Illegal Migration Bill risks breaching human rights obligations, watchdog warns
- Published
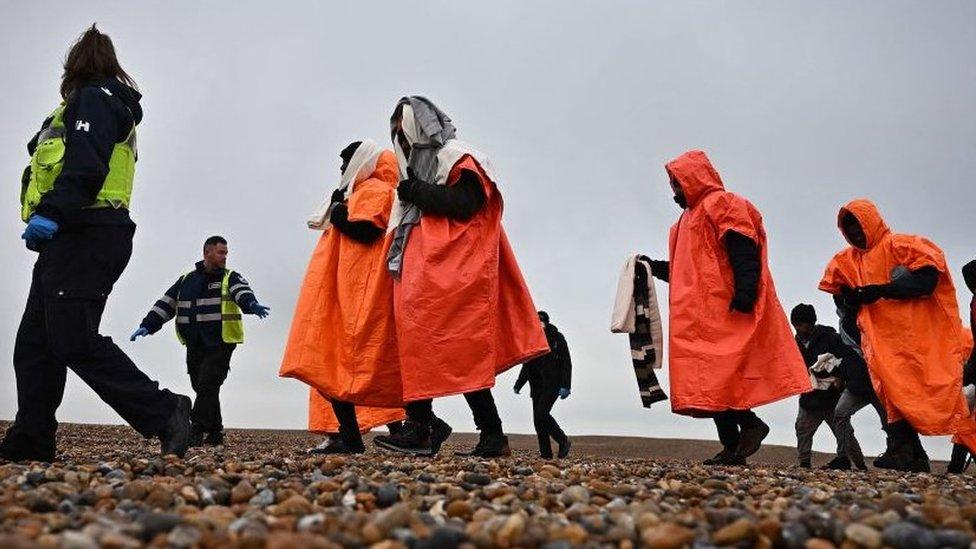

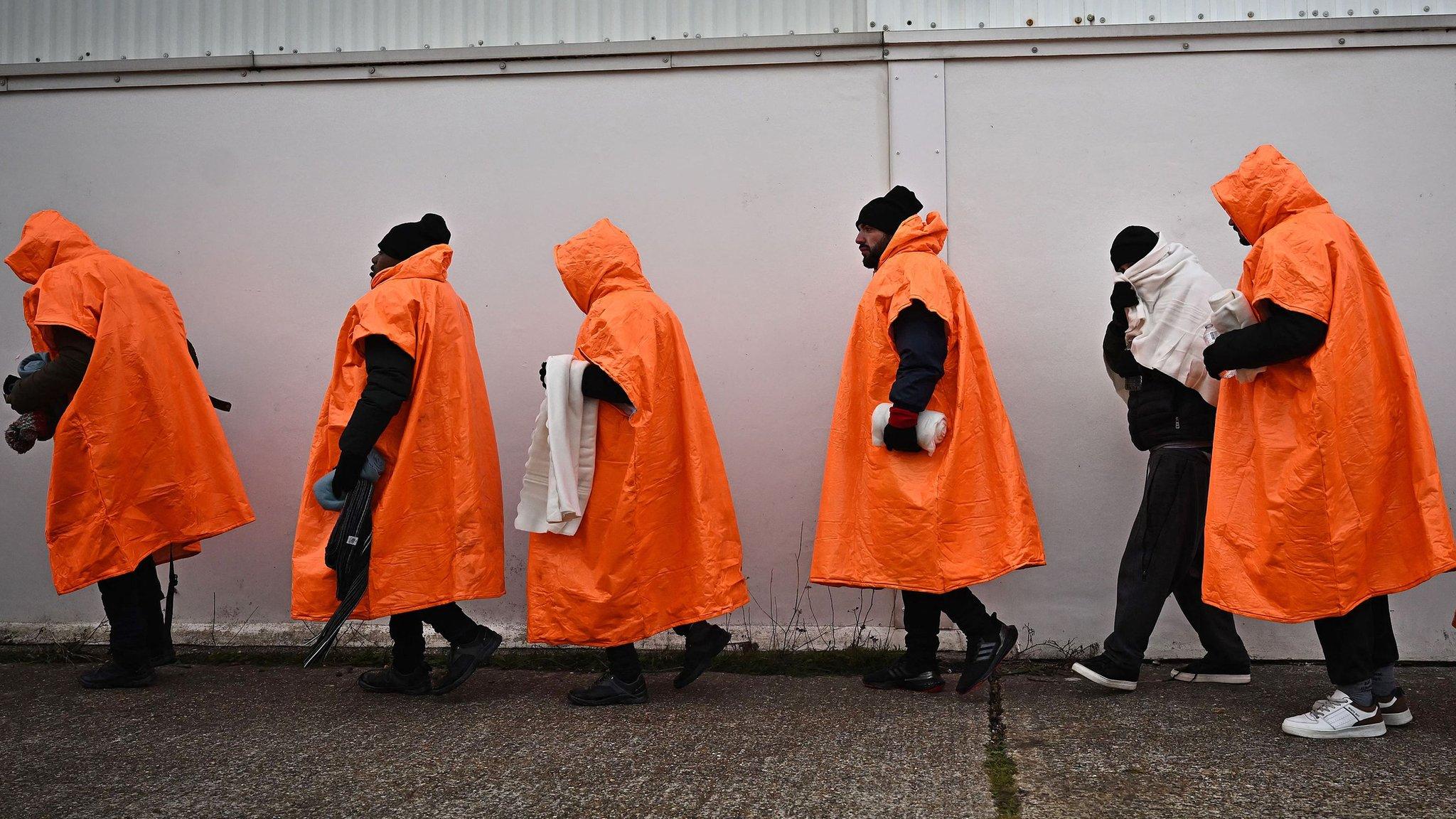
Plans aimed at stopping people crossing the Channel in small boats risk breaching the UK's human rights obligations, a watchdog has warned.
The Equality and Human Rights Commission (EHRC) said the government's Illegal Migration Bill also risked exposing people to serious harm.
It said it was particularly worried about the possibility of children and pregnant women being detained.
The government said the bill was "within our international obligations".
The legislation, which will see its remaining stages debated in the Commons on Wednesday, would prevent anyone arriving in the UK illegally from claiming asylum.
Instead they would be detained and removed, either to Rwanda or another "safe country".
The power to detain and remove individuals also covers children and pregnant women, although the home secretary has said unaccompanied children would only be removed before they reach 18 under limited circumstances, such as for the purposes of family reunion.
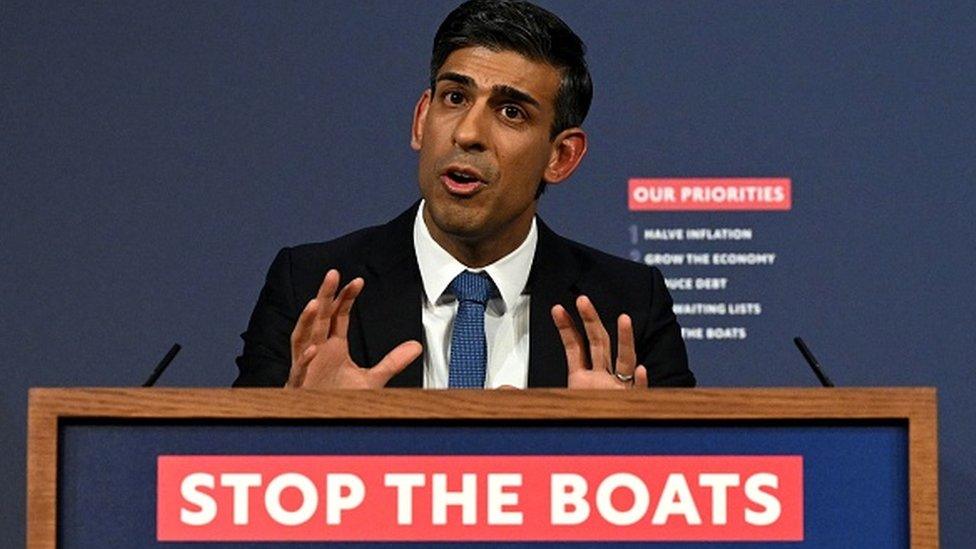
The government says the plans are central to achieving Prime Minister Rishi Sunak's pledge to stop small boat crossings - one of his five key priorities.
However, they have faced criticism from opposition parties and charities, who have argued the bill is unworkable and could breach international law.
The EHRC said it was "seriously concerned" the legislation risked "placing the UK in breach of its international legal obligations to protect human rights".
It said the bill "undermines the core principle of the universality of human rights" and risked breaching the international Refugee Convention, which the UK is signed up to, by restricting the right to asylum and penalising refugees.
The commission also highlighted provisions removing protections for victims of trafficking and modern slavery as "particularly worrying".
However, it welcomed the government's commitment to increase safe routes for those seeking asylum to come to the UK and recommended these were brought forward alongside the bill.
The government promised to set out details of safe and legal routes and any proposals for new routes in an amendment to the bill, following calls from some Conservative MPs including Tim Loughton.
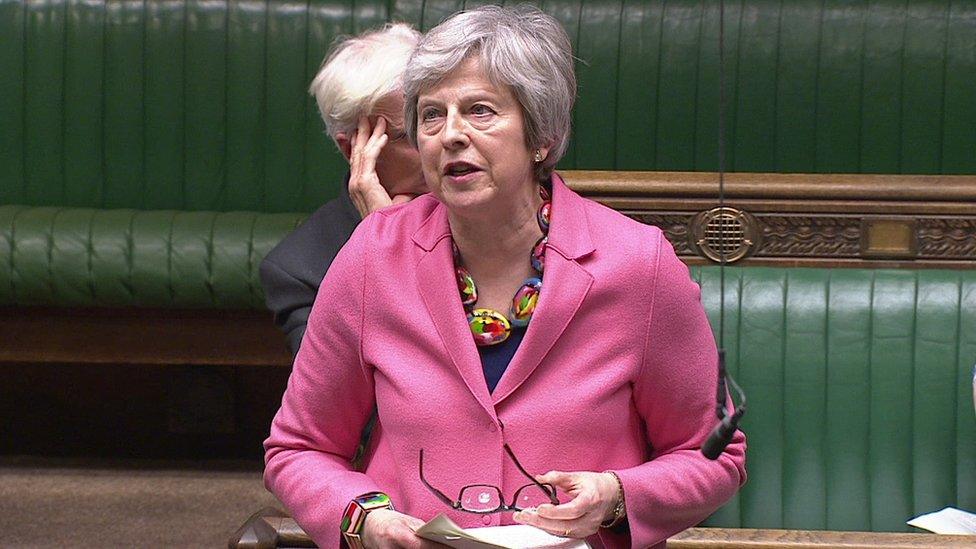
Senior Tories including former Prime Minister Theresa May have raised concerns victims of modern slavery would be denied help under the bill, while others are worried about provisions allowing children to be detained.
But the government has also been under pressure from Tory MPs on the right of the party to toughen up the bill and make it easier for the home secretary to ignore attempts by European judges to halt deportations of migrants from the UK.
A government amendment to the bill published on Monday states that interim injunctions by the European Court of Human Rights do not affect the duty to remove individuals who arrive in the UK illegally.
However, any amendments have to be approved by MPs and peers, some of whom have already raised concerns the proposal could breach international law.
The bill is expected to face significant opposition in the House of Lords and legal challenge if it becomes law.
Asked about criticism of the bill, the prime minister's official spokesman said: "We cannot allow a system to continue which incentivises people to risk their lives and pay people smugglers to come here illegally."
Related topics
- Published20 April 2023

- Published13 March 2023

- Published13 December 2023

- Published9 March 2023
