Covid: Will Scotland hit its January booster jabs target?
- Published
- comments
About 1.7 million booster shots have already been given in Scotland
Accelerating the booster vaccination programme has become the UK's main line of defence against the Omicron variant.
There are fears the strain could be more infectious, cause more serious illness and be better at evading vaccines than previous variants.
Every adult in Scotland will now be offered a booster, following the latest guidance from the JCVI - the UK government's vaccine advisors.
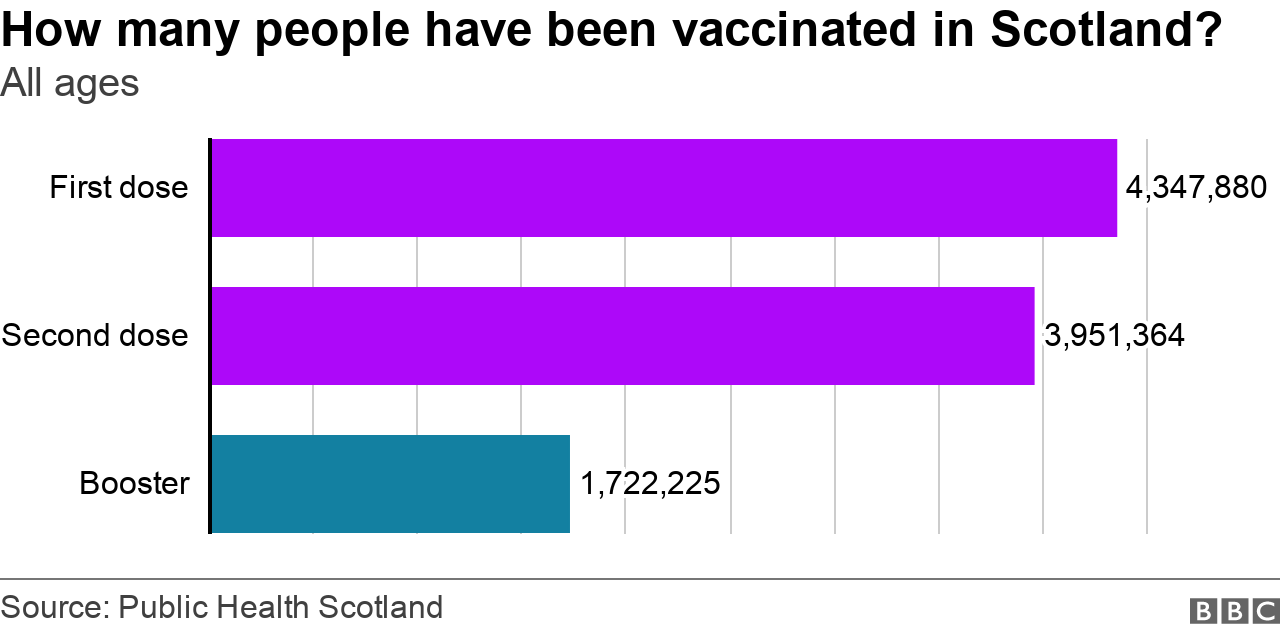
More than 1.7 million boosters have been delivered so far and the Scottish government says all eligible over-18s will be offered one by the end of January.
How easy will it be to meet the January target? At first glance, it's an easy question to answer.
As of 30 November, about 3.92 million adults in Scotland have had a second dose of a Covid vaccine and will need a booster shot.
Take away the number of boosters already delivered to over-18s (close to 1.7 million) and you're left with about 2.2 million people who will need the jab.
Given current vaccination rates, Scotland would need about 70 days to complete the booster programme, taking us into the second week of February.
However, that number of eligible adults is growing every day as more people receive second doses.
To add a bit more complexity, not everyone in that group is eligible right now. Even if it were possible to line up 2.2 million people and jab them in a single day, you wouldn't want to do it.
There needs to be a period of time between the second and third doses - there's no point in boosting immunity if it hasn't already started to wane.
That period was six months, but has now been reduced to three months following new guidance from the JCVI, the UK government's vaccine advisors.
So how do we figure this out?
The first part of the equation is to estimate how many boosters a day are likely to be delivered over the coming months.
Delivering booster shots became the focus of Scotland's vaccination programme in September and the number of first and second doses being given each day has reduced significantly since the summer.
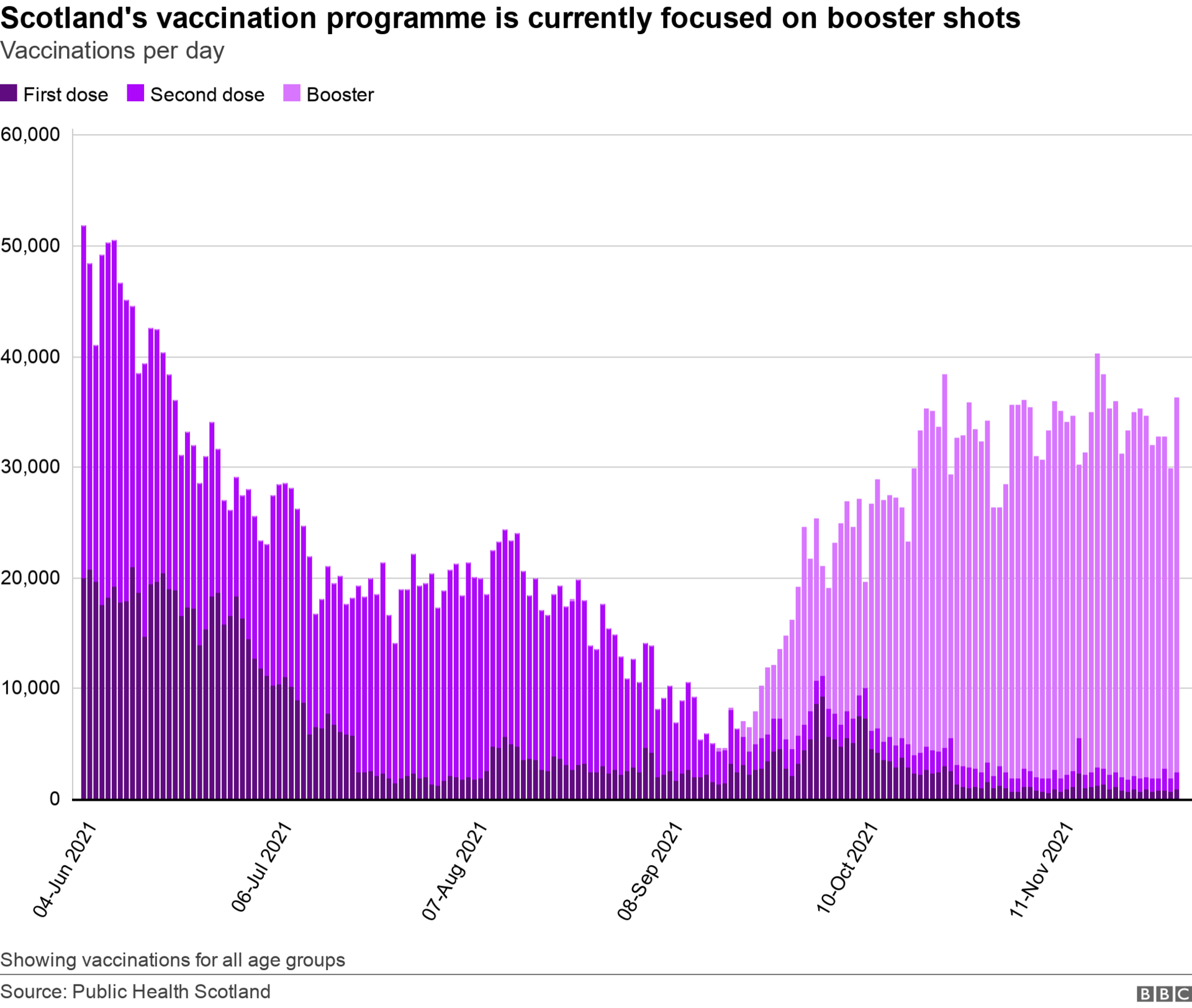
We can see from Public Health Scotland figures, external that over the past two weeks an average of 32,158 boosters have been given to over-18s each day.
Clearly this figure could change over time.
It could go up if the Scottish government directs more resources towards vaccination - or it might go down during the Christmas holiday period.
However, it does give us a reasonable figure to project vaccination rates over the next few months.
The next part of the equation - working out how many over-18s will be eligible for a booster over the coming months - is easier.
That three-month delay between doses means we know exactly how many over-18s will become eligible between now and the end of February.
By plotting the number of eligible people against the estimated number of vaccinations we can see where the lines cross, which is the point where the booster gap will be closed.
Given current vaccination levels, this will be around 5 February.
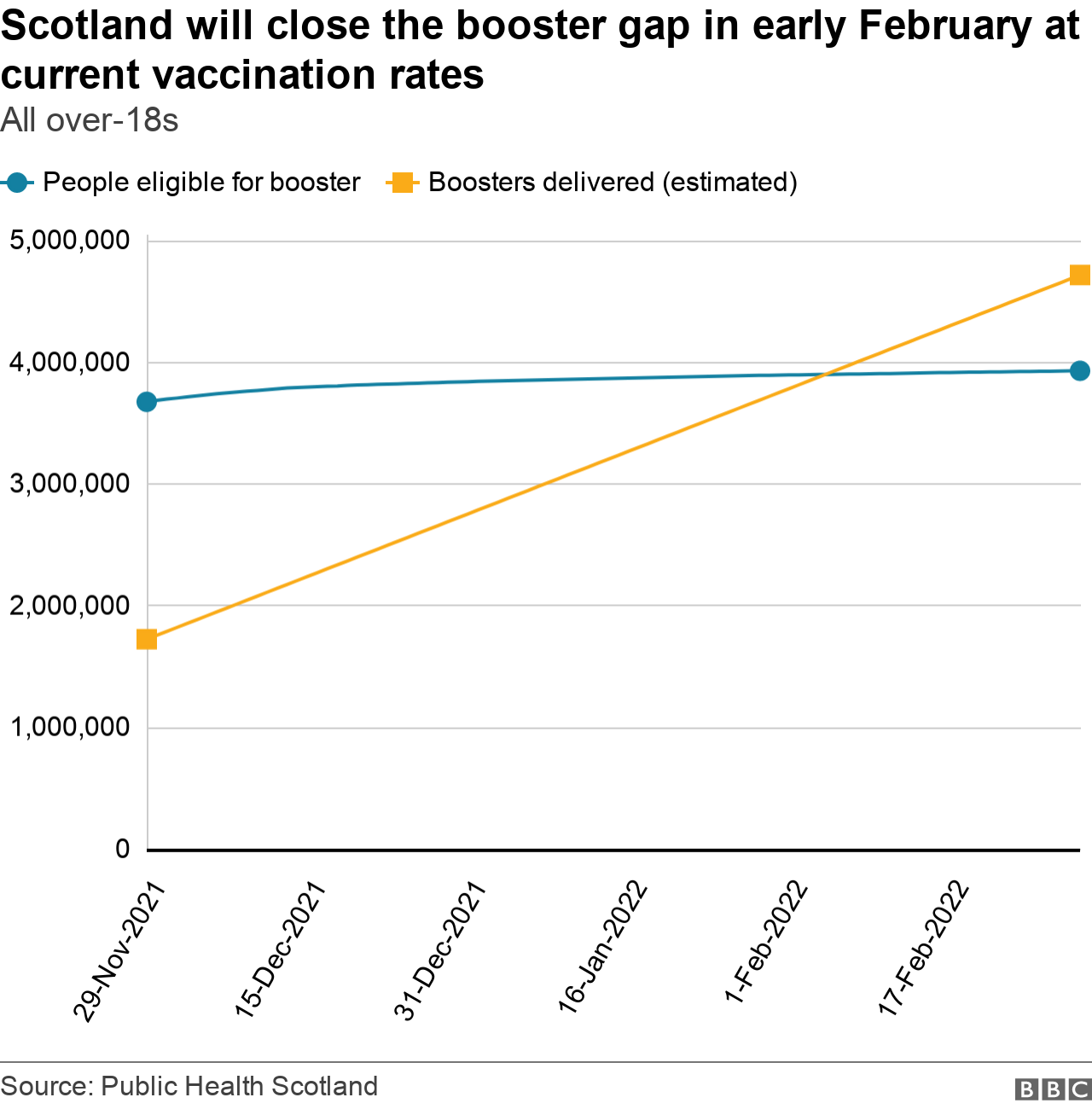
If we wanted to get those two lines to cross by the end of January, we'd need to be delivering about 34,000 jabs a day - 5.7% higher than current levels.
There's also a continuing demand for first and second doses to keep up with, especially in the youngest age groups.
The Scottish government says it's "aiming to offer the booster vaccine to everyone aged 18 or older who is eligible by the end of January". Boris Johnson has set the same target for England.
A Scottish government spokesperson also told the BBC that its approach to vaccine deployment would be confirmed "very soon".
Offering the vaccine is, of course, different to actually getting a jab into an arm. It's also worth noting that the job won't be complete at the end of January.
More people will continue to become eligible for a booster, but the number will start to dwindle as second dose coverage moves closer to 100%, and by then it should be easier to keep up with demand.


- Published2 December 2021