Smartphone ECG device 'could save lives'
- Published
- comments

Researchers have called for a smartphone device that can help detect serious heart conditions to be rolled out to A&E departments across the UK.
It follows a study that showed the technology was five times more effective at diagnosing heart rhythm problems than standard tests.
The device, trialled at 15 A&E sites across the UK, also significantly cut the cost of diagnosis.
About 300,000 people a year visit A&E complaining of heart palpitations.
The smartphone-based ECG works by recording a patient's heartbeat at home while they are experiencing symptoms.
The ECG result can then be accessed by a doctor who will interpret the result.
'Harmless palpitations'
Lead author Dr Matthew Reed, from Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, said: "We've shown that this device is an easy, cheap way to diagnose heart rhythm problems which usually see people attending emergency departments several times before they're diagnosed.
"For those with harmless palpitations this device can quickly give reassurance, whilst for those with serious underlying heart conditions it can act as a lifesaver.
"We are now calling for this technology to be rolled out in emergency departments across the country."
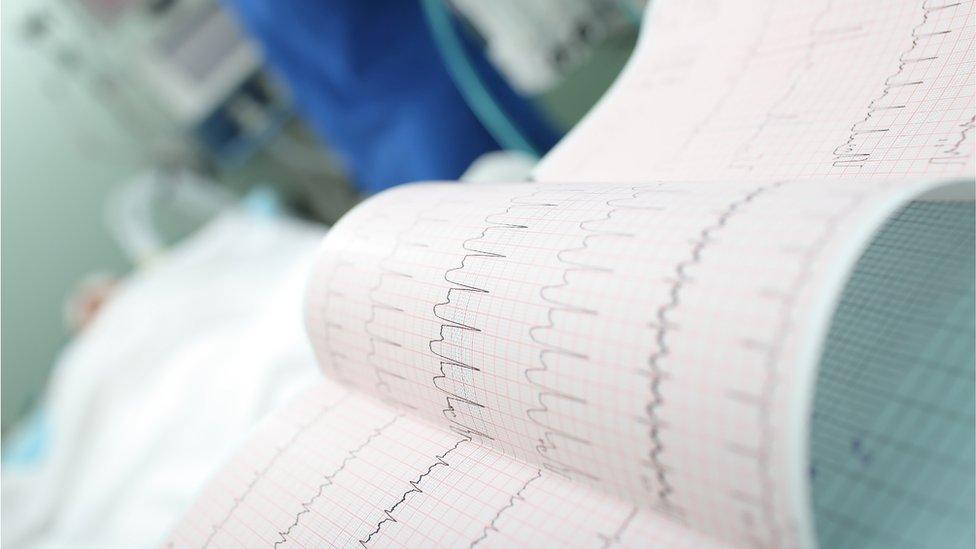
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used by doctors to detect heart rhythms and help diagnose patients
Palpitations are often not serious but are sometimes caused by underlying heart rhythm disorders such as Atrial fibrillation, which can lead to a stroke.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used by doctors to detect heart rhythms and help diagnose patients.
However, by the time a patient reaches A&E their symptoms have often subsided and their ECG is normal.
The study involved about 240 people who turned up at A&E departments with palpitations or who felt lightheaded.
About 300,000 people visit A&E with palpitations each year
The AliveCor KardiaMobile device was given to 124 of the patients to take home.
They were told to activate it when they experienced a palpitation, with the ECG result sent to a doctor.
Meanwhile, 116 patients were given standard tests and, if undiagnosed, told to return to A&E or visit their GP if they experienced more symptoms.
'Carry in our pockets'
After 90 days, the smartphone device helped doctors diagnose 56% of patients, in an average time of 9.5 days.
Of the patients given standard testing, only 10% were diagnosed in an average time of 43 days.
The technology also cut the cost of diagnosis from £1,395 to £474, the researchers said.
The study, part funded by the British Heart Foundation (BHF) and Chest Heart and Stroke Scotland (CHSS), was published in EClinical Medicine.
Prof Jeremy Pearson, BHF associate medical director, said: "By taking advantage of the tech that we carry around in our pockets every day, this cutting-edge device makes sure that it's easy for people experiencing palpitations to directly record their heartbeat.
"They can then relay the information rapidly to a doctor and improve their diagnosis.
"This device could spare people from further anxiety, save the NHS money and, more importantly, save lives."
Dr Matt Kearney, national clinical director for cardiovascular disease prevention at NHS England, said: "Untreated heart conditions like Atrial fibrillation put people at high risk of stroke but can often be difficult to diagnose.
"New technologies such as AliveCor can make diagnosis easier, and that's why in the last year, NHS England has already made thousands of these devices available to GP practices across the country as part of the Long Term Plan commitment to prevent 15,000 heart attacks, strokes and cases of dementia."