Stop, rewind: the scientists slowing the ageing process
- Published
- comments

The ageing process has been linked with many biological mechanisms
Scientists are slowly unlocking the secrets of ageing, and some suggest treatments may soon be at hand to slow or even reverse the ageing process.
But what can science really achieve, and what are the dangers of meddling with our biological clocks?
Could such treatments induce cancers in humans, for example, and what about the world's burgeoning population and the West's "pension time bomb"?
Chromosome tips
The ageing process is a complex one, and for long remained an impenetrable mystery, but progress is now being made.
Late last year, a team at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston published a Nature paper, external in which they detailed the reversing of the ageing process in mice.
They targeted the chromosomes that reside within the nuclei of all cells, and specifically telomeres, caps at the tips of chromosomes. The telomeres protect the chromosomes from damage, but also shorten with age, until the cells are no longer able to replicate.
Professor Ronald DePinho and colleagues manipulated the enzyme that regulates these tips - known as telomerase - and witnessed dramatic results. Mice engineered to lack the enzyme aged prematurely, but when the enzyme was replaced, the mice appeared to rewind the clock.
Should we be meddling with something as fundamental as ageing?
"What we were expecting was a slowing or stabilisation of the ageing process," he told the BBC. "Instead we witnessed a dramatic reversal in the signs and symptoms of ageing."
"These animals had their brains increase in size, they improved their cognition, their coat-hair was restored to a healthy sheen and their fertility was also restored."
Of course, this was a story of mice, not men, and applying such principles to humans could be an altogether bigger challenge. Telomerase has been linked with cancer, and there are likely to be many other mechanisms involved in ageing.
Many believe mitochondria may play a bigger role - genetic material contained within the cell but outside the nucleus. Mitochondria are the "power houses" of cells, but have also been seen to generate harmful chemicals linked with aging.
Then there is the role played by free radicals, highly reactive atoms or molecules that attack our bodies.
Anti-ageing drug
But even though a comprehensive picture of how we age is still to be constructed, there are scientists who are already testing anti-ageing treatments on humans.
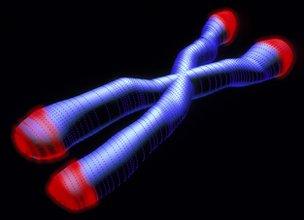
Telomeres (in red) are found at the ends of each chromosome, and shorten with age
Professor David Sinclair also works in Boston at an ageing laboratory at Harvard Medical School. He and his colleagues have been working on synthetic drugs called "Sirtuin activating compounds" or STACs.
Animal studies have indicated STACs can restore the health and life prospects of obese mice and early-stage trials in humans are now underway.
The research follows earlier work, external on resveratrol, a naturally-occurring ingredient of red wine. Both resveratrol and STACs appear to mimic the effects of restricting calorie intake, which has been seen to slow ageing in animals.
"This isn't going to be an excuse to eat French fries all day and watch TV but is a way to augment your healthy lifestyle and give you the ultimate benefits of perfect health which your body is capable of," Professor Sinclair told the BBC.
"It doesn't change food intake - the mice eat just normally or they get fatter, but their body doesn't seem to know they're fat and their organs and even their longevity is as good as a really healthy mouse."
But should we be experimenting with something so fundamental as ageing in the first place? And what of the ethical issues?
Professor Tim Spector of King's College London, who also works on the ageing process, says the focus is not on extending life, but on extending good health.
"If it means by living a long time you're crippled by arthritis and can't get out of the house that's not much use to anyone."
"But by understanding the ageing process, we can help combat arthritis, diabetes, heart disease, all these things which are age-related."
Professor James Goodwin, head of research at Age UK, believes access will quickly emerge as a key issue, should effective anti-ageing medical treatments be developed.
"Will everybody be able to get this technology which will give them a longer healthier life, or will it be restricted to the rich and wealthy?" he asks.
"Or how will the poorer countries regard the richer countries of the world where everyone is living well and living longer?"