Tim Berners-Lee says 'surveillance threatens web'
- Published

Sir Tim Berners-Lee said important issues had been raised by recent leaks
Web creator Sir Tim Berners-Lee has warned that the democratic nature of the net is threatened by a "growing tide of surveillance and censorship".
The warning came as he launched his World Wide Web Foundation's annual web index report, tracking global censorship.
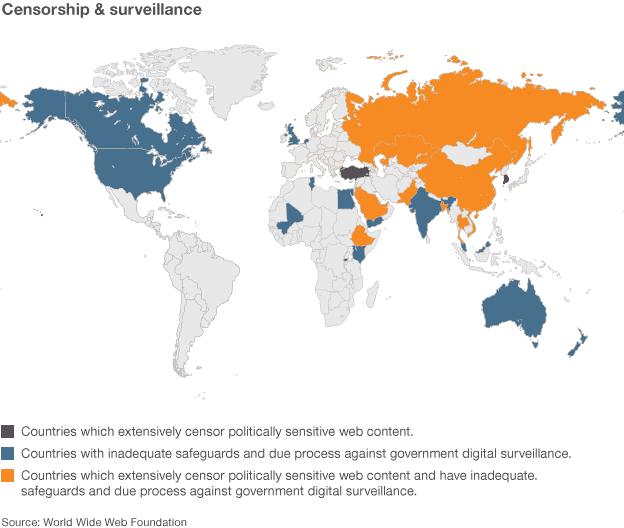
It suggests that 94% of the countries in the index do not adequately monitor government internet interception.
Thirty per cent of countries block or filter political content, it indicates.
The report concludes that the current legal framework on government snooping needs urgent review.
"One of the most encouraging findings of this year's web index is how the web and social media are increasingly spurring people to organise, take action and try to expose wrongdoing in every region of the world," said Sir Tim.
Berners-Lee: Protect whistleblowers like Edward Snowden
"But some governments are threatened by this, and a growing tide of surveillance and censorship now threatens the future of democracy.
Bold steps are needed now to protect our fundamental rights to privacy and freedom of opinion and association online," he added.
'Appalling and foolish'
Sir Tim has been an outspoken critic of government surveillance following the revelations from whistle-blower Edward Snowden.
He described attempts by the spy agencies to crack encryption as "appalling and foolish".
He has previously said that the checks and balances to oversee GCHQ and its US counterpart, the National Security Agency (NSA), have failed.
It is a view shared by digital forensic expert Professor Peter Sommer.
"GCHQ is a spying agency. It needs to produce good results. But how far anyone understands the techniques they are using is more unclear."
"The things they are doing need a ministerial warrant but the ministers have a lot of other things to do. Did they have sufficient understanding of the technology? Who is doing the risk analysis?"
A Cabinet Office spokesperson told the BBC: "The success of our intelligence agencies relies on secrecy. But secrecy does not mean lack of accountability. The United Kingdom's intelligence agencies operate under the tightest of controls and oversights.
"Our agencies only act in line with their strict legal mission, above all keeping people safe from harm.
"There is a triple lock to ensure every action is lawful, necessary and proportionate - interception underpinned by Ministerial warrants, world class internal controls and three safety nets of outside scrutiny by the Interception Commissioner, the Intelligence and Security Committee of Parliament and the Investigatory Powers Tribunal."
Measure of influence
The report compiled by Sir Tim's World Wide Web Foundation ranks countries in terms of the social and political impact of the web.
Sweden tops the annual web index, ahead of Norway, and followed by the UK, US and New Zealand.
It found that in 80% of the countries studied, the web and social media played a role in mobilising the public on a range of issues.
It also found that rich countries did not necessarily rank higher in the index. The Philippines, with a per-capita income of $4,410 per year, is more than 10 places ahead of Qatar, the world's richest country.
Meanwhile Saudi Arabia is outperformed by 10 sub-Saharan African countries, and Switzerland, the third wealthiest nation, is only one place ahead of Estonia.
But in poorer countries the digital divide is growing ever more marked, according to the report.
"Ten years after world leaders committed to harnessing technology to build an inclusive information society, parents in 48% of countries can't use the web to compare school performances and budgets, women in over 60% of countries can't use the web to help them make informed choices about their bodies, and over half the population in developing countries can't use the web at all," said Anne Jellema, the foundation's chief executive.
- Published7 November 2013
- Published5 September 2012
- Published4 December 2012