Bloodhound Diary: All models are wrong...
- Published

World's fastest car driver: Andy Green hopes to be running later this year
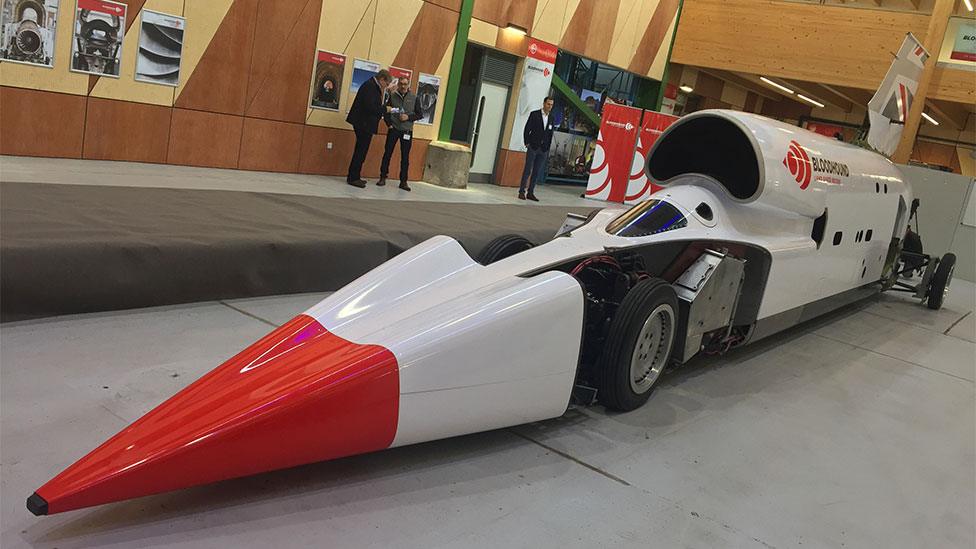
A British team is developing a car that will be capable of reaching 1,000mph (1,610km/h). Powered by a rocket bolted to a Eurofighter-Typhoon jet engine, the vehicle aims to show its potential by going progressively faster, year after year. By the end of 2020, Bloodhound, external wants to have demonstrated speeds above 500mph. The next step would be to break the existing world land speed record (763mph; 1,228km/h). The racing will take place on Hakskeen Pan in Northern Cape, South Africa.
Bloodhound LSR is a hive of activity as we prepare the car for its first high-speed test runs in South Africa.
All the technical bits are coming on really well, so our test dates will probably be decided by the paperwork (import/export licences for classified military jet engines, rocket systems, etc, take a bit of time…).
We're still aiming to go as soon as we can, hopefully late this year - we'll confirm as soon as we know.
The high-speed test runs will give us some key data to confirm the aerodynamics of the car.
In the age of supercomputers and artificial intelligence, it may seem old fashioned to go out and do test runs - surely computers can predict everything nowadays? The simple answer is no, they can't.
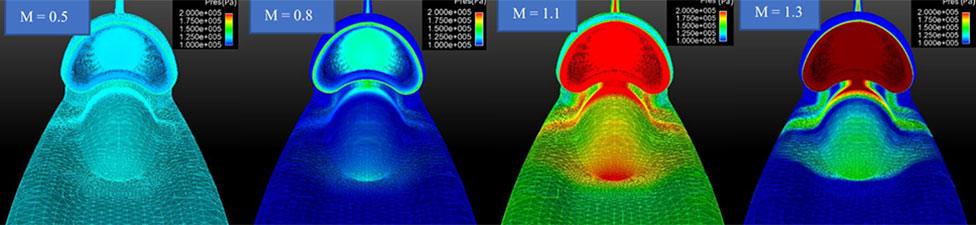
Computer models: Useful, not perfect
An American statistics expert called George Box is credited with the saying: "All models are wrong, but some are useful."
That's all very well for statistics, but slightly worryingly, Bloodhound's Chief Engineer Mark Chapman has also started quoting it.
Mark and his team are building the car, based on computer models, that I'm going to drive at supersonic speeds. Should I be worried at this point?
No, I'm not worried, for the very reason that we are going to be doing high-speed test runs.
We'll explore how accurate our models are during our step-by-step testing, correcting the models as we go.
Cutting edge technologies from Formula 1 to spaceflight do a lot of modelling AND a lot of testing. We're no different.
In advance of the high-speed test runs, there is still of lot of background work going on to understand what the computer models can tell us, and how we can check them against the test results once we start running.
This is the bit where the models will prove "useful", even if they are not perfectly accurate.

High-speed metal wheels

Our computer modelling guru, Dr Ben Evans, is keeping his students busy at Swansea University trying to understand the airflow around the world's first 1,000mph car.
It won't be long before they will have some real data to plug into the models. That's where it will get really interesting, both for them and for us.
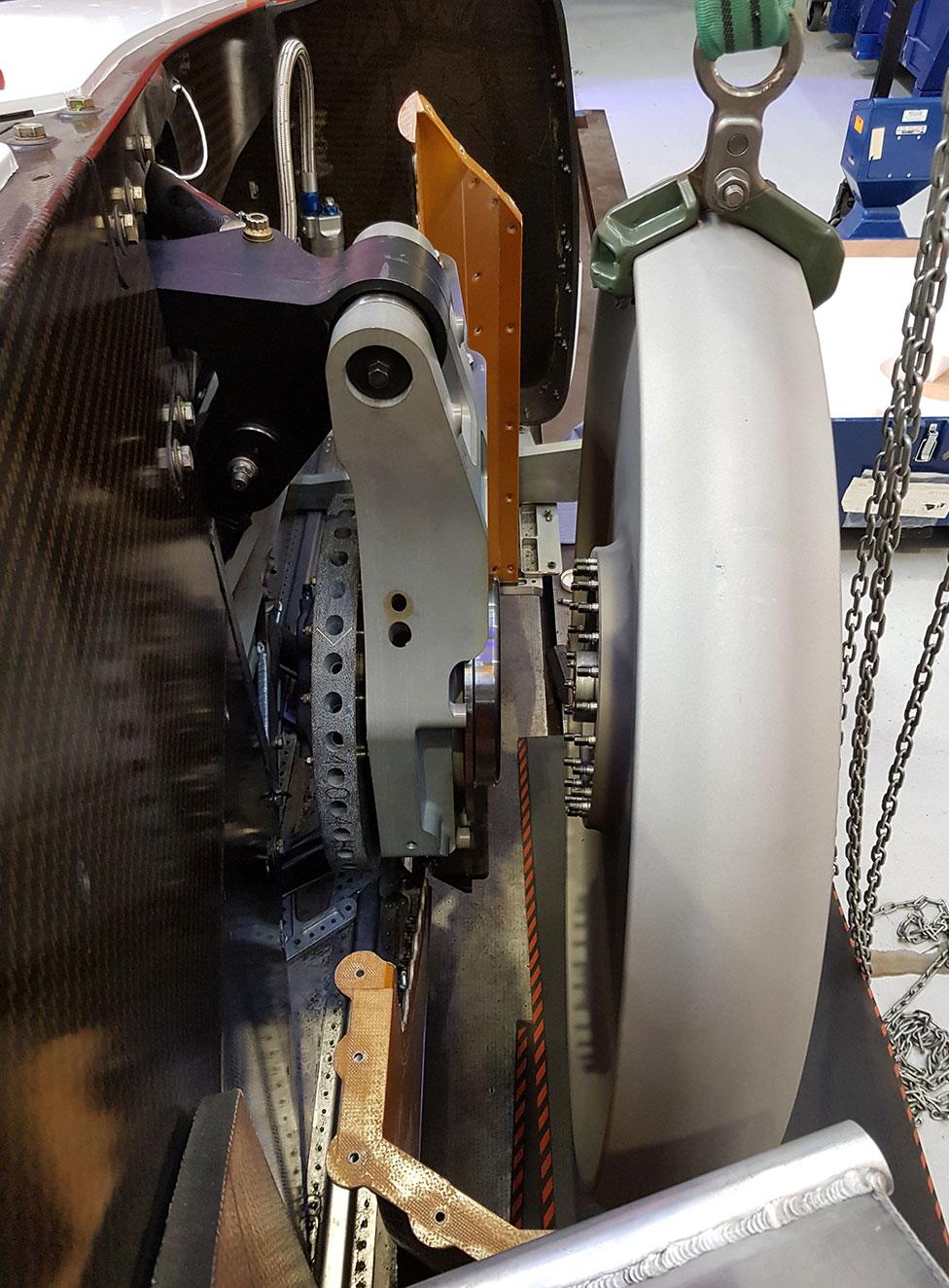
Another fascinating area for us is understanding how the high-speed solid metal wheels will behave on our desert track.
Hakskeen Pan in South Africa is a very firm, smooth, dry mud surface, which (we believe) is the ideal surface for supersonic record breaking.
Before we get to supersonic speeds, though, we want to know more about how the wheels will interact with the surface.
At slow speeds the wheels will simply make shallow ruts in the desert surface, perhaps 7-8mm deep, due to mass of the car (about 5.5 tonnes for our initial tests).
However, at high speeds the wheels will start to "plane" on the surface like high speed boat hulls, reducing the depth of the wheel ruts to around 3mm.
Of course, all these figures are based on models, so they are probably all wrong (see above!), but they are useful in understanding how the car will behave.
One of the side-effects of planing like a high-speed boat is that the wheels will throw up "spray" from the surface.
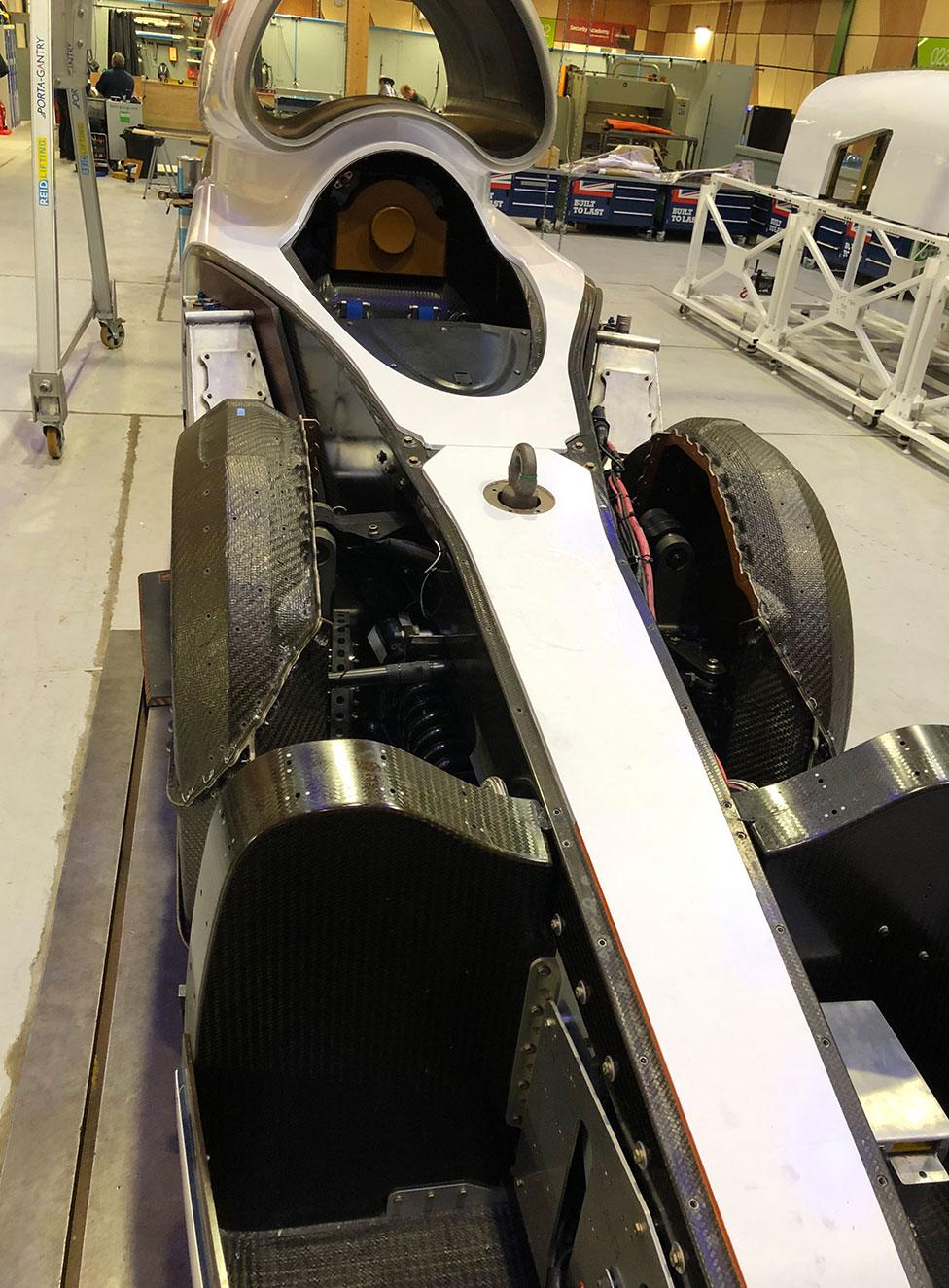

Composite Car, composite wheel covers

As the mud particles of the track surface are pulverised by the passage of a solid wheel doing several hundred miles per hour, the resulting dust will spray out like a fluid - hence the boat hull comparison.
This gives us a couple of problems.
The first problem with the spray from the wheels is what Ron Ayers, our legendary aerodynamics and performance expert, has termed "spray drag".
Just as high-speed boats encounter drag from water spray, Bloodhound will see spray drag from the huge clouds of dust that it is throwing up.
Measuring the effect of this spray drag will give us a more accurate indication of how much power Bloodhound needs to get to 1,000mph.
The second problem with the dust spraying up from the wheels is that the rotating storm of supersonic air around the wheels will suck a lot of the dust up into the bodywork.
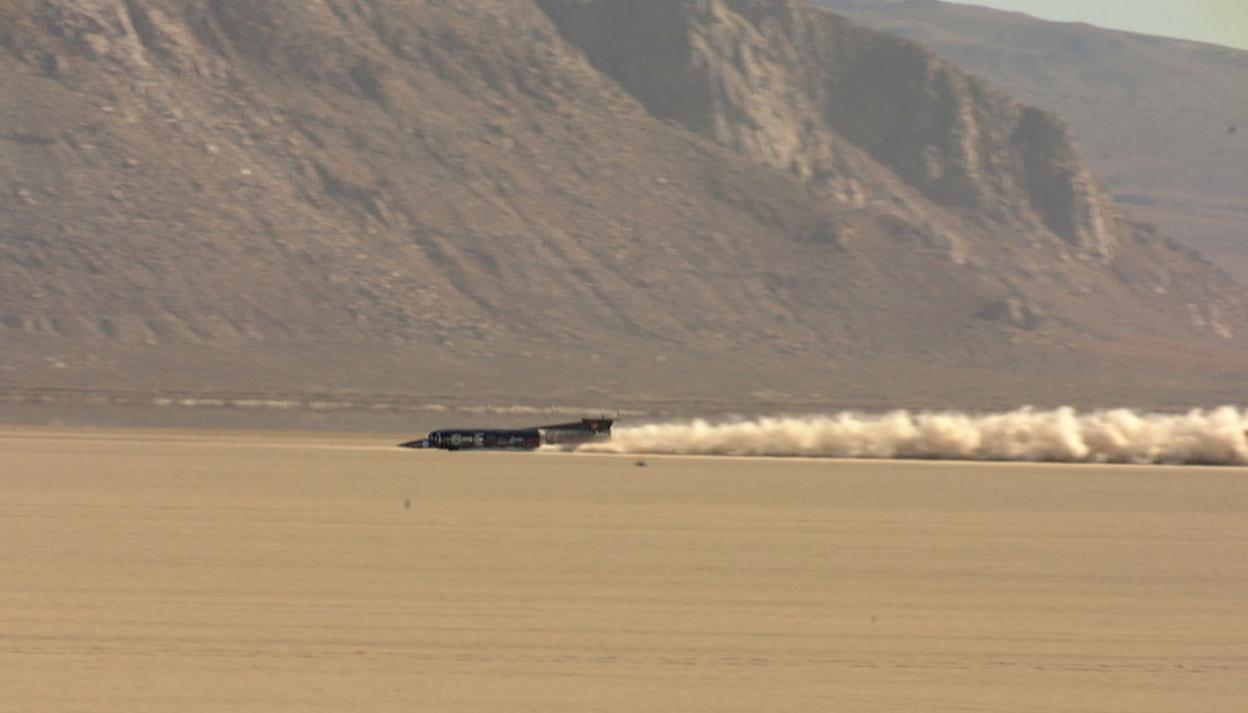

Supersonic dust clouds in 1997
We saw exactly the same effect with Thrust SSC back in 1997, when the car on that occasion generated massive supersonic dust storms inside the bodywork.
This didn't matter very much for Thrust SSC, as the structure around the wheels was all metallic.
However, Bloodhound's front end is composite, raising the prospect of rapid erosion of the carbon fibre structure and (to quote our Chief Engineer again) the front end of the Car "suddenly going all floppy"…
To counter any possible erosion, we are putting aluminium liners inside the composite wheel arches. This will also allow us to monitor the erosion effects (if any) of the desert dust, without any risk to the bits of the car that stop the nose from becoming unexpectedly floppy.
It's been interesting to see that this has generated some discussion online (click here if you want to join in, external) that as we're not driving the wheels, they shouldn't be throwing up any debris, so this shouldn't be a problem.
If that's the case then someone really ought to have told Thrust SSC back in 1997 - it threw up huge clouds of dusts from the wheels!
It's exciting to see Bloodhound sitting in its new workshop at Berkley UTC, gradually being modified from its "runway" test configuration (rubber tyres, partial bodywork, no brake parachutes) to its desert test spec.
This includes fitting the brake chutes, all the bodywork panels, and the desert wheels and fairings (complete with aluminium liners, of course), as we get the car ready to do some high-speed tests in South Africa. Won't be long now.
- Published28 March 2019

- Published21 March 2019
