Facebook turns 10 but are its days numbered?
- Published
Facebook is celebrating its 10th birthday this week with record earnings and 1.2 billion users. But who is using it and how?
The candles on Facebook's 10th birthday cake will barely have been blown out before someone somewhere starts speculating on whether it will ever make 11.
If a glut of recent studies are to be believed, its days are definitely numbered. Various reports suggest it is haemorrhaging users, that teenagers find it boring - one survey even comparing it to an infectious disease.
Such surveys, usually accompanied by a picture of boss Mark Zuckerberg looking sad, are picked up widely by the press and equally vigorously pulled apart by Facebook.
So when researchers at Princeton used Google search data to predict Facebook would lose 80% of its users within three years, the social network hit back.
Its in-house data scientists used the same methodology to predict the university would have no students by 2021 and the world would run out of air by 2060.
"As data scientists we wanted to give a fun reminder that not all research is created equal - and some methods of analysis lead to pretty crazy conclusions," they said.
The Princeton report's comparison of Facebook to an infectious disease missed the mark, thinks Nate Elliott, analyst with Forrester Research.
"One of Facebook's greatest strengths is its practice of regularly adding new features and functionality to its site; this both ensures it infects new users and also makes sure existing users don't become immune to its charms," he said in his blog., external
He also pointed out net measurement firm Comscore's data that showed that 89% of US 18- to 24-year-olds used Facebook in November 2013.
"Facebook claims far more young users than any other social network - indeed, probably more than any other media property on Earth," he added.
Older demographic
profile.jpg)
Facebook has been through several redesigns since it launched in 2004
Some surveys are harder for Facebook to shake off, though.
Digital agency iStrategylabs used Facebook's own social advertising data to extrapolate that three million US teenagers had left Facebook in the past three years.
It was echoed by earlier research conducted by the Pew Internet Centre research, which reported that teenagers were put off Facebook because of their parents.
The fact that notoriously capricious teenagers don't want to hang out in the same digital space with their parents will hardly come as a surprise to anyone who knows any.
Parents can be embarrassing on Facebook - they post pictures of their offspring that they find hilarious but their children don't, they add ill-advised comments to their children's status updates and they often fail to understand the basic etiquettes of online discourse.

Facebook may be getting older, but Mark Zuckerberg still looks fresh-faced and care-free
It has led, concluded Pew, to teenagers maintaining lower profiles on Facebook while spending the majority of their time on services such as WhatsApp or Snapchat.
But while the report noted a 25% drop in the number of younger users, it indicated that there was an 80% surge in users with an age of 55 and above.
So is it a case that as Facebook gets older, so does its core audience?
"The demographic has shifted and it is a positive thing when it come to ad revenues. These older users have more spending power than young teens," said Ovum analyst Eden Zoller.
But she added Facebook could not afford to be complacent about its younger members because if they could be persuaded to stick with the social network, they would become the spenders of tomorrow.
"Facebook needs to keep innovating with things like mobile video apps, with mobile commerce," she said.
Speculation about whether Facebook can maintain its audience and its appeal are not likely to be giving Mark Zuckerberg sleepless nights anytime soon.
Especially since he got an early birthday present last week in the form of record results.
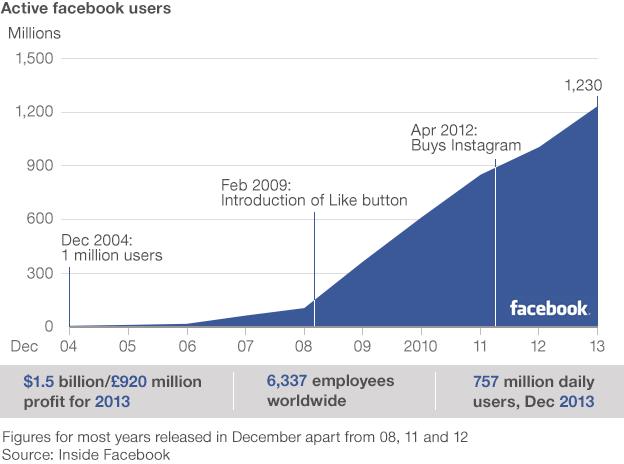
The network he started in a Harvard dormitory room, where ironically teenagers were its only demographic, now has 1.23 billion active users.
Its revenues jumped 55% to $7.87bn in 2013 while profits grew sevenfold, bringing the annual total to £1.5bn.
Interestingly, teen decline was off the agenda in this quarter's earnings call, in contrast to the previous one, when chief financial officer David Ebersman did admit it was losing some of its younger audience.
Shortly afterwards, Facebook's bid to buy Snapchat failed, so this time around, the social network was concentrating on the positives - mobile advertising.
This brought in a whopping $2.34bn, over half of its total revenue, with the firm promising to further improve data tracking and the usefulness of its ads.
Anyone bemused by why their newsfeed is serving up cures for baldness when they have a full head of hair or miracle diets when they are stick-thin will be pleased to hear that Facebook is working to make ads more relevant.
"Facebook is often criticised for how much customer data it mines but actually it isn't doing it very effectively," said Ms Zoller.
"The targeting simply isn't very good."
And as Facebook plans even more mobile advertising, it absolutely needs to make a much better job of it if it, she thinks.
"Mobile adverts have the potential to be incredibly intrusive unless they are very well targeted," she said.
Human curiosity

Is it curiosity that keeps people on Facebook?
Among all the surveys speculating about Facebook's future, there is surprisingly little analysis about why people keep using it.
In a recent status update, Facebook's communication manager and former BBC tech desk editor Iain Mackenzie summed up why he thought it endures.
"Today people have shared the birth of their first child, wedding, hooked up, broke up, mourned, outed themselves, said something dumb, said something profound, confessed that life's got too hard for them, been brought back from the brink by a friend, or a stranger, found a job, posted something that lost them their job, learned a fact that will save their life one day, found their new favourite song, and hit 'like' on a cat picture - all on Facebook."
Its appeal could boil down to the fact that it taps into that most basic of human characteristics - curiosity.
Whether we like it or not, Facebook has become the digital novel of people's lives. And for many, it remains essential reading.
- Published4 February 2014
- Published29 January 2014
- Published24 January 2014