Blackberry stops designing its own phones
- Published
TIMELINE: How did Blackberry get here?
Blackberry is to stop designing smartphones in-house after 14 years, the company has announced.
Once a market leader, the company has struggled to keep pace with modern handsets produced by rivals such as Apple and Samsung.
In May, the company's chief executive, John Chen, said he would know by September whether the hardware business was likely to become profitable.
Now, Blackberry says it will outsource hardware development to partners.
Blackberry is repositioning itself as a software company
The company has not yet confirmed when any further Blackberry phones will be released, but Mr Chen said on Wednesday that further devices including one with the "iconic" physical keyboard would go on sale.
"I always wanted to make sure that we keep having the iconic devices," Mr Chen told BNN, external.
"I just need to find a way to be efficient and be able to make money. I think we found the model."
The company said it sold about 400,000 smartphones in its second quarter - fewer than the previous three months.
"Blackberry can't keep producing its own phones indefinitely just to serve a small subset of its clients addicted to its home-grown devices," said Ben Wood of the CCS Insight consultancy.
"Blackberry had made no secret of the fact that it might shut down its own phone-making business. Pushing it out to a third party is a sensible solution - but any manufacturer making Blackberry branded devices will ultimately face the same challenges."
'I said a year'
WATCH: Blackberry's latest device was not designed in-house
Mr Chen has been candid about the future of Blackberry's handset business, saying he would consider closing the division if it could not become profitable.
In May, he told Bloomberg, external that he would know by September whether that was likely.
"The first time I made that statement was September a year ago," said Mr Chen.
"When people ask me, 'How long will it take?'... I said a year. So, it's going to be September this year."
In October 2015, Blackberry changed the direction of its handset business by producing its first smartphone running Google's Android operating system, rather than its own BB10 software.
However, Mr Chen has admitted the device, which featured a slide-out physical keyboard, was too expensive to appeal to a mass market.
The company has since launched a less expensive touchscreen-only Android handset, based on a phone released by Alcatel owner TCL.

A bumpy history
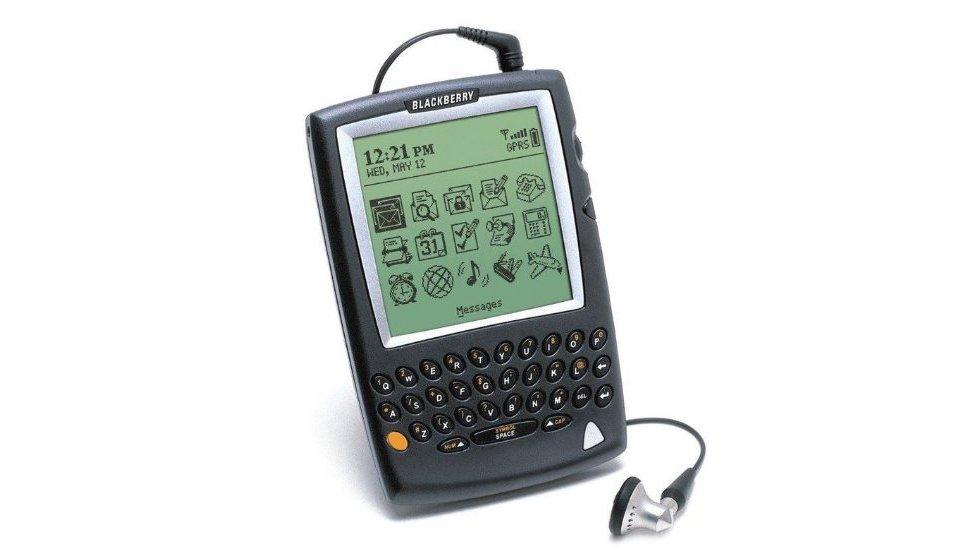

The Blackberry 5810 is described as one of the first smartphones
March 2002: Technology company Research In Motion (RIM) released the Blackberry 5810 - a phone, email and mobile web-browsing device with a full Qwerty keyboard. Described as one of the first smartphones, it was able to make and receive calls when connected to a headset.
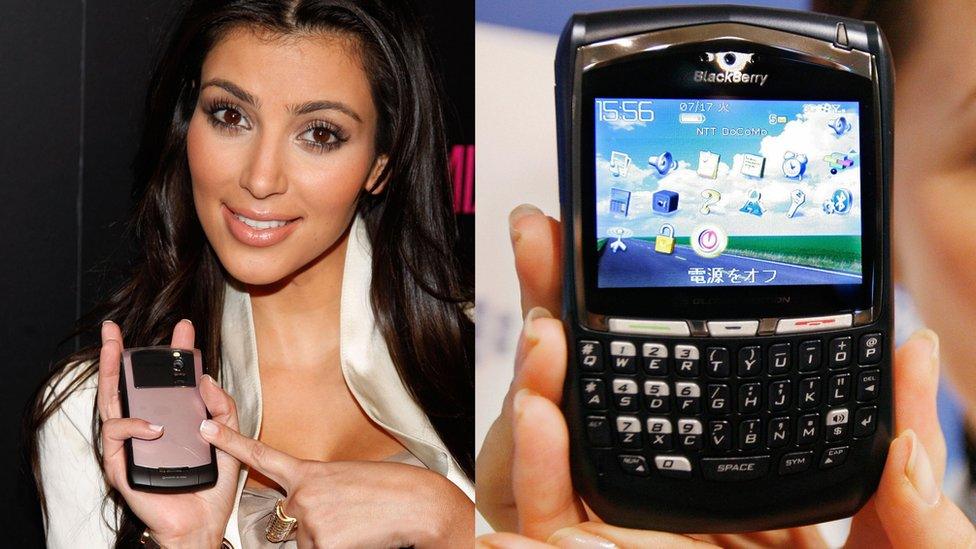

Kim Kardashian used a Blackberry Curve smartphone in 2008
2007: Now featuring a colour screen, camera and an improved mobile web browser, Blackberry handsets became popular in the business world and soon enjoyed celebrity endorsements from the likes of Kim Kardashian.
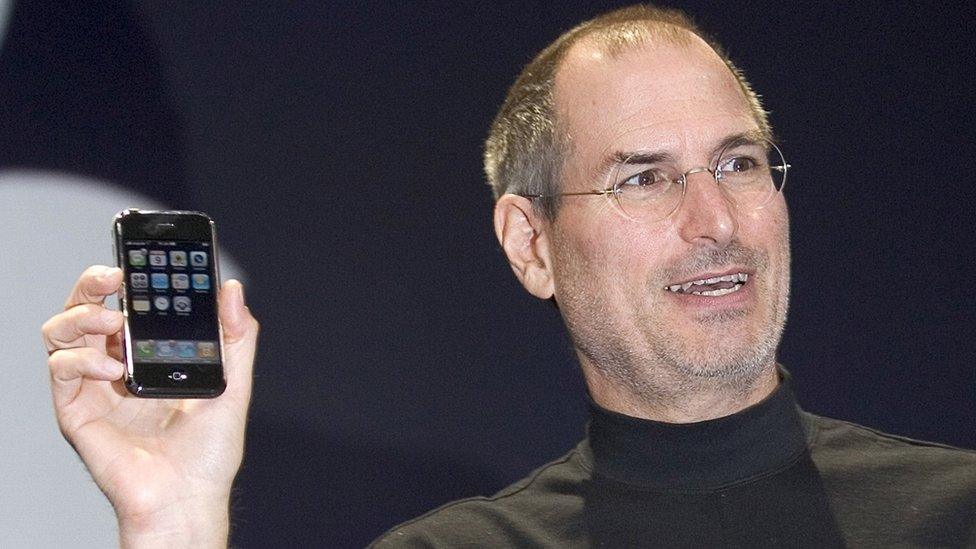

Steve Jobs with the iPhone
June 2007: Steve Jobs introduced Apple's iPhone. The device is said to have changed the course of the smartphone industry by introducing downloadable apps and bringing an easy-to-use touchscreen device to the mass market. The iPhone was the first mobile phone to feature a "full" web browser, something Blackberry executives are reported to have thought, external would cause mobile phone networks to collapse.

The Blackberry Storm was designed to battle the iPhone
November 2008: Under pressure from mobile networks to develop an "iPhone killer", Blackberry produced the Storm. The handset featured a touchscreen that physically clicked when pressed, to emulate the feeling of the firm's famous keyboards. The device ran Blackberry OS - the firm's legacy operating system, which had been built before the advent of downloadable apps. Critics said the Storm was glitchy and slow, and its web browser paled in comparison to the iPhone's offering.
Despite the Storm's poor reception, Blackberry continued to grow its market share until 2010.

Blackberry founder Mike Lazaridis launched the Playbook tablet
April 2011: The company launched its Playbook tablet, its first device to ditch Blackberry OS in favour of a new, modern operating system. The Playbook was marketed as a larger-screen "companion" for the firm's smartphones but lacked basic features such as a built-in calendar and email app. By December, the company had written $485m (£370m) off the value of its unsold tablets.
The firm's chief executives Mike Lazaridis and Jim Balsillie stepped down soon after.
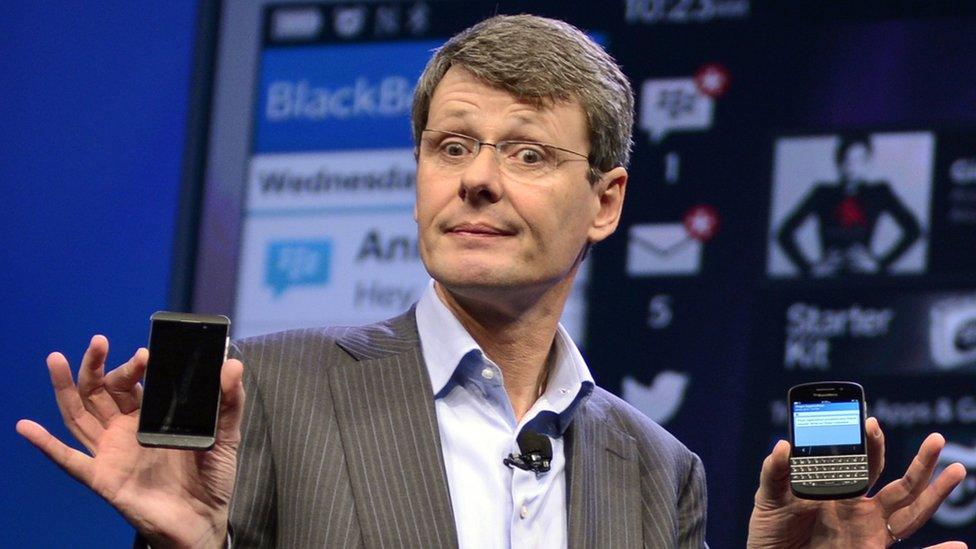

Thorsten Heins replaces Mr Lazaridis and Mr Balsillie, and introduced BB10
January 2013: RIM became Blackberry Limited and launched its BB10 operating system, six years after the appearance of the iPhone.
The platform struggled to attract app developers, who were already occupied producing software for Android and iOS and were reluctant to support a third platform. Big-name apps such as Google Maps, Instagram and Snapchat never officially made it to BB10.
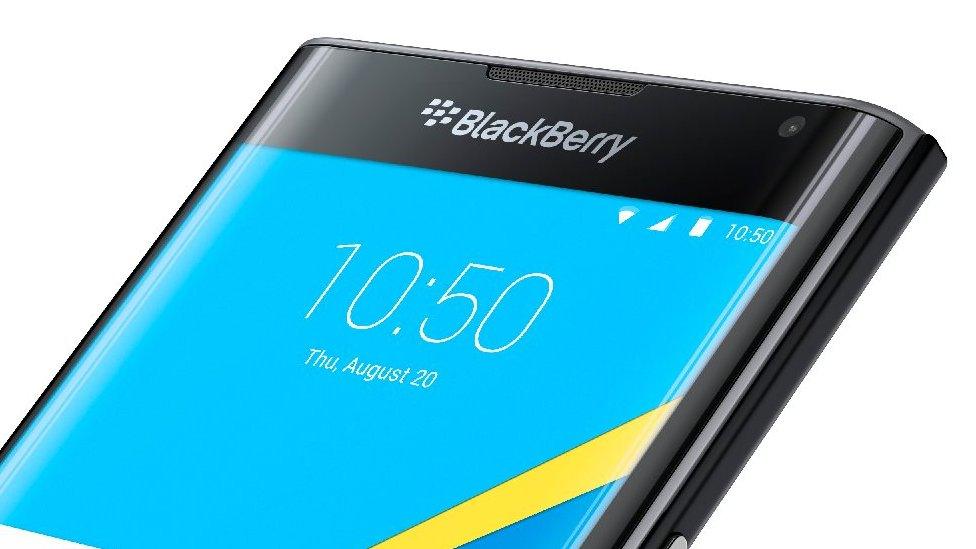

Blackberry Priv was the final device designed in-house
October 2015: Blackberry released its first Android-powered smartphone, Priv, seven years after rivals produced the first Android devices.
Sales of Priv were thought to have missed targets and the firm's current chief executive John Chen later admitted the device had been too expensive.
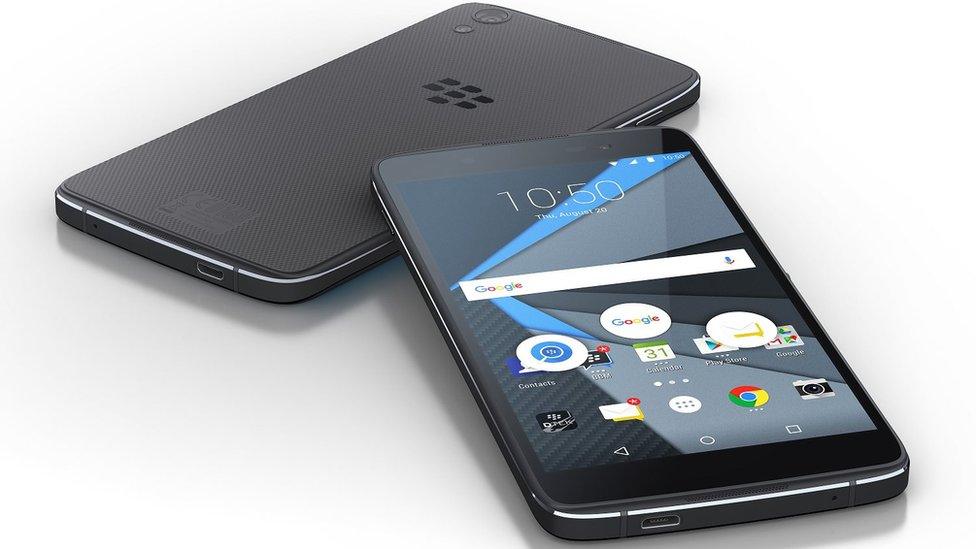

Blackberry's latest handset was designed by Alcatel owner TCL
July 2016: The company's first touchscreen-only Android device, Dtek 50, was released. To reduce costs the handset was based on a phone manufactured by Alcatel owner TCL.
- Published26 July 2016