China coronavirus: UK tracing up to 2,000 Wuhan visitors
- Published
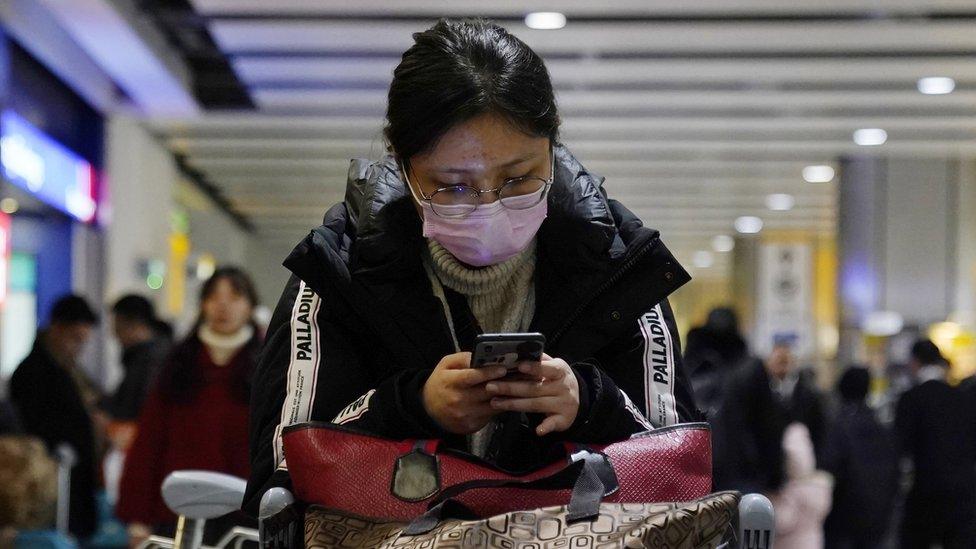

A health team is available at Heathrow Airport for travellers from China
Officials are attempting to trace as many as 2,000 visitors who have flown in to the UK from the Chinese city of Wuhan, where the new strain of coronavirus first broke out.
Tests on 14 people in the UK have come back negative, Chief Medical Officer for England Chris Whitty said.
Prof Whitty said there is a "fair chance" Britain will see cases of the new virus, which has killed 26 people.
Health Secretary Matt Hancock said the risk to the public "remains low".
It came after Public Health England said that, while cases of the new virus in the UK are "highly likely", most of those affected abroad by the virus were making a good recovery.
Globally, there are more than 800 confirmed cases of the virus, which has killed 26 people in China.
Mr Hancock chaired a meeting of the UK government's emergency committee, Cobra, to discuss the outbreak. A Downing Street spokesman said there were still no confirmed cases in the country.
'Marathon not sprint'
Prof Whitty said further tests on a number of other patients are still being processed but that he did not want to provide exact numbers.
"This is a marathon not a sprint," he said, adding that clinicians are now implementing a system to deal with the new virus that can be scaled up if needed.
Prof Whitty said attempts are being made to trace those who have arrived in the UK from Wuhan - the Chinese city where the virus first broke out - over the last 14 days.
It is understood that the aim is to eliminate those who have flown on to other destinations and to check on the health of others in case they might have the coronavirus.
It is believed that this could involve as many as 2,000 people.
Meanwhile the Chinese Ambassador to London, Liu Xiaoming, has said his country's government "is very much determined to curb" the virus.
"We think we can get it under control," he added ahead of a No 10 reception for the Chinese New Year.
All the people who have been tested in the UK had visited Wuhan in the last two weeks.
In Scotland, where five people were tested, an incident team has been set up to deal with the health threat. Four of the patients were believed to be Chinese, Downing Street said.
Those tested in the UK included one person in Wales, who was given the all clear last week, and one man in Belfast.
One of those cleared was British artist Michael Hope, 45, who spent two days in quarantine this week after developing "a nasty cough" on returning to Newcastle from Wuhan.
Prof Cosford told the BBC "we will not be surprised" if people return from China to the UK with the infection, which can cause lung problems such as pneumonia.
"I think it's highly likely that we will have cases in the UK - and of course every so often we do get new infections coming from the animal kingdom such as this one."
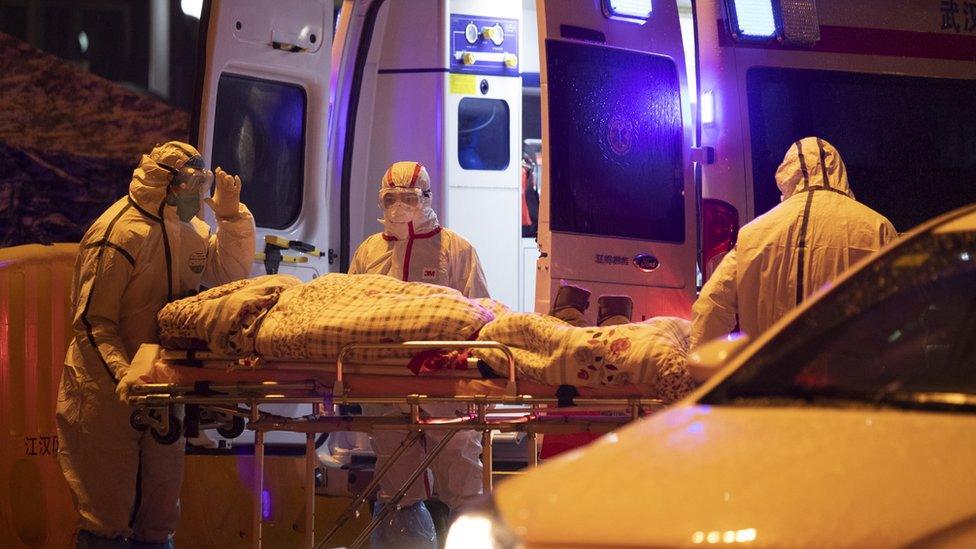
There are no planes or trains in or out of Wuhan, where people are being treated
He added: "These are early days yet with this virus. The vast majority of people who are infected do seem to be getting better.
"The people who have done particularly badly, and sadly died, they seem to be people who have other conditions that might make them more likely to suffer badly with this virus."
The Foreign Office has advised against all but essential travel to Wuhan and the UK is monitoring direct flights arriving from China as a precaution.
Passengers are receiving leaflets and advice on what to do if they fall ill, and a health team is available at Heathrow Airport to check for symptoms.
GPs have been told to isolate any patients showing symptoms and avoid physically examining them if they have recently travelled from Wuhan.

What should you do if you think you have the virus?
Public Health England is advising anyone who has been to Wuhan within the past 14 days and has developed respiratory symptoms to phone NHS 111.
Those symptoms include a cough, a sneeze, shortness of breath, or a fever.
People who are concerned should phone ahead before going to any medical facility and mention their recent travel to the city.
PHE also advises anyone travelling to China to maintain good hand, respiratory and personal hygiene, and avoid visiting animal and bird markets or people who are ill with respiratory symptoms.
The agency is currently not advising people to wear face masks.

China has widened a lockdown in Hubei province - the centre of the coronavirus outbreak. The travel restrictions will affect at least 20 million people across 10 cities.
The lockdown comes on the eve of Lunar New Year - one of the most important dates in the Chinese calendar, when millions of people travel home.
The virus has spread across China and to countries as far as Japan, Thailand and the US.
What's life like in quarantined Wuhan?
The World Health Organization has not classed the virus as an "international emergency", partly because of the low number of overseas cases, but said it "may yet become one".
Peter Piot, professor of global health and director of the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said "data to date suggests that this virus may have a lower mortality than Sars", which killed hundreds in the early 2000s.

What do we know about the virus?
Currently known as 2019-nCoV, the virus is understood to be a new strain of coronavirus not previously identified in humans.
The Sars (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) virus that killed nearly 800 people globally in the early 2000s was also a coronavirus, as is the common cold.
The BBC's online health editor talks us through what we know about the virus
The first human cases were identified in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019. There have not been any other suspected human cases reported prior to this.
Authorities have said it originated in a seafood market that "conducted illegal transactions of wild animals".
The market has been shut down since the beginning of the year.
The incubation period (how long it takes for symptoms to appear after catching the infection) is days, rather than weeks.
At the moment, there is no vaccine that can protect people against it, but researchers are looking to develop one.
Learn more about the new virus
Your questions: You asked, we answered
The story explained: How worried should we be?
Wuhan profiled: The city now in lockdown
In detail: Follow all our coverage here

Have you been affected? Share your experiences. Email haveyoursay@bbc.co.uk, external.
Please include a contact number if you are willing to speak to a BBC journalist. You can also contact us in the following ways:
WhatsApp: +44 7756 165803
Tweet: @BBC_HaveYourSay, external
Send pictures/video to yourpics@bbc.co.uk, external
Please read our terms & conditions and privacy policy
- Published24 January 2020

- Published23 January 2020

- Published22 January 2020

- Published24 January 2020

- Published22 February 2022
