Toothless dinosaur with just two fingers discovered
- Published
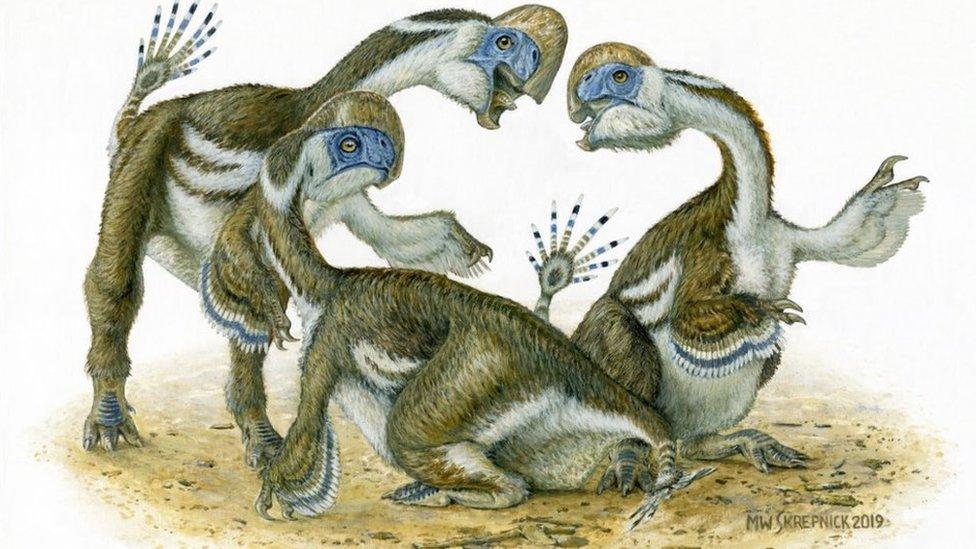

The feathered creature had a large, toothless beak and, unusually for the period, was two-fingered.
A new species of toothless dinosaur that had just two fingers on each arm has been discovered in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia.
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh found multiple skeletons of the species, named Oksoko avarsan.
The feathered creature, which dates from about one hundred million years ago, also had a large, toothless beak.
The team said the discovery could help explain how animals lose fingers and toes through evolution.
They said the species had one fewer finger on each forearm compared with its close relatives, suggesting an adaptability that enabled the animals to spread during the Late Cretaceous Period.
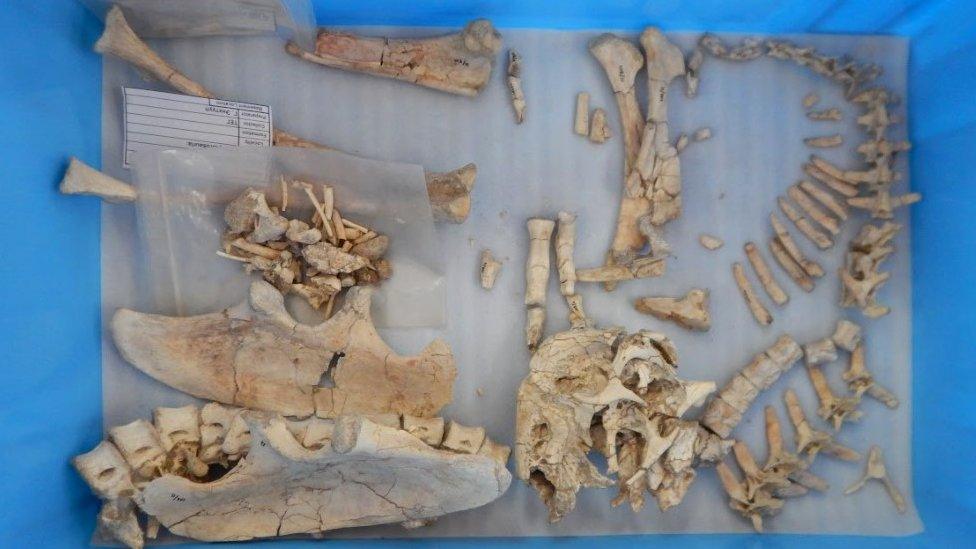
Researchers from the University of Edinburgh found multiple skeletons of the new species, named Oksoko avarsan
Several complete skeletons of the feathered, omnivorous creatures were unearthed.
The animals, which grew to two metres long, had a large, toothless beak similar to the type seen in parrots.
It is the first evidence of digit loss in the three-fingered family of dinosaurs, known as oviraptors.
The team said the discovery that the dinosaurs could evolve forelimb adaptations suggested they could alter their diets and lifestyles, and potentially diversify and multiply.
The team also discovered that Oksoko avarsan, like many other prehistoric species, were social as juveniles.
The fossil remains of four young dinosaurs were preserved resting together.
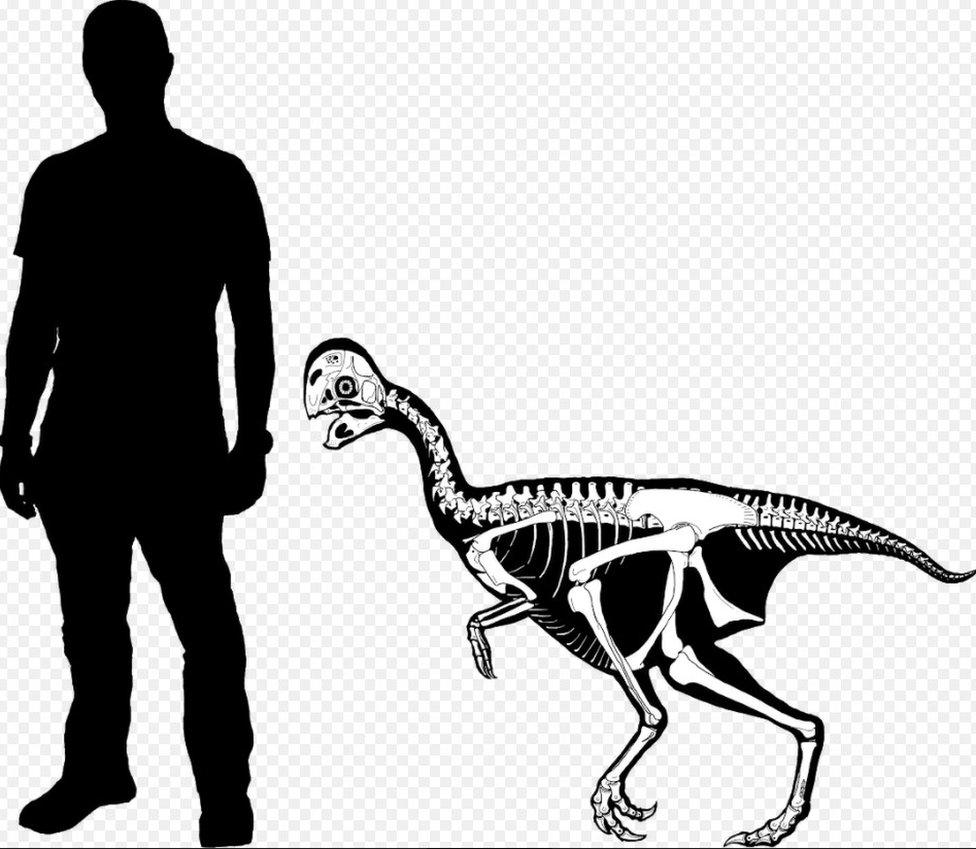
The dinosaur was about half the size of an adult human
Dr Gregory Funston, of the University of Edinburgh's school of geosciences, said the discovery shed light on how a group of parrot-like animals thrived more than 68 million years ago.
"Oksoko avarsan is interesting because the skeletons are very complete and the way they were preserved resting together shows that juveniles roamed together in groups.
"But more importantly, its two-fingered hand prompted us to look at the way the hand and forelimb changed throughout the evolution of oviraptors, which hadn't been studied before.
"This revealed some unexpected trends that are a key piece in the puzzle of why oviraptors were so diverse before the extinction that killed the dinosaurs."
The study, published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, external, was funded by The Royal Society and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada.
It also involved researchers from the University of Alberta and Philip J Currie Dinosaur Museum in Canada, Hokkaido University in Japan, and the Mongolian Academy of Sciences.