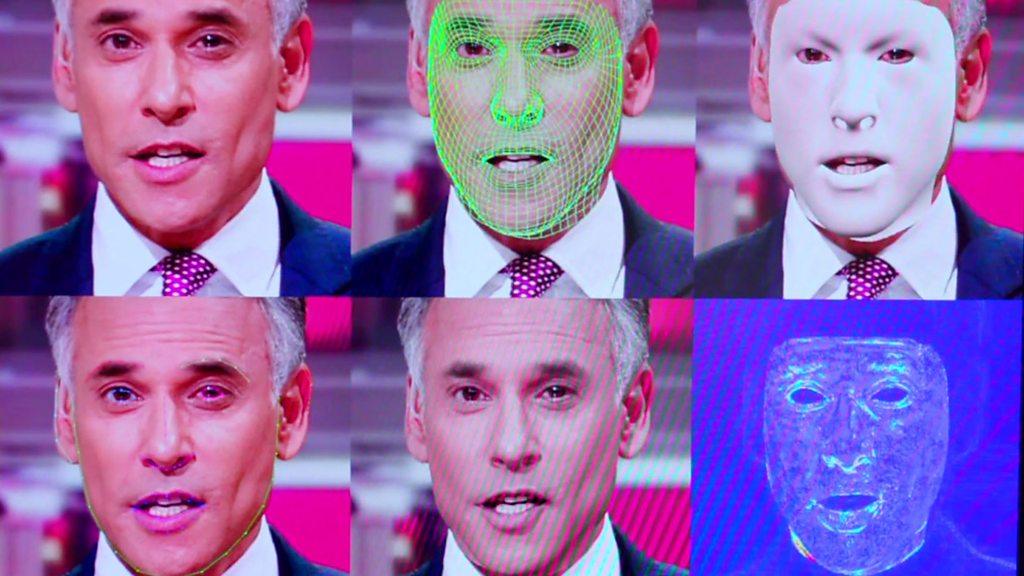
'Deepfake' app causes fraud and privacy fears in China
- Published
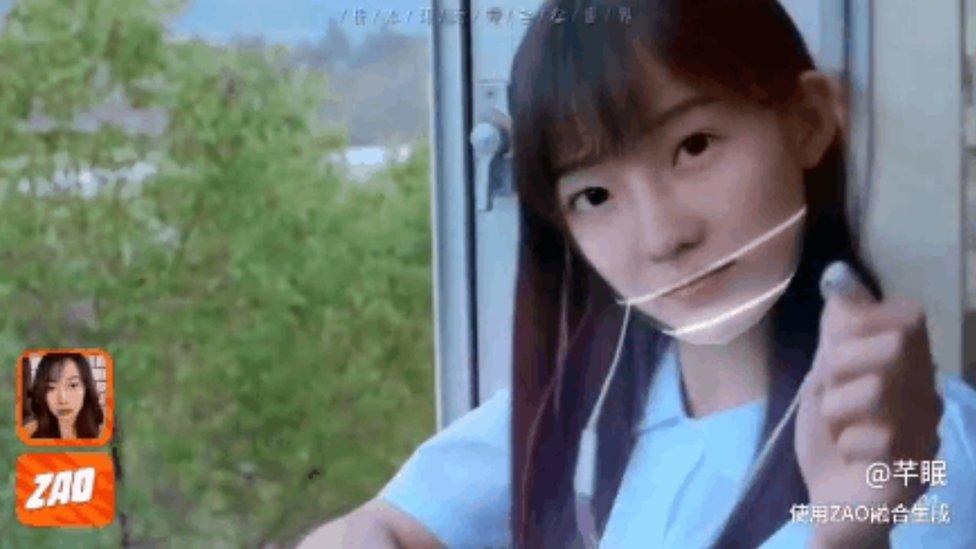

Could this app be a threat to China's national security?
An artificial-intelligence app that allows users to insert their faces in place of film and TV characters has caused controversy in China.
Zao has sparked privacy fears and suggestions it could be used to defeat systems using facial recognition.
It appeared in China on 29 August and has proven wildly popular.
But it has led to developers Momo apologising for its end-user agreement, which stripped users of the rights to their images.
And as the app went viral, Zao's owners aired fears users were devouring its expensively purchased server capacity.
Its popularity has also lead to assurances from Alipay, part of the Chinese web giant Alibaba, saying that it's impossible for so-called deepfake videos created by the app to be used to cheat its Smile to Pay facial-recognition system.

Zao maps the user's face on to one of an existing library of video clips
What's Zao and why is it so controversial?
Zao is a face-swapping app that uses clips from films and TV shows, convincingly changing a character's face by using selfies from the user's phone.
But some users had noted the app's terms and conditions "gave the developers the global right to permanently use any image created on the app for free", Hong Kong's South China Morning Post reported, external.
"Moreover, the developers had the right to transfer this authorisation to any third party without further permission from the user," the paper said, adding experts believed this broke Chinese law.
Momo had subsequently deleted the controversial clause and issued an apology, saying its app would not store users' biometric information nor "excessively collect user information", Shanghai-based The Paper said, external.
But popular social media platform WeChat quickly banned users from uploading Zao videos via its platform, citing "security risks".
WATCH: The face-swapping software explained
The app may also be a victim of its own success, with Zao saying, on its Sina Weibo social media account,, external it had used up a third of its monthly server capacity, budgeted at 7m yuan (£805,000), on its first night.
And the following day, as users complained of a slow service, it said, "with a heavy heart", servers were at fully capacity.
Could Zao be used to defraud banks?
Alipay, the world's largest mobile payment platform, with over 870 million users, has assured its users videos created in Zao cannot be used to defraud its systems.
Many Alipay users take advantage of its Smile to Pay system, external, which allows payment verification by the user looking into a camera at a shop or restaurant's point-of-sale.
Alibaba, which owns Alipay, says it uses sophisticated anti-spoofing algorithms to make sure it isn't fooled by still photographs or deepfake videos.
"There is a lot of online face-changing software - but no matter how realistic, it is impossible to break through the facial payment system", the company said on its Weibo account, external.
Even before the system attempts to match the face, it detects whether the presented image is a still, video or software simulation.
"This avoids fraud caused by face-changing technology," Alibaba said.
Momo also moved to calm fears Zao could be used for fraud, clarifying Alipay's point it only used and adapted still photographs for its deepfake videos.
"The facial payment security threshold is extremely high, and 'face-changing' technology realised by only one photo can't break through the security system," the developers said.
It was "completely impossible" for deepfakes of this kind to threaten payment security, Momo told The Paper., external
And last year, academic Pan Helin told, external China Daily Alipay's facial recognition was "theoretically a more secure and convenient method than the conventional use of passwords".

Alipay is the world's largest mobile payment system
What's the reaction been?
Concerns over the app reached state-run Chinese press.
Global Times said it was, external another example of "concerning" AI-powered apps "which could be used maliciously".
China was already considering tightening regulations governing AI face-stitching technology, the paper said.
And lawyer Zhang Xinnian told it the laws governing phone apps' terms and conditions needed to be tightened.
Zao's initial terms "violated user privacy and once personal information is leaked and abused it could lead to criminal incidents", he added.
Meanwhile, law professor Zhu Wei told state news agency Xinhua, external: "People are using a mobile client that involves information about personal identity, property, scan codes and mobile payments and they can't see exactly what information is obtained by the app, so it is very dangerous."
Zao topped the app chart in China almost immediately after its release
A commentary in the Beijing News, external even asked whether the app could become "a threat to national security".
With genuine concerns about national and personal security from Zao and future deepfake services, "it is necessary to regulate them as soon as possible with clear legal provisions", it added.
A Guangzhou Daily editorial, external said: "Changing-face videos is fun but the potential security risks cannot be ignored."
And The Paper, external said while Zao's popularity would be short-lived, its arrival had made it easier for dark actors to take advantage of face-changing technology.
BBC Monitoring reports and analyses news from TV, radio, web and print media around the world. You can follow BBC Monitoring on Twitter, external and Facebook, external.
- Published12 June 2019

- Published24 May 2019

- Published14 November 2018
