Aerial surveys of Viking shipyard on Skye
- Published
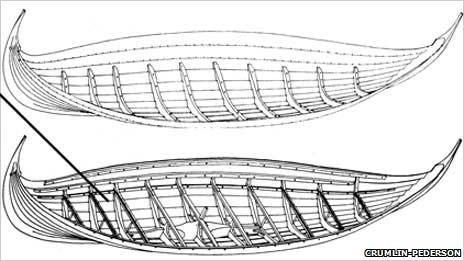
An illustration from RCAHMS of the type of boat built on Skye
Aerial surveys are being carried out over Skye to help archaeologists investigate a 12th Century Viking shipbuilding site.
Boat timbers, a stone-built quay and a canal have already been uncovered at Loch na h-Airde on Skye's Rubh an Dunain peninsula.
The Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland (RCAHMS) has launched the air surveys.
Staff hope to pinpoint new sites for investigation.
Working with marine archaeologists, RCAHMS also hope to find potential dive sites for searches for the remains of ships and other artefacts.
Archaeologists now believe the loch was the focus for maritime activity for many centuries, from the Vikings to the MacAskill and Macleod clans of Skye.
RCAHMS said the loch and canal would likely have been used for protecting boats during winters and also for their construction and maintenance.

Boat building may have been done for centuries at the site
Colin Martin, a marine archaeologist specialising in ship wrecks, has been investigating Loch na h-Airde.
He said: "This site has enormous potential to tell us about how boats were built, serviced and sailed on Scotland's western seaboard in the medieval period - and perhaps during the early historic and prehistoric eras as well.
"There is no other site quite like this in Scotland."
RCAHMS aerial survey manager Dave Cowley said the sea had been vital for connecting communities in the past.
He added: "The aerial perspective gives us an excellent sense of this, showing the inter-relations of land and sea, and helping us to understand how people may have travelled, traded - and fought - on the waters around Scotland's western isles."
In 2009, a crofter uncovered an ancient anchor while digging a drain on the Isle of Skye.
Graeme Mackenzie, 47, made the find after hiring an excavator to open the drain on rough pastureland 50yds (48m) from his home near Sleat.
Rain had partly washed away the bottom of the drain and exposed a corroded 4in (10cm) iron spike.
National Museums Scotland said the type of anchor was in use from the Viking period until the Middle Ages.
Experts were unable to date it any more precisely.
- Published5 July 2010