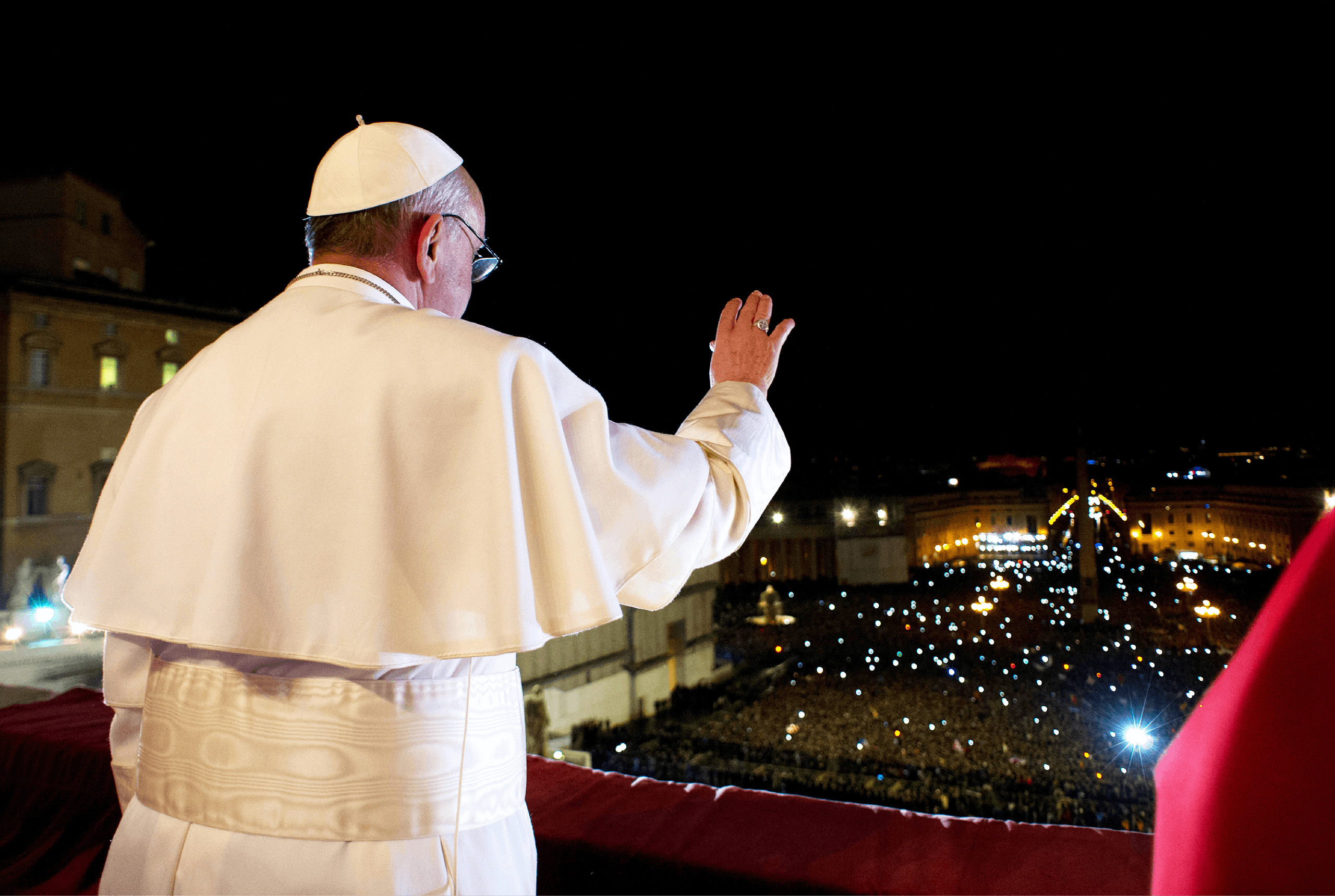
On a balcony in St Peter’s Basilica overlooking the square, the new Supreme Pontiff of the Catholic Church will introduce himself to hundreds of faithful from all around the world.


Produced and edited by
Camilla Costa, Pilar Tomas, Chris Clayton, Krystina Shveda, Richard Moynihan, Tom Finn and Dominic Bailey
Designed by
Kate Gaynor, Gerry Fletcher, Daniel Arce, David Blood, François De Montremy and Louise Hunter
Development by
Shawn Hardern, Giacomo Boscaini-Gilroy, Dan Smith and Lewis Bellwood
Images by
Google and Getty