BBC Micro Bit computer's final design revealed
- Published
BBC technology correspondent Rory goes hands-on with the Micro Bit
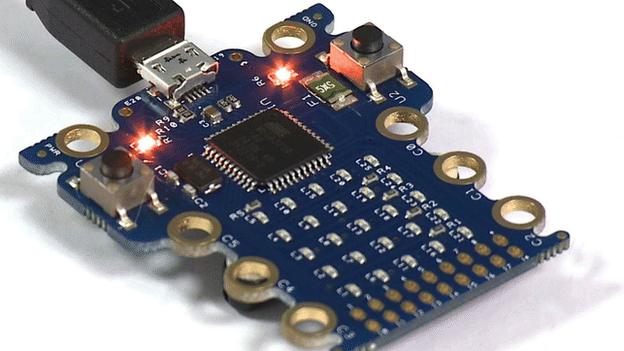
The BBC has revealed the final design of the Micro Bit, a pocket-sized computer set to be given to about one million UK-based children in October.
The device - which features a programmable array of red LED lights - includes two buttons and a built-in motion sensor that were not included in a prototype shown off in March.
But another change means the product no longer has a slot for a thin battery.
That may compromise its appeal as a wearable device.
An add-on power pack, fitted with AA batteries, will be needed to use it as a standalone product.
The BBC's director general Tony Hall said the device should help tackle the fact children were leaving school knowing how to use computers but not how to program them.
"We all know there's a critical and growing digital skills gap in this country and that's why it's so important that we come together and do something about it," he said at a launch event in London.

The Micro Bit no longer contains a slot for a watch battery, which was featured in a prototype
Flashing lights
Children will be encouraged to write simple code for the Micro Bit via a new website, which will be accessible on both PCs and mobile devices.
Young coders explain what the Micro Bit can do
They will be able to save and test their programs on the site before transferring them to the tiny computer via a USB cable or wireless Bluetooth connection.
The Micro Bit can then be made to interact with its built-in sensors and buttons to make its 25 LEDs flash in different patterns, letting it display - for example - letters and numbers.
In addition, it can be connected to other computing kit via its input-output rings - including the Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Galileo - to carry out more complex tasks.
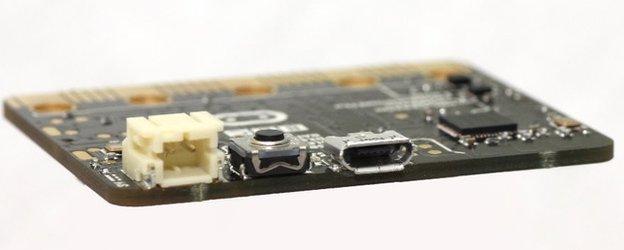
The Micro Bit can be powered via a USB cable, but will otherwise require a battery-pack accessory
It is suggested:
the Micro Bit's built-in magnetometer sensor could be used to help create a metal detector
its accelerometer to make a hi-tech spirit level
its Bluetooth chip to control a DVD player
its two buttons to create a video games controller
The BBC describes the 4cm by 5cm (1.6in by 2in) device and an associated Make It Digital campaign as its "most ambitious education initiative" since the release of the BBC Microcomputer System in the 1980s.
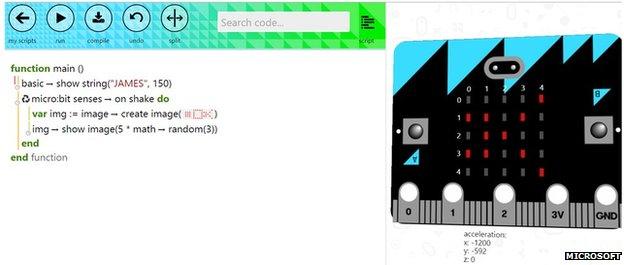
Microsoft has helped develop a web-based tool that can be used to program and simulate the Micro Bit
But while the earlier computer was sold for hundreds of pounds, the Micro Bit is being given away to every 11- and 12-year-old child in Year 7 or equivalent at school.
BBC Learning head Sinead Rocks said: "The BBC Micro Bit is all about young people learning to express themselves digitally.
"As the Micro Bit is able to connect to everything from mobile phones to plant pots and Raspberry Pis, this could be for the internet-of-things what the BBC Micro was to the British gaming industry."

The Micro Bit is being pitched as a complementary device, rather than a competitor, to the Raspberry Pi, Arduino and Galileo computers
When the device was announced, four months ago, the BBC promoted the fact it could be easily pinned to a child's clothing.
However, one of the revisions has involved replacing a watch-battery slot with a bulkier battery pack, which may make that less practical.
A spokesman said: "The initial prototype utilised a smaller battery, however in reviewing the design and examining the health and safety implications of using small batteries for a young audience, where siblings may be able to access the device, the partnership took the decision to re-engineer this element.
"Each BBC Micro Bit will now use a discrete battery pack, which can be removed from the device."

The Micro Bit requires an add-on battery pack to work as a standalone device
Sales plan
While the BBC instigated the project, other organisations - including the chip designer ARM, Barclays Bank, Samsung, Microsoft and Lancaster University - are also providing expertise and funds to bring the scheme to fruition.
In addition, the Wellcome Trust, ScienceScope and others will help prepare school teachers for the rollout, while volunteer-led groups, including Coderdojo and Code Club, have also promised support.
Although supplies will initially be limited to the schoolchildren qualifying for a free Micro Bit in late October, the BBC has confirmed that the computers will go on sale to others in the UK and overseas before the end of the year.
It also intends to make the machine's specifications open source.
One of ARM's engineers helped design its hardware while on a flight over Russia
Prof Mitchel Resnick, who leads the team developing Scratch, a popular programming tool already used to help children learn to code, at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, said: "I see coding as a new type of literacy.
"When kids learn to code, they learn new ways of expressing themselves and organising their ideas.
"These skills are important for everyone, not just those who plan to pursue computing careers."

BBC Micro v BBC Micro Bit

The BBC Micro first went on sale in 1981 as part of the BBC's original Computer Literacy Project
One advantage the BBC's original computer had over the new Micro Bit was the fact that you could write programs directly onto it without requiring a separate PC or mobile device.
But in many other ways the new device has its advantages, not least because you do not need to plug it into a TV to see what it is doing and it is many times cheaper to manufacture.
The broadcaster has highlighted three other advances:
The Micro Bit is 18 times faster than its predecessor at running code
It is a 70th of the size
It is 617 times lighter
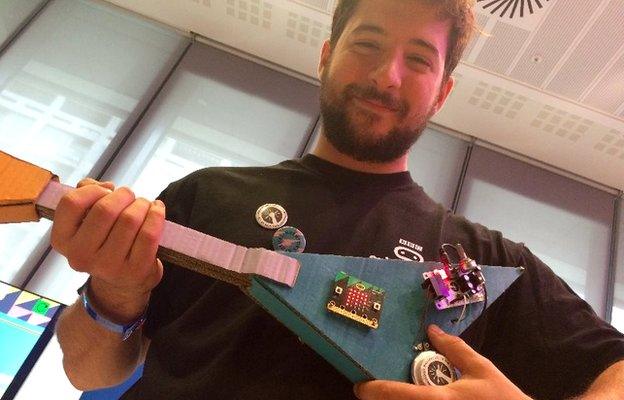

The Micro Bit's small size makes it possible to integrate it into portable projects - including this "guitar" from the Technology Will Save Us team that makes sounds when it is moved
- Published7 July 2015

- Published7 July 2015
- Published12 March 2015
- Published12 March 2015