Astronauts tackle air leak on International Space Station
- Published
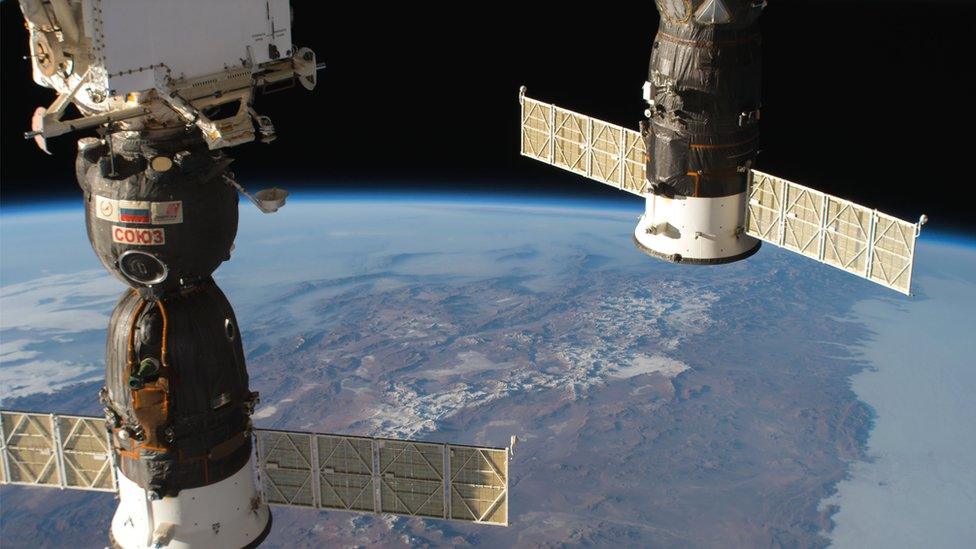

The Russian Soyuz spacecraft (L) brought a new crew to the International Space Station (ISS) in June
Astronauts on the International Space Station (ISS) are having to deal with an air leak from a possible collision.
It has been traced to a small hole in a capsule that was used to deliver a new crew to the laboratory 400km (250 miles) above the Earth in June.
It is thought the damage was caused by the impact of a high-speed rocky fragment flying through space.
Mission controllers in Houston, Texas, and Russia's capital, Moscow, say the six-strong crew are in no danger.
Impacts from tiny meteoroids are a permanent threat to the orbiting platform and it was built to withstand the constant bombardment from the dusty fragments that whizz about above the Earth.
A sunrise from space
Mission controllers were first alerted to the issue by air pressure sensors on board the station.
The astronauts were asleep at the time, but when they rose for their day's work on Wednesday they were instructed to search for the leak.
They found it in the Russian Soyuz vehicle used to bring three crewmen to the station on 8 June, among them Europe's Alexander Gerst, who is set to take command of the outpost.
"Overnight and in the morning there was an abnormal situation - a pressure drop, an oxygen leak at the station," chief of the federal space agency Roscosmos, Dmitry Rogozin, was quoted as saying by Russian news agencies.
"A micro-fracture was found; most likely it is damage from the outside. The design engineers believe it is the result of a micrometeorite," he said.
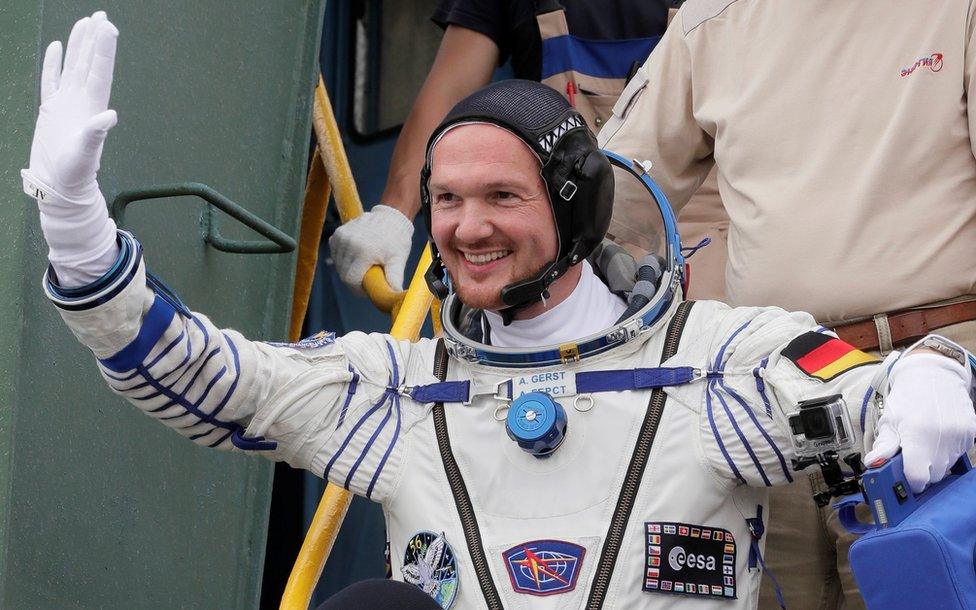

German astronaut Alexander Gerst will be the second European to command the ISS
Germany's Gerst confirmed the presence of the hole by running his finger over it.
An immediate fix was implemented using a sealant and tape to cover the hole, which is said to measure a couple of millimetres in diameter.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.
The astronauts are now working with engineers on the ground to assess whether a more robust repair is needed.
Gerst, along with US astronaut Serena Auñón-Chancellor and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Prokopyev, are due to use the same Soyuz vehicle to return to Earth at the end of the year.
Fortunately, the puncture is in the craft's orbital module - the segment that is dumped before the Soyuz' crew capsule enters the atmosphere .
- Published30 August 2018
- Published29 June 2018
- Published6 June 2018

- Published5 December 2017
