The 'completely childish' man hanged for murder
- Published
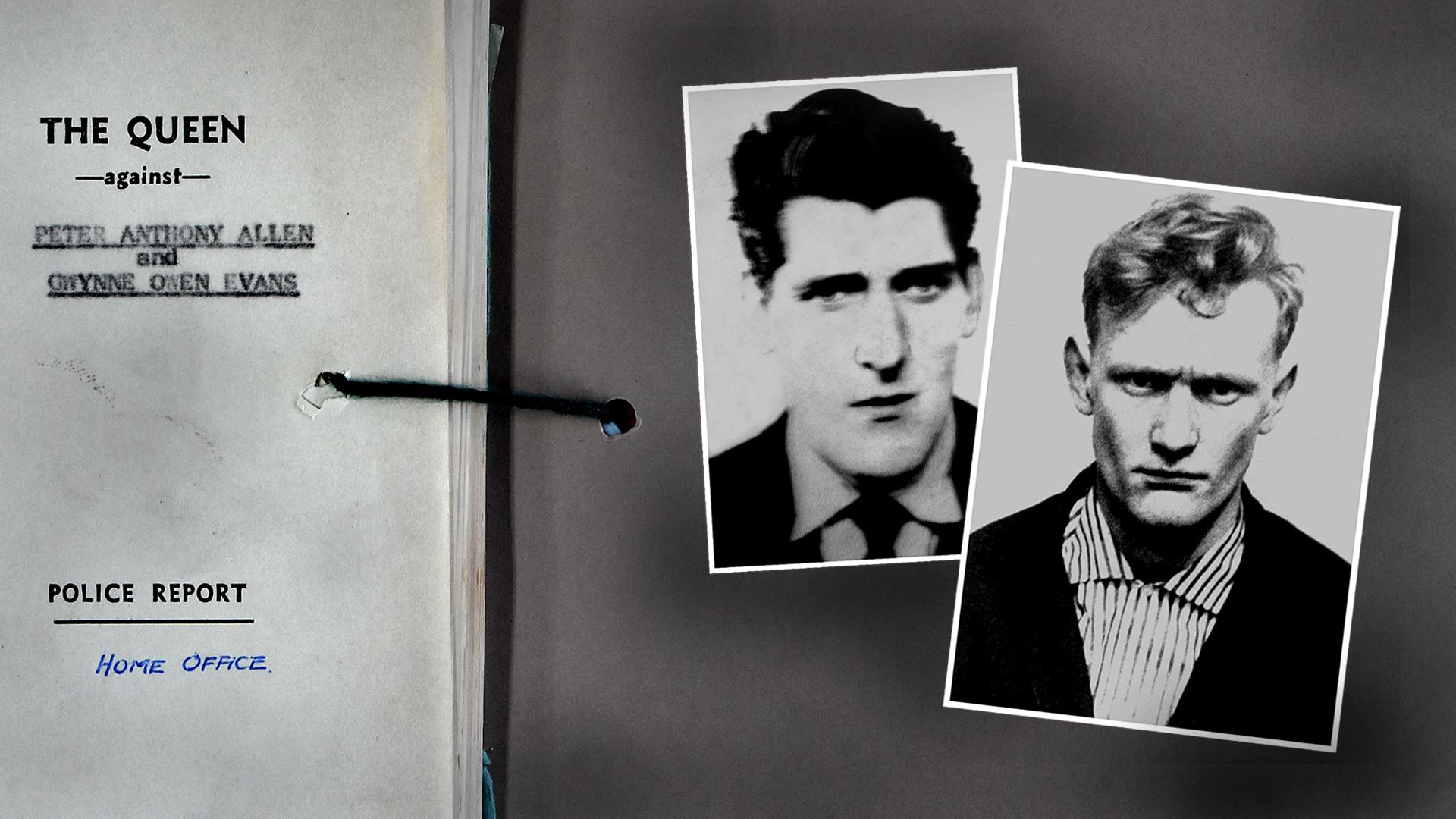

He was one of the last two men hanged in Britain. A habitual liar convicted of murdering a man who had been his friend, and perhaps his lover. But according to a leading criminal lawyer, who has viewed documents uncovered by the BBC, he was the victim of a miscarriage of justice.
Medical reports released to the National Archives this summer show that Gwynne Owen Evans, who was hanged in 1964 at the age of 24, had serious psychological problems. But his defence team made no attempt to enter a plea of diminished responsibility - a plea that, if accepted would have saved his life.

The crime
Just after three o'clock in the morning, on Tuesday 7 April 1964, Mr and Mrs Fawcett, an elderly couple living in the village of Seaton, Cumbria, were awakened by a series of thuds, a shrill scream, and then more bumps coming from the adjoining house.
Mr Fawcett got up, and as he was getting dressed he saw the lights in the house being switched on, upstairs and down. Then he heard a car driving away towards the village centre. He looked out, but it was going too fast for him to make out the number plate or any other details.
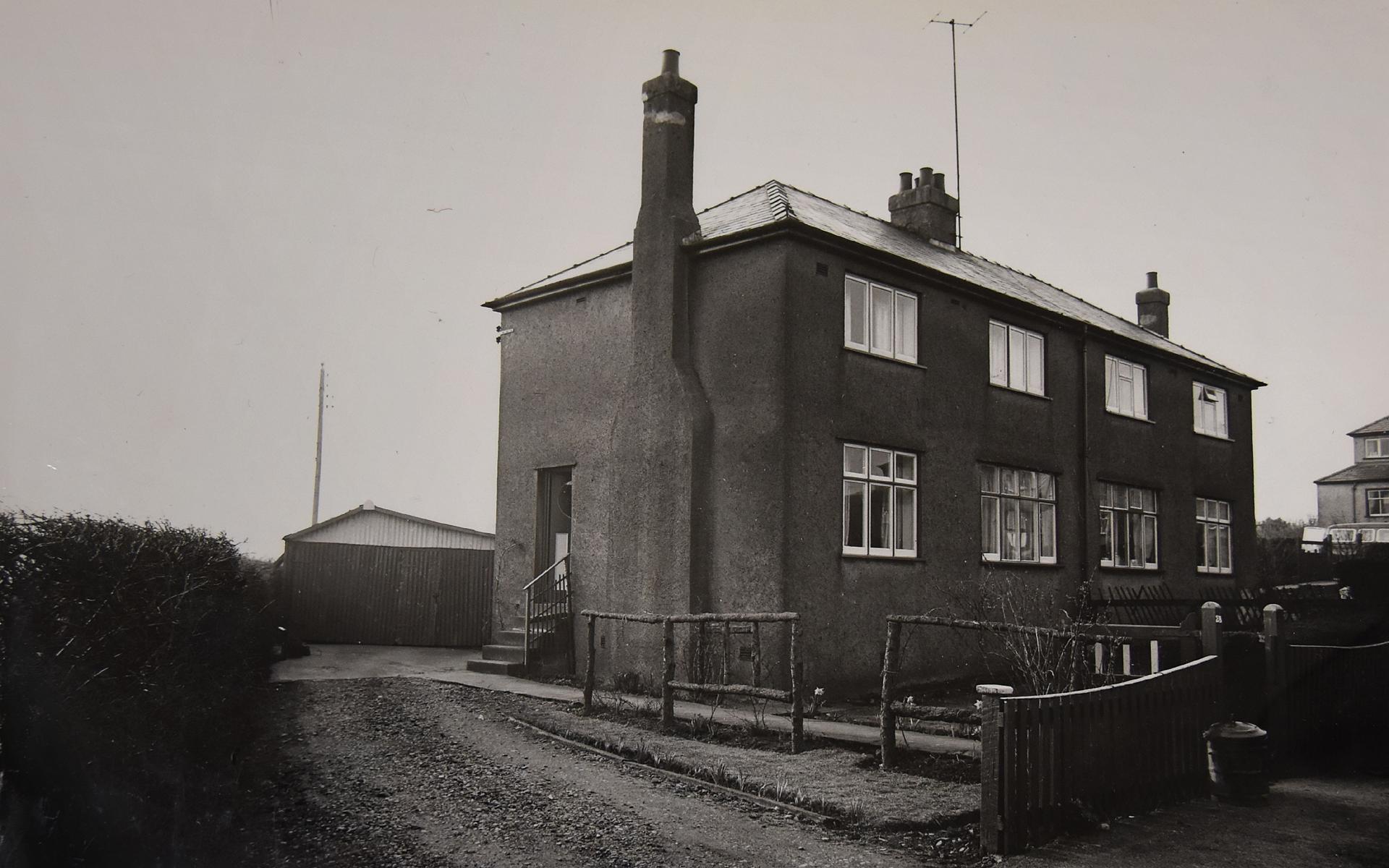

He called a neighbour, Walter Lister, who walked over to the house and knocked on the door. When no-one answered, he called the police. By 03:25 a group of officers, led by Sgt Park, had entered the house
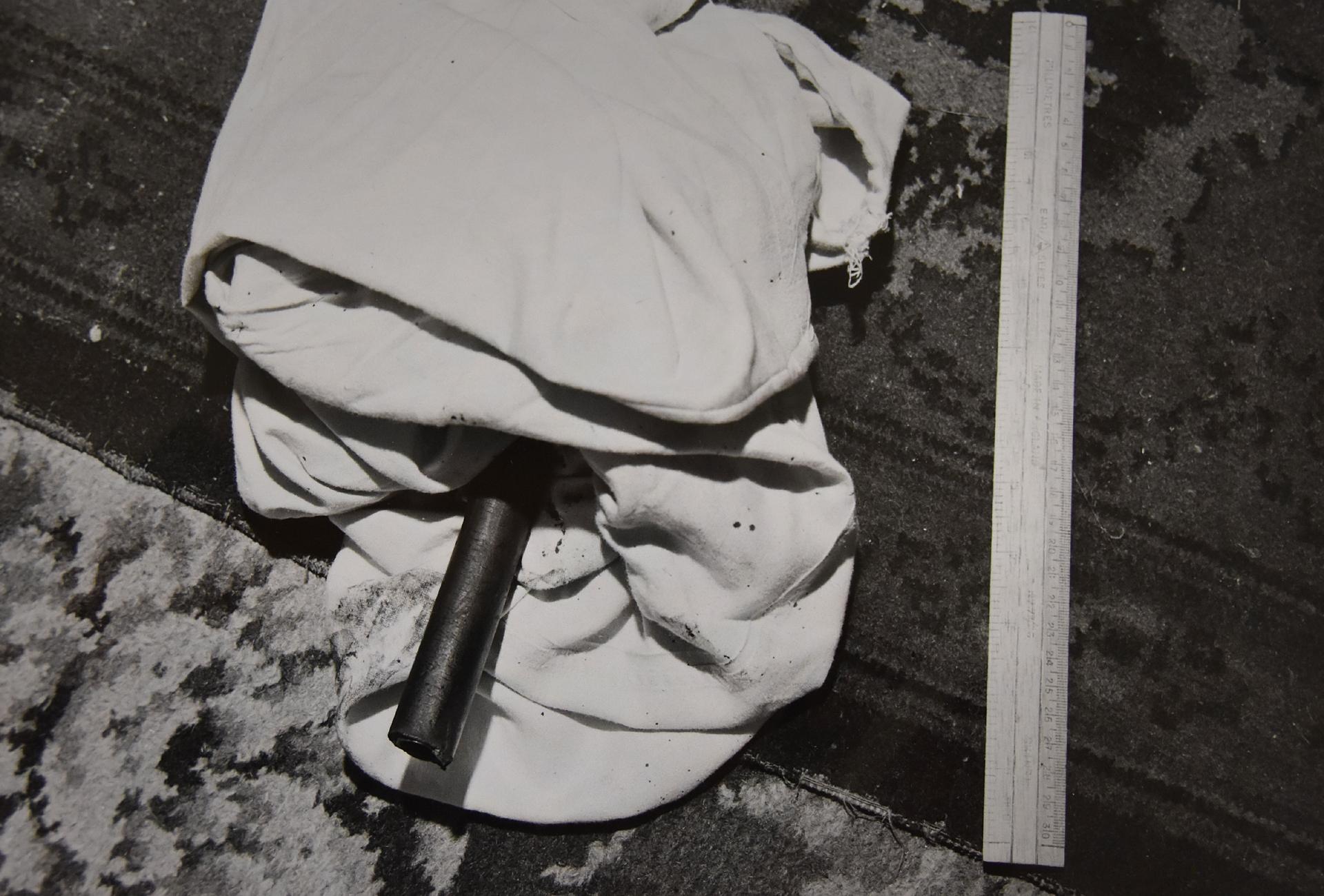
They found the occupant, John West, lying dead at the foot of the stairs, on his back and naked from the waist down. A single 53-year-old man who worked as a driver for a local laundry, West was in a pool of blood, his head covered with cuts. More blood was spattered on the walls, down the side of the stairs, and on the banister. On the floor near the body was a home-made cosh - a piece of rubber tube with a short piece of steel tube at one end, and putty at the other.

Searching upstairs, police found a lightweight raincoat folded on a chair in West's bedroom. In the pocket was a lifesaving medallion inscribed "G O Evans", and a piece of paper with the name Norma O'Brien written on it, next to an address in Liverpool.
That tied Gwynne Evans to the murder.

When police interviewed the 17-year-old O'Brien in Liverpool the next day, she remembered meeting Evans and seeing his medal while visiting her brother-in-law, a soldier at Fulwood Barracks in Preston, four months earlier. Evans had then been in the Army too, but had been discharged shortly afterwards.
Police learned that Evans was one of the dead man's friends. The year before he'd been seen chauffeuring him around the neighbourhood, which suggested they were close: West was very particular about his car and hardly anyone else was allowed to drive it.
They also quickly discovered that Evans was a local boy - his parents lived in Workington, just down the road from Seaton - and that until recently his name had been John Walby. He'd changed it in a third attempt to join the Army, having been kicked out twice under his original name.
From Evans's parents police had obtained his current address, a small terraced house in Preston, 100 miles (160km) away. He was living there with Peter Allen, 21, Allen's wife and two young children. At the house, though, police found and arrested only Allen. Evans was out with Allen's wife, Mary, in Manchester. When the police tracked them down, Evans had in his pocket a wristwatch that had belonged to West, and Mary had a bloodstained shirt in her basket. It belonged to her husband.

Find out more
Listen to Sanchia Berg's report for the Today programme on BBC Radio 4, on Monday 18 December

According to police records, Gwynne Evans quickly volunteered information about the murder - putting all the blame on Allen. He and Allen had stolen a car to drive up to Seaton to borrow money, he said, as West was an old friend who'd offered to help him in the past. Both Allen and Evans were hard up, with fines and bills to pay.
Allen's wife and children came along for the drive too, and waited, asleep, outside in the car. Evans went in first, by his account, and he told police he just had a chat with West, whom he called Jack.
"I had some tea and a cheese bun and as we were talking there was a knock at the door. I honestly didn't know who it was, anyway Jack went to the door and I heard some banging. I went into the hall and I saw Peter hitting Jack with something that looked like a pipe... There was a lot of blood and I shouted to Peter, 'For Christ's sake stop it!'"

Evans insisted he hadn't hit Jack himself. "Peter did the thumping," he said. Evans told police the two men had stolen bank books from West's home, and managed to withdraw £10 cash from his accounts. He said he knew the police had found his coat, with the medallion and keys in the pocket.
"If I wanted, I could have said that my coat had been stolen and my keys were in it and no judge in the country would convict me. But I am glad I have got it off my chest," he said.
An odd thing to say, but as further questioning would show, characteristic of Evans.
That evening, in Preston, Peter Allen was interviewed. Initially, he claimed ignorance of the murder.
"You can get a stack of Bibles in here and I'll stand on them and swear I know nothing about it," he told Det Supt Roberts, who was leading the investigation.
But just a few minutes later, according to the police notes, Allen struck the desk with his fist, buried his head in his arm and said, "All right. I'll tell you. I'd like to tell the whole flipping world about it."
He said it started out as an innocent robbery. Sandy, as he called Evans, was to go in first, and let Allen in. But as Evans opened the front door West came out of his bedroom, and saw him. So Allen hit the older man with his fists. Then, Allen claimed, Evans gave him "the bar" and he set upon West with that too. Later, he revised his statement to say that Evans had also beaten West.

That evening, at a quarter to midnight, the detective superintendent interviewed Gwynne Evans. First, he asked if that was his real name. The reply was surprising.
"No, I adopted it after I found out I was born in Innsbruck in 1940 and that both my parents were German," Evans said.
This was not true.
The post-mortem showed West hadn't only been hit around the head, with a cosh - he'd also been stabbed through the heart. Initially, neither man said anything about that, but according to the police report Evans - unprompted - said: "I don't know anything about a knife. I don't have to use a knife to kill a man. I'm an expert at judo and karate. I never hit Jack- it was Peter that did all the hitting."
He wasn't a karate expert either.
Police found Allen's account more credible. It tallied with the crime scene. Allen said Evans had opened the door for him, and West had unexpectedly come out of his bedroom upstairs. Evans, by contrast, claimed both he and West had been downstairs.
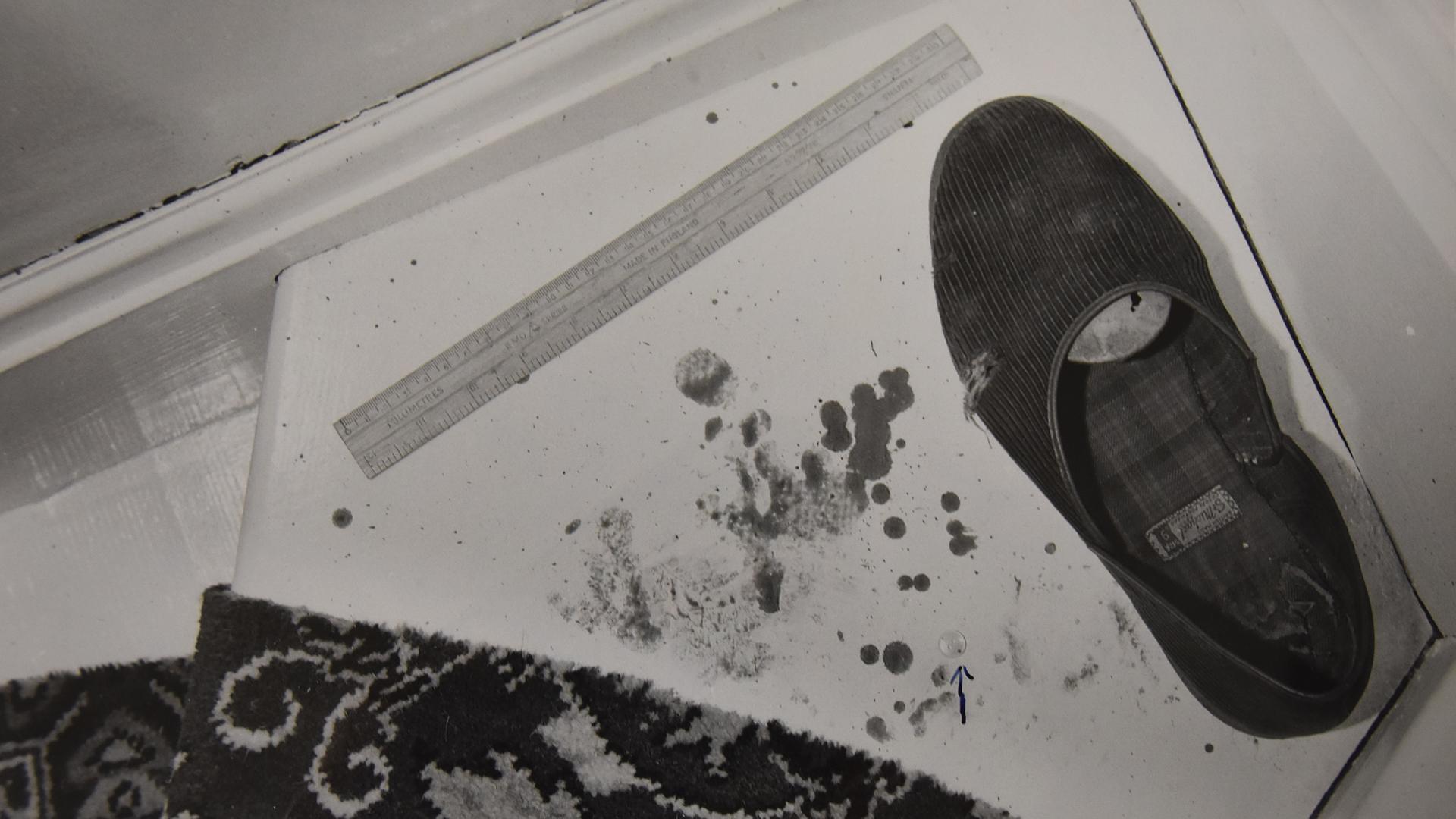
Police thought it unlikely West would have answered the door without any trousers on, his false teeth were found on the landing at the top of the stairs, and there was blood on the wall by the staircase.

Just after midnight, police interviewed Allen's wife, Mary. She said Evans had gone in first, and had come out about two hours later to get Allen. Then the two men had run out. When she asked them what had happened they said West had punched Peter - who'd punched back. Evans, she said, had told her he'd joined in.
The two men appeared in the magistrates' court a few hours later, on Thursday 9 April.
Mary Allen then revised her evidence, telling police Evans had stopped the car on the drive back to Preston and she'd seen him throw something away. That afternoon, she showed officers the spot, on the road between Workington and Windermere. A police dog easily found a bloodstained knife.
And after reading a local newspaper report of the court hearing, Mary Allen remembered something else. She told police that when they'd all returned to Preston, early on Tuesday morning, Evans had said "he never expected it to go in below the alarm clock". She now realised, she said, that he was referring to the stab wound to the heart.


'Abnormal personality'
After his appearance in court, Gwynne Evans was remanded in custody at Durham prison, where he was seen by the senior medical officer, P J Waddington.
There was no evidence of medical disorder, he wrote. Evans was "correctly orientated". In other words, "He knew where he was and he was fully aware of the reasons for his arrest and his committal to prison."
Waddington described Evans as being "of spare physique", just over 5ft 9in tall, with no physical ailments except flat feet and some small cuts on his face, possibly from picking pimples.
In another report the following month, he noted that from a very young age Evans had experienced psychological problems. As a boy he'd been referred to a child guidance clinic (elsewhere identified as Dovenby mental hospital) because he was "untrustworthy, lacked moral sense, was untruthful, and inclined to steal".
Evans confused truth with fantasy. "Evans believes that he was born in Innsbruck and his reasons for doing so are quite absurd…" the doctor wrote.
He said he was married to a German girl, and had two children - which also seemed entirely invented.
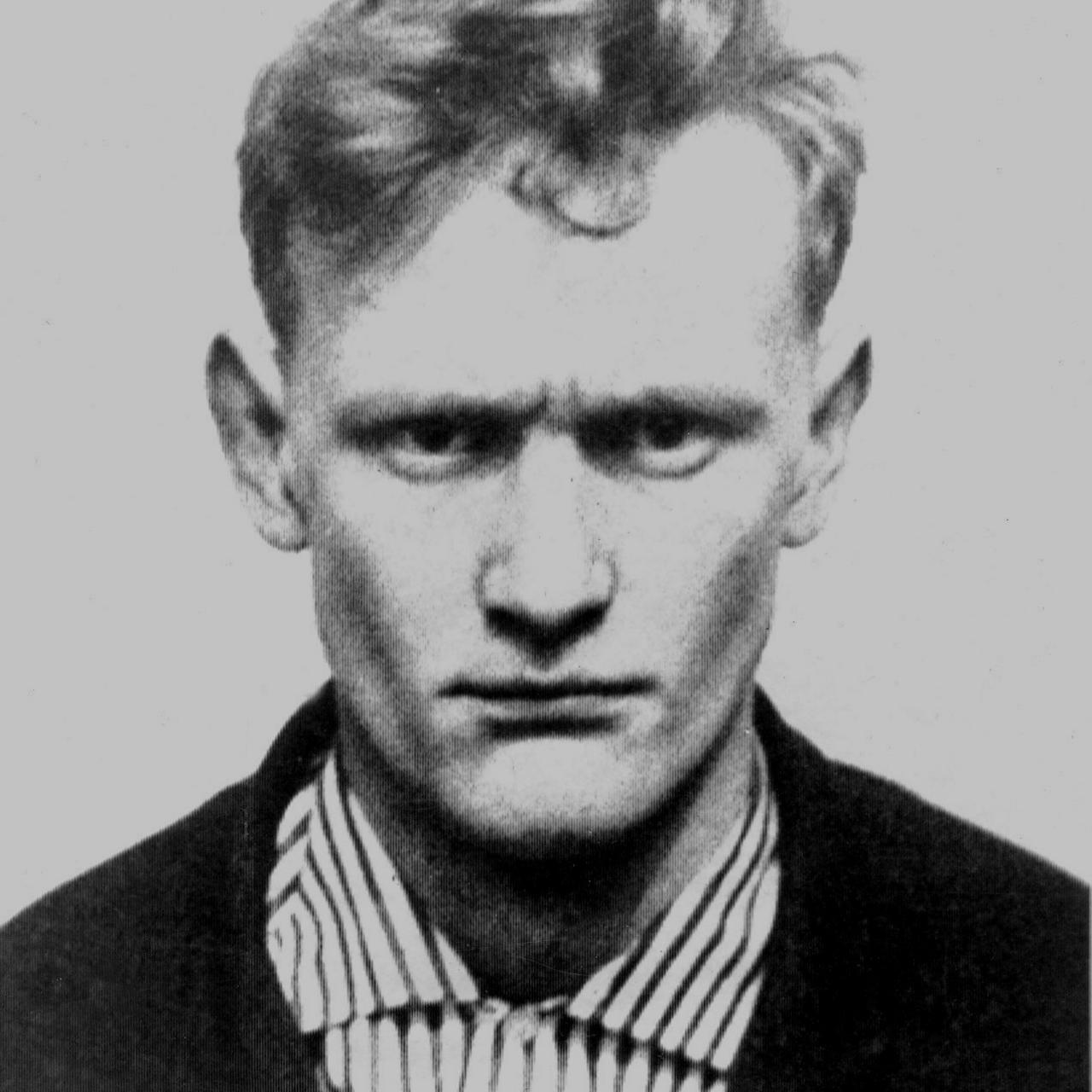
Evans claimed too that he'd been employed by Securicor for a year, and there become an expert in judo. In fact he'd only worked there for a week; he left as soon as his references had been checked, presumably because they were unsatisfactory.
He lied constantly. The doctor said these were for the most part "prestige lies" to enhance his standing.
On four occasions he joined the services, only to be medically discharged.
Evans had enlisted at 17 in the Border Regiment, where his fabrications led to him being sent for a psychiatric assessment. "This soldier was sent to me by his training wing officer," wrote one doctor, "on account of his frequent telling of big lies which he apparently believed himself." His first expulsion followed four months later.
In less than a year, he signed up for another regiment, the Royal Inniskilling Fusiliers - but here too, his lies brought about his downfall. Within three months he was before a medical board which recommended discharge on the grounds of "personality inadequacy".
His commanding officer remarked: "He is a failure. He cannot make friends because of feeling superior and telling complete fairy tales all the time."
The following year he joined the Royal Air Force, but was quickly discharged on the grounds of "nervous instability". In 1963, he signed up for the Army again, under the name of Evans, but was soon found out, and discharged for the final time.
Waddington, the medical officer at Durham Prison, acknowledged Evans's "abnormal personality" and thought most doctors would consider him an individual with a "psychopathic personality, using this term in the broadest sense".

But he didn't believe this amounted to an "abnormality of mind" that would substantially impair his "mental responsibility for his acts and omissions" - the legal definition of diminished responsibility under the 1957 Homicide Act.
Evans's own lawyers commissioned Dr G F Duggan Keen, an experienced consultant psychiatrist, to examine him. He noted that Evans had been employed in 32 jobs, by his own account, from the age of 15, excluding the spells in the Army and RAF. Many had just lasted a few weeks, due he thought, to Evans's problems forming relationships, and excessive drinking.
After four meetings with Evans, he said there was "absolutely no doubt in my mind that this man is a psychopathic personality". But he could not identify a condition or disease. He said Evans was not "subnormal", nor schizophrenic, nor epileptic. He too concluded that Evans's mental responsibility was not "substantially impaired".
Neither Waddington nor Duggan Keen explained why they came to that conclusion, and this surprises Dr Tim McInerney, a consultant forensic psychiatrist at the Bethlem Royal hospital in South London, who often gives expert assessments in murder cases.
"If, as an expert now, giving advice to the courts or to a jury as to why I don't support diminished [responsibility] I would have to explain very clearly why I reached that position," he says.
The psychiatric reports are cursory by modern standards, running to just a few pages. Though McInerny says that was the style at the time, John Cooper QC, an experienced defence barrister and professor of law, says their brevity strikes him as a cause for concern.
"For those reports to be relied upon without them being tested, without further questions being asked of them, without further experts being used, as far as I'm concerned, is quite startling. And I would say quite startling not just to the modern eye but also at the time."
But these psychiatric judgements would play an important role in the events that led to Gwynne Evans's conviction - and his hanging.

Trial and sentence
Evans and Allen went on trial at Manchester Crown Court on 29 June 1964. The prosecution expected Evans to plead diminished responsibility. They had lined up their own psychiatrist, Dr Begg, who had met Evans twice. Like the other doctors, he said Evans was a "grossly psychopathic personality", and that responsibility for his actions was impaired - but, again, not substantially.
However, the following day, without explanation, Evans's lawyers decided to drop the diminished responsibility plea. The note on the Director of Public Prosecutions file reads simply: "Def advise Dim Res not being raised. Dr Begg informed."

Each man blamed the other for the murder. The evidence against Allen was much stronger - he admitted beating West and his clothes had been soaked in blood. There was no blood on Evans.
There was, admittedly, evidence incriminating Evans from Allen's wife - but she would have had good reason to try to shift the blame.
Evans said he'd been friendly with West, who "was like a father to me", and that he would never have hurt him.
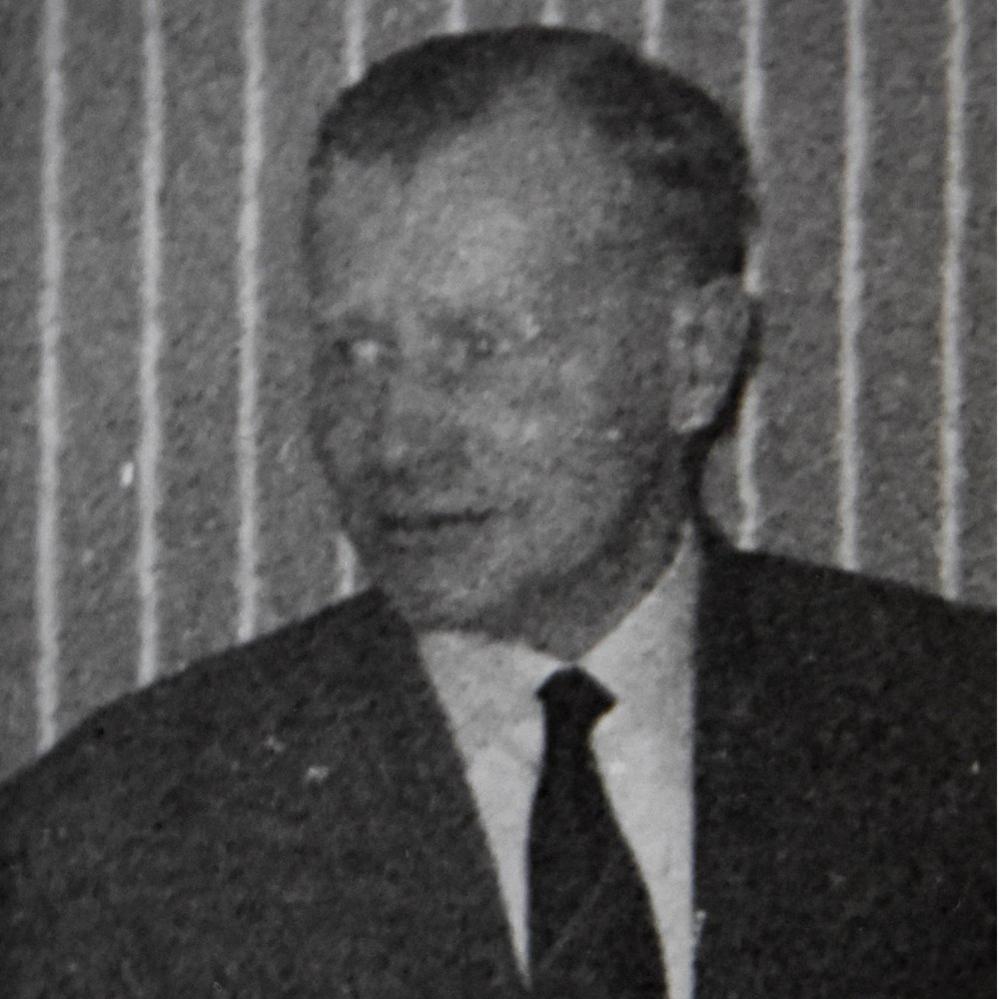

The murdered man, John West
However, both agreed they'd been ready to rob West. And unsurprisingly, Evans lied in court - and was shown to be lying.
Allen's barrister undermined Evans further by suggesting he'd had sex with West just before the murder, something Evans vehemently denied, but which was supported by medical evidence. At the time homosexuality was illegal, and it's likely this would have lowered the jury's opinion of Evans even further.
The trial ran until 6 July. The prosecution argued that the men were acting "in concert" and it did not matter who delivered the fatal blow.
Without much deliberation the jury found both guilty of capital murder - that is, murder and robbery.

This doesn't surprise John Cooper QC.
"Without diminished responsibility, on my reading of these papers, the verdict of guilty was all but inevitable," he says.
A successful plea of diminished responsibility, on the other hand, would have saved Evans's life.
Evans's mother, Hannah Walby, wrote to him in clumsy round handwriting on blue notepaper: "Please don't give up hope yet." The verdict had been a great shock to her, she continued, and to his brothers and sister. "All is being done possible, you may get a reprieve."
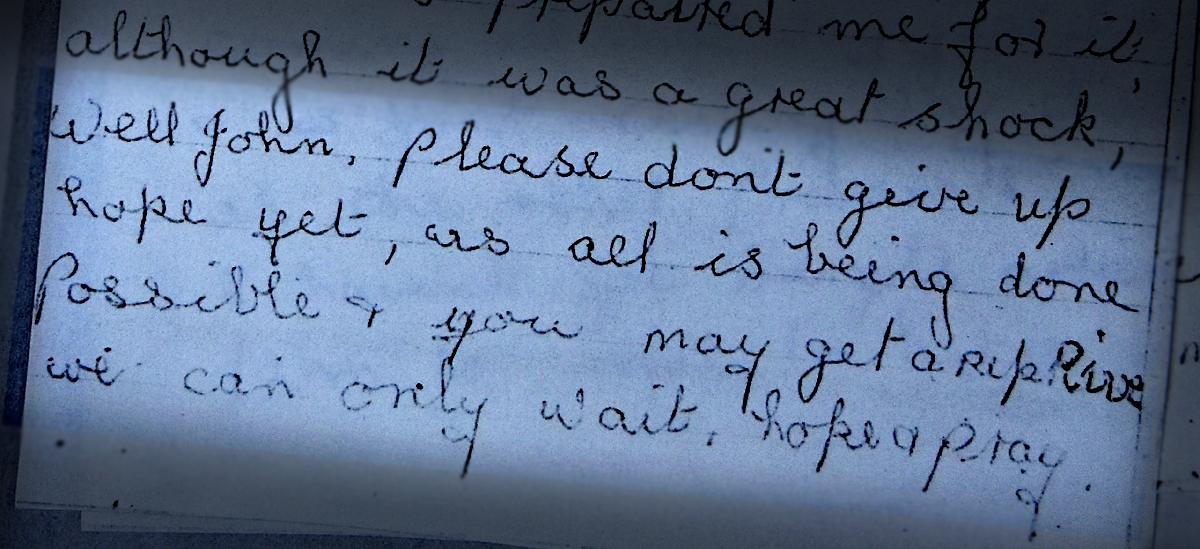

No reprieve
At his appeal, heard at the High Court in July, Evans's lawyers also made no attempt to argue that he was not fully responsible for his actions.
Instead his barrister, Guthrie Jones QC, sought to challenge Mary Allen's evidence, on the basis that she was Allen's wife. However, the judge had flagged this up to the jury at the trial, warning them that she was not an impartial witness - so the appeal was dismissed.

The only avenue left was a reprieve.
On 24 July Evans's solicitor, John Marsham of Midland Bank Chambers in Whitehaven, Cumbria, wrote to the Home Secretary, Henry Brooke.
He pointed out that three doctors agreed Evans suffered mental impairment. He referred to a statement - not presented in court - from the father of a girl Evans had been seeing, a Mr Hampton. He'd put an end to their relationship because he had been so concerned about Evans's immaturity. He was "completely childish in everything he did" wrote the lawyer, "he would make toys that a child would make and play with them for hours before pulling them to pieces."
Marsham added that Evans had been shown in court to be a liar, which made his conviction "inevitable". "Even in the witness box he could not refrain from telling stupid and unnecessary lies" - a story about being chased by a police car, for example.
The letter was dismissed by the Home Office. Officials did nonetheless commission a final medical assessment. Three psychiatrists, Dr Pickering, Dr Mather and Prof Anderson, visited him in prison, on 27 and 28 July.
"He was a pallid slightly built young man, clearly tense, tremulous, with knitted brows throughout the interview," they wrote. He admitted being a habitual liar, and even lying to the doctors themselves.
Prison staff also reported that he lied often, to boost his self-confidence. The governor thought him a "happy-go-lucky extrovert liking to stand high in people's favour". No staff thought him insane, as "no sign of fits or transient losses or changes of consciousness were observed".
The news that there would be no reprieve reached Evans's family. On 3 August, Mrs Walby sent a letter to the Home Secretary.

"I write to you on behalf of my son who is under sentence of Death at Manchester Prison," she wrote.
She said Evans had never been in serious trouble before he met "this Preston couple". He had been brought up in the church, a member of the choir and the Boy Scouts, she explained. She pointed out he had been friends with West for five years, often staying overnight at his house.

"My son is mentally impaired and I had him under a mental doctor at the age of 8 years but he is not a wicked boy," she pleaded.
"Please may God guide you to make a mercyful judgement. I remain, yours respectfully Mrs H Walby."
It had no effect.

Three days later, on 6 August the Home Secretary wrote in red ink on the file: "I regret I can find no mitigating circumstances such as would justify a reprieve in either case. The law must take its course."
The two men were hanged, in different prisons, at the same time: 08:00 on 13 August.

I came across Evans's medical reports by chance, while checking newly released files at the National Archives earlier this year. I then showed them to John Cooper QC and Dr Tim McInerney.
Cooper has no hesitation in saying that Evans was the victim of a miscarriage of justice.
"Evans was a vulnerable individual," he says. "And that vulnerable individual was sent into court, into trial without the proper defence put forward for the jury to consider."
The proper defence, in his view, would have been a plea of diminished responsibility. And this plea, he argues, would have had a far greater chance of success if there had been a more thorough psychiatric examination.
The 1957 Homicide Act led to a sharp drop in the number of hangings for two reasons. One was that murder became punishable by death only when combined with other offences. This did not help Evans and Allen, because they were charged with robbery as well as murder.
The other reason was the new defence of diminished responsibility. It allowed many to escape the noose, and might have saved Evans.
Tim McInerney has seen one case from 1963, a double murder, where the killer - with a similar psychiatric profile to Evans - escaped trial entirely, being sent instead to a special hospital.
Doctors operate on the principle of "do least harm", he says. So he wonders what went through the minds of the doctors who examined Evans - knowing that if they didn't support diminished responsibility, he'd be hanged.
John Cooper also points out that in the last years of the death penalty, "it was in essence a postcode lottery - depending on which prison you were in, as to whether you survived". This "adds to the macabre nature of the last few months of the death penalty", in his view.
In 1964, Allen and Evans were the only people hanged in the UK. There were only two hangings the year before, as well. And less than a year after the two young men were executed, capital punishment was suspended in Great Britain.
Parliament voted to make the suspension permanent in 1969.


Pictures courtesy of the National Archives. Peter Allen and Gwynne Evans images copyright Mirrorpix.
Join the conversation - find us on Facebook, external, Instagram, external, Snapchat , externaland Twitter, external.