Facebook friends network 'quadruples voting behaviour'
- Published
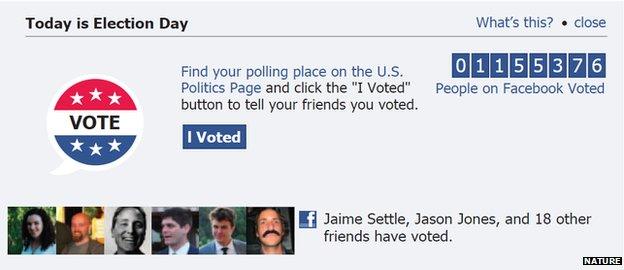
Many users saw a message with pictures of friends who had voted; others saw a version without the friends
A banner message on Facebook showing users' friends who had voted drove a third of a million more voters to the poll booths, research shows.
Sixty-one million Facebook users in the US were shown the message, while 600,000 others simply saw a message imploring them to vote.
A report in Nature, external shows the message drove about 60,000 extra votes in the 2010 US Congressional elections.
But the message appearing on friends' pages drove a further 282,000 votes.
The work was led by James Fowler of the University of California, San Diego, whose prior work has shown, among many other things, that the friends we choose may in part be down to genetics.
For the current work, he and his colleagues were interested in examining the oft-cited claim that online social networks influence offline decision-making - a claim that has until now been difficult to pin down.
"There's been a lot of work in online social networks showing that app adoption can spread from person to person, and there's been a lot of work in the real world showing that things like obesity and drinking and smoking can spread from person to person," Prof Fowler told the Science In Action programme on the BBC World Service.
"But there hasn't been any work that showed what happens online affects the real world."
To look into that question, the team arranged for Facebook to post a non-partisan "social" message along the top of 61 million users' pages, including a reminder that it was voting day, a clickable "I voted" button, a link to information about nearby polling places, and a list of up to six of the users' friends who had already clicked the button.
About 600,000 users were shown an alternate, "informational" message, identical except for the absence of the friends data. A further 600,000 were shown no message at all.
The data on which users sought polling station data or clicked the "I voted" button could then be cross-correlated with publicly available data on who actually went to cast a vote.
The results showed to a high statistical significance that those who received the "social" message were more than 2% more likely to report having voted and 0.4% more likely to actually vote than those shown the "informational" message.
And users were 0.22% more likely to vote for each "close" friend - as measured by the degree of Facebook interaction - who received the message.
By correlating the findings with polling data and comparing with the "no-message" case, the team estimate that the message resulted in more than 340,000 extra votes being cast.
Prof Fowler conceded that the results represented a small fraction of the voting public, but that it was enough to sometimes make a large difference.
"I doubt it changed the outcome of the overall election, but it's possible it had an impact on local elections," he said. "There are certainly circumstances in our history where a far smaller number of votes would have mattered: in 2000 in the US the presidential election was decided by just 537 votes in Florida."
Peer to peer
The findings are intriguing from a political point of view, but the study is also finally shedding light on the thorny problem of extracting these "peer influence" effects from the factors that drive the network's formation in the first place.

What happened in the 2010 elections is a big hint at what happens all the time on Facebook
What confounds that problem is what is called homophily - we tend to befriend people in real life or online with whom we share significant similarities.
"If we were just going to do an observational study where we just looked at the network to see whether or not people who voted tend to be connected to others who voted, we wouldn't know if that was because they tended to become friends because they both like politics or if one friend influences another," Prof Fowler said.
But the random selection of friends to show to users in the "social" message - some close friends, some only peripheral - should sidestep issues of homophily, Prof Fowler explained.
"The beauty of this experiment is that we can rule that out as an explanation for what we found," he said.
And the scale of peer influence they found was notable.
"The 'friend' vote is really critical," he said. "In this experiment we were able to show that if you just looked at the users and whether or not the message directly affected them you'd be missing the whole story; for every user that changed their behaviour, there were four friends who changed their behaviour.
"In other words, the network quadrupled the effect of the 'get out the vote' message."