Courts waved through warrants to forcefit prepayment meters
- Published

Courts waved through applications by energy firms to forcibly install prepayment meters in people's homes, according to internal advice from a top magistrate leaked to the BBC.
Previous guidelines required careful scrutiny of warrant applications, but new advice to courts deems those rules "disproportionate".
Energy firms can apply for warrants when bills go unpaid for a long period.
But suppliers were told to stop force-fitting meters earlier this week.
The energy regulator Ofgem told energy companies not to forcibly install the meters following a report from The Times showing debt agents had broken into vulnerable people's homes, external.
But in recent days warrants are still being issued. Privately industry voices are concerned that having ruled out disconnecting customers, and pausing prepayment meters, there is now a "charter for non-payers".
The new advice for magistrates was posted within the last month on an internal website for magistrates, by the National Leadership Magistrate Duncan Webster.
In an internal FAQ post for magistrates, Mr Webster told magistrates the "advice given to justices has not kept up with changes in the way utility companies operate". As the remedy sought by energy companies for unpaid bills is no longer disconnection, but installation of a prepayment meter, "checks magistrates have been asked to make are now disproportionate and go far beyond the legal requirements".
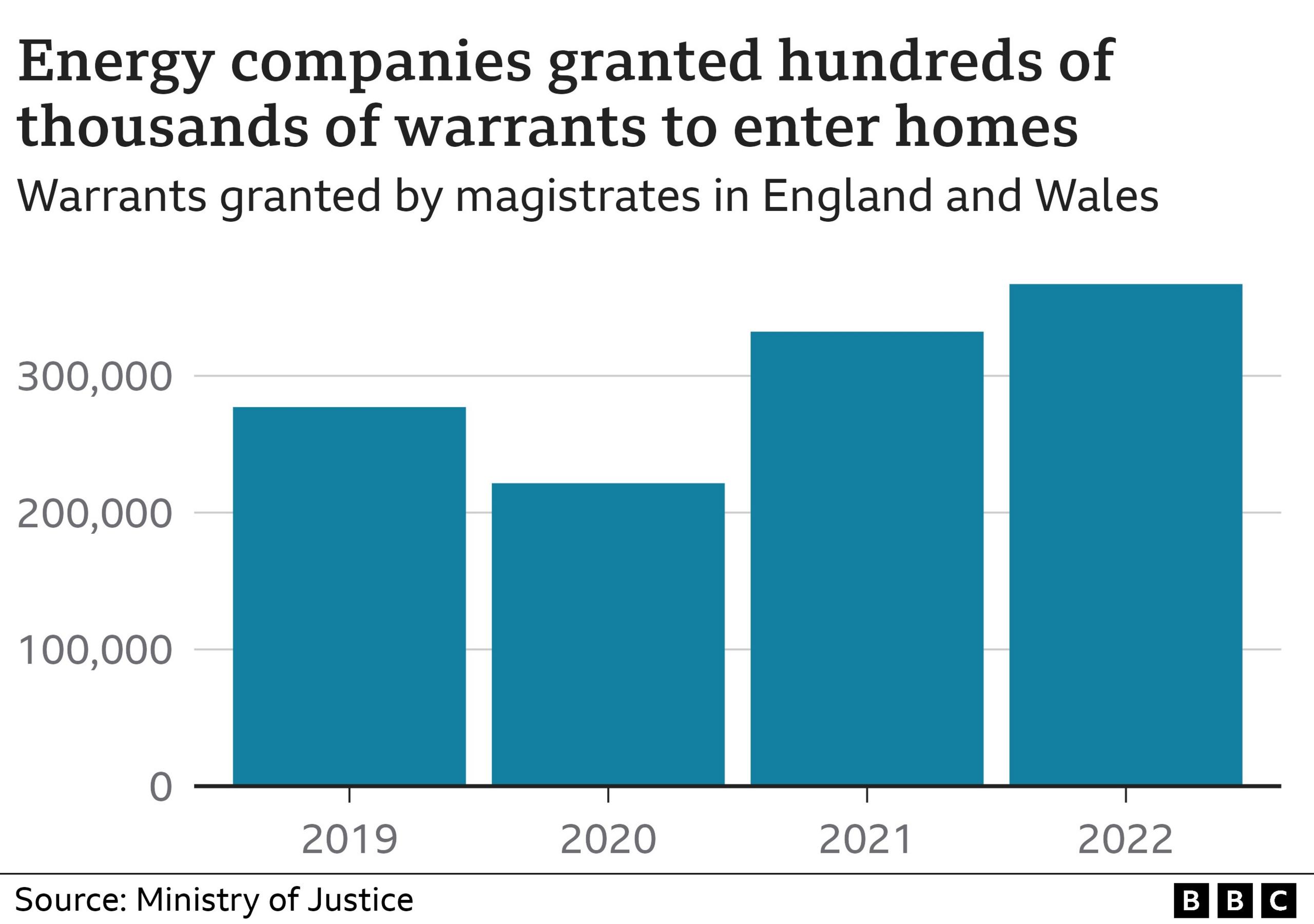
In 2022, as the cost of living crisis took hold, magistrates approved more than 1,000 warrants a day. Almost all of these claims are now authorised electronically or over the phone, by specific magistrates courts allocated to each energy company.
Energy company agents apply by telephone and send in large spreadsheets with between 100 and 1000 cases, where customers are told they do have the right to contest the warrant, but many do not respond. The hearings will sign off, issue and send all the electronic warrants in "a maximum of 15 minutes" according to evidence from pilots.
Legal experts suggest that the advice showed that magistrates were no longer safeguarding vulnerable people and were instead accepting the word of big energy companies "in good faith".
Calls are being made for the almost automated system of approval for warrants to be overhauled. Caroline Flint, chair of the government's Committee on Fuel Poverty, said it was making the situation "worse for already fuel-poor households".
The committee said no action by an energy company should make it harder for anyone to heat their home and that the system needed a complete overhaul.
The court system earns a per case fee from the arrangement, an important source of income after a decade when funding for the judicial system has been cut back substantially.
Watch: The whole system of prepayment meters needs review
One magistrate, and former Justice of the Peace, stepped down last August after being left unable to check vulnerable people were being protected when a warrant for a prepayment meter was sought.
Robin Cantrill-Fenwick told BBC Newsnight changes to the court system meant magistrates "were doing nothing more than rubber stamping" warrants.
He said the lack of scrutiny is putting vulnerable households at risk.
Government officials have suggested current advice is a matter for the judiciary. A judicial source said "it just explains what the current law and processes that magistrates are bound to apply".
Scotland's court service has said it will review the process for utility warrants following outcry over forced installation of pay-as-you-go meters.
The Magistrates' Leadership Executive has been approached for comment.
Related topics
- Published4 February 2023

- Published31 January 2023

- Published23 January 2023

- Published9 November 2022
