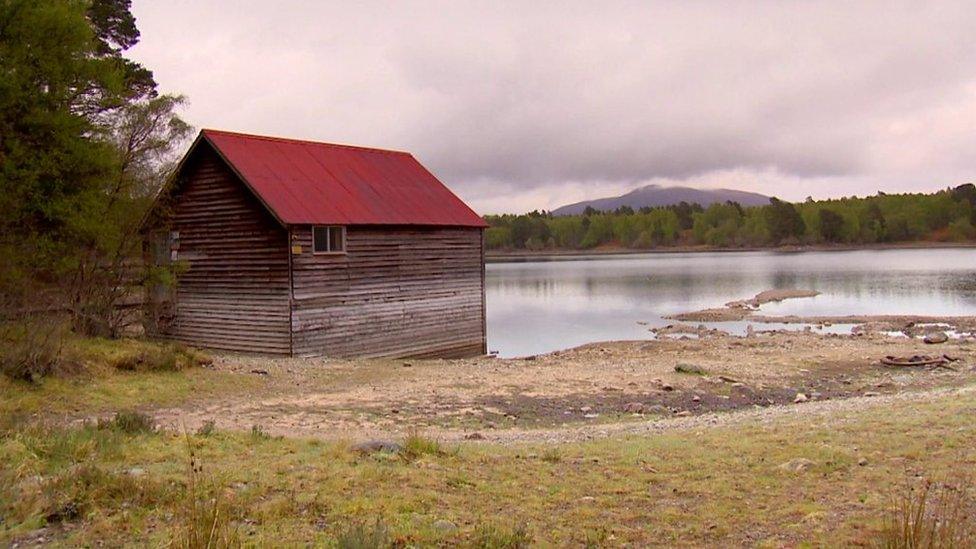
Cairngorms loch dropped to lowest level in '750 years'
- Published
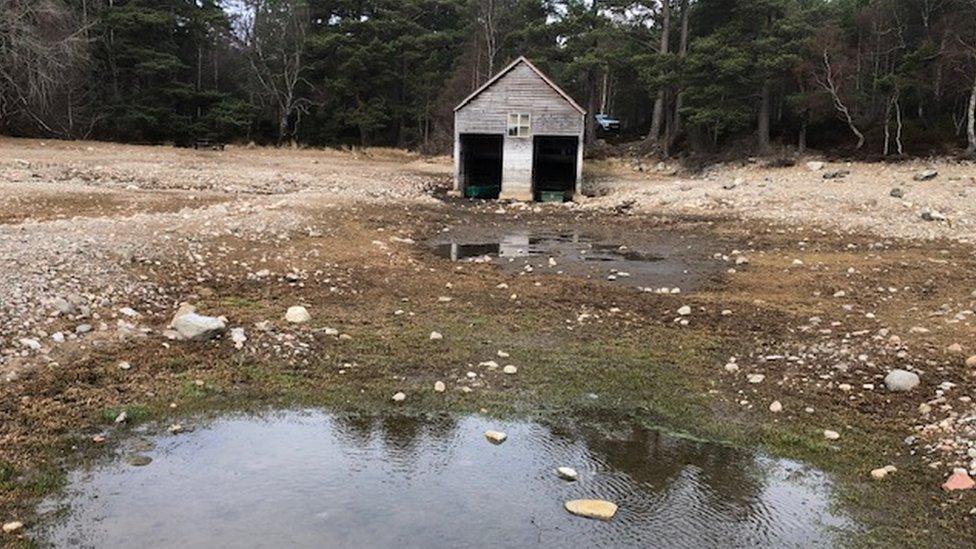

Millions of litres of water disappeared at Loch Vaa between September 2018 and May this year
The water level of a Highlands loch likely dropped to its lowest in at least 750 years in May this year, according to archaeologists.
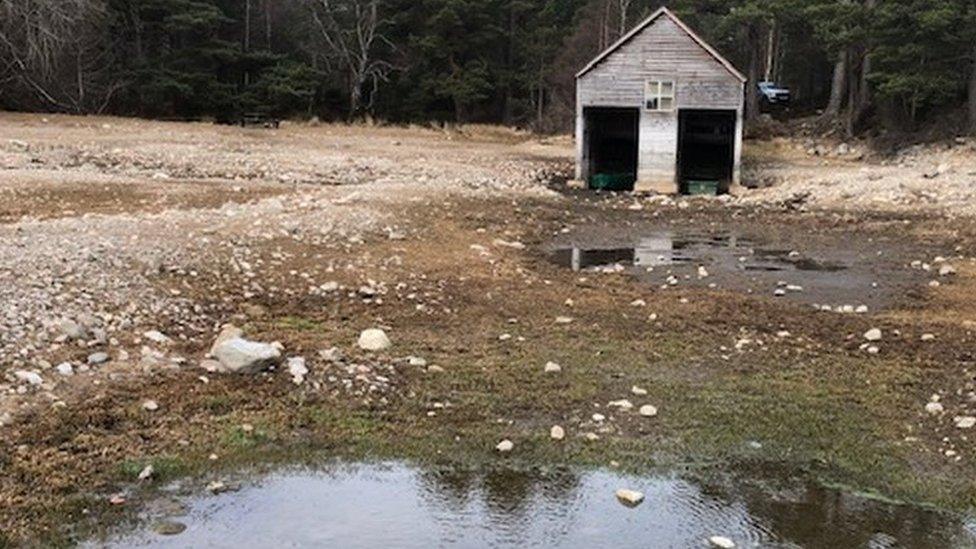
Loch Vaa, near Aviemore, had been mysteriously losing water since September last year.
Archaeologists were asked to check for any impact on a crannog, an ancient fortified settlement, in the loch.
Just below the water's surface they found pieces of wood that had survived since the 13th Century.
Any old wood which was not underwater at the crannog site has been long lost through exposure to the elements.
By May this year Loch Vaa, which is fed by a spring, was estimated to have dropped by 1.4m (4.5ft) since September 2018 - with no clear explanation of the reason.
'It's like somebody's pulled the plug' on our loch
There were concerns that timbers which had been used in the construction of the crannog, and preserved for centuries in the loch, would be exposed to damage by the dramatic fall in water level.
Archaeologists and the Living On Water crannog project were asked to investigate the state of the archaeological site in the Cairngorms.
The site was found to have survived the drop in water level unscathed.
The archaeologists also radiocarbon dated samples of timbers found just a few centimetres underwater.
The birch, a species of tree "not known for being particularly robust" according to the archaeologists, was dated back to the 13th Century.
The research confirmed a medieval phase of the crannog, and that the water level likely reached its lowest level since that time in May this year.
The water level has since returned to normal.
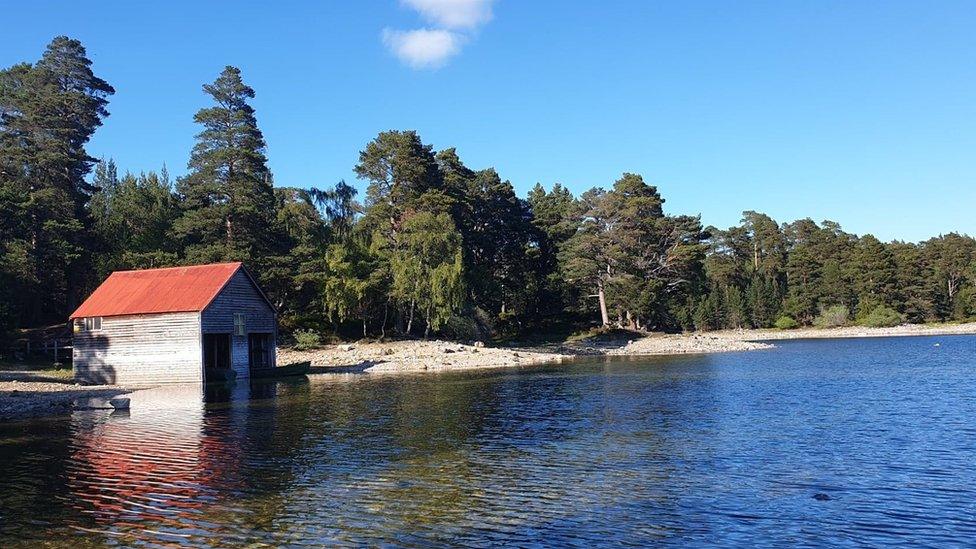
Loch Vaa is managed as a community asset for recreational fishing and water sports.
The Scottish Environment Protection Agency suggested the loch had suffered due to a "relatively dry" winter.
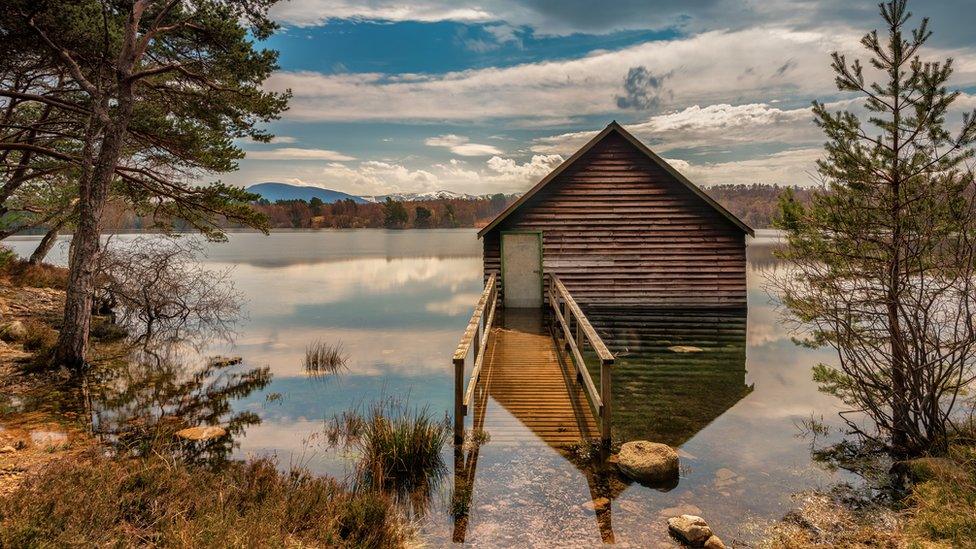

Loch Vaa at its usual water level
Scottish Water countered claims it might be responsible by saying that an underground aquifer and boreholes that supplied water to the Badenoch and Strathspey area were located about three miles (6km) upstream of Loch Vaa, and too far away to affect it.
Crannogs were fortified settlements constructed on artificial islands in lochs.
It was thought they were first built in the Iron Age, a period that began around 800 BC.
But four Western Isles sites have been radiocarbon dated to about 3640-3360 BC in the Neolithic period - before the erection of Stonehenge's stone circle.
Archaeologists said it was possible there was earlier activity at the crannog in Loch Vaa dating back to Pictish or Iron Age times.
- Published2 July 2019

- Published3 May 2019

- Published3 May 2019
