Plastic waste found by archaeologists at Pembrokeshire hill-fort
- Published
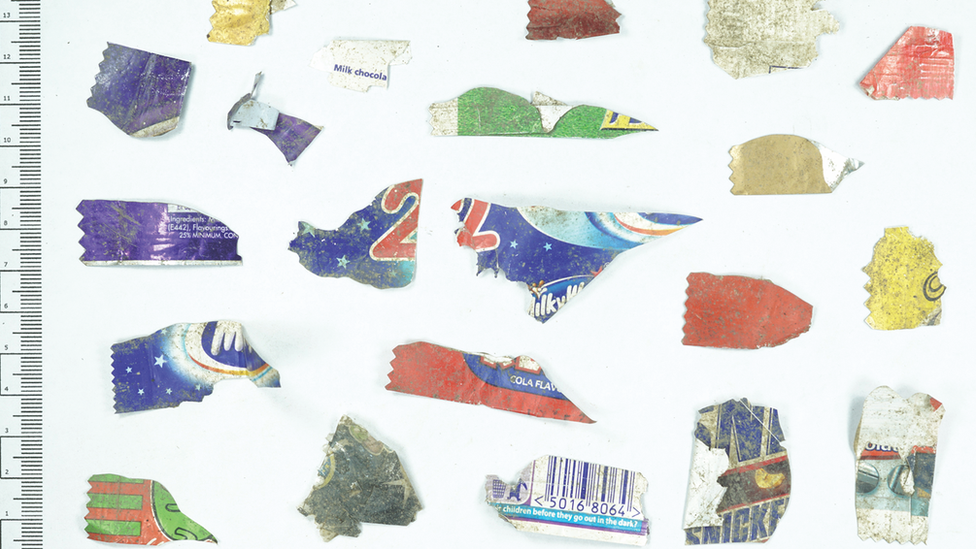

Wrappers from well known chocolate bars and snacks were among 2,000 items found trampled into the ground
It was not what archaeologists at an ancient Welsh hill-fort expected to find - a mountain of plastic.
Academics uncovered more than 2,000 items at the Castell Henllys site in Pembrokeshire.
But these were not ancient artefacts - they were discarded food wrappers and bottle tops from old school lunches.
University of Liverpool researchers said future archaeologists may now well refer to our modern times as the Plastic Age.
The discoveries were made by a team led by Harold Mytum, and their findings published in the academic journal Antiquity.
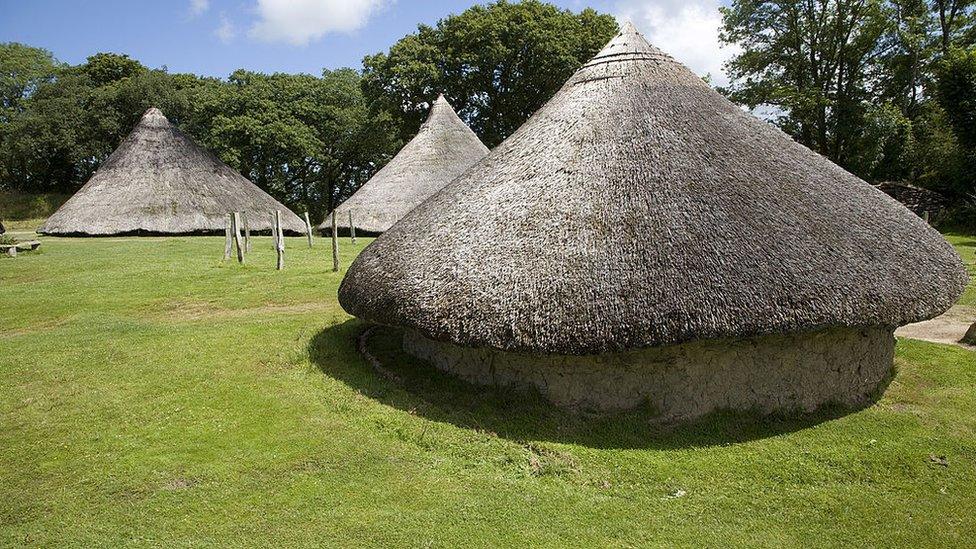

The roundhouses at Castell Henllys were reconstructed from excavations made at the Iron Age site between Newport and Cardigan
The researchers had originally set out to examine the reconstructed Iron Age village at Castell Henllys, which had been used as an educational resource for the last 30 years.
The village's thatched Celtic roundhouses were being demolished and a dig in and around the old buildings would give archaeologists an insight into how original roundhouses may have also decayed.
"We had not anticipated the large amounts of rubbish - mainly plastic - that was deposited, even though the houses did not look untidy," said Prof Mytum.
"Plastic spoons, straws, snack bar wrappers and cling film, and even labels from apples, were all very common finds."
What was found?
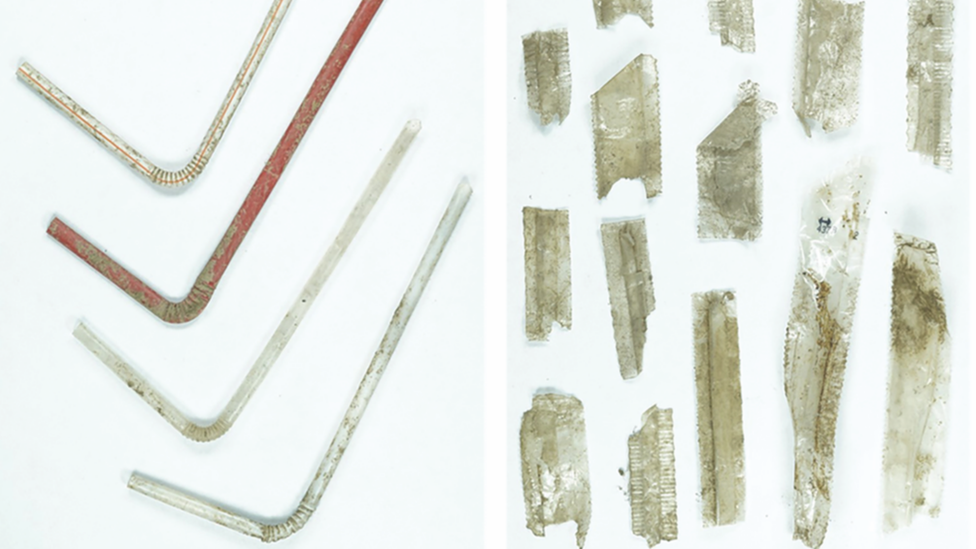
Plastic food wrap was the most common find
Plastic forks and spatulas
Salami snack wrappers
Cheese snack wrappers
Ketchup plastic sachets
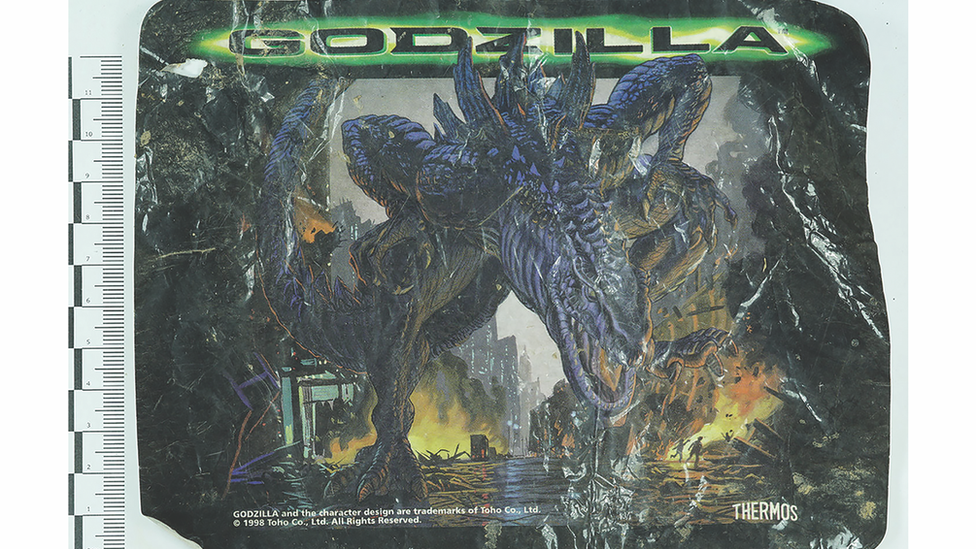


A complete noodle pot foil lid
Over 200 plastic drinking straw and wrapper fragments
Chocolate bar and sweet wrappers
Drink bottle labels
Plastic bottle caps
Elastic hair bands
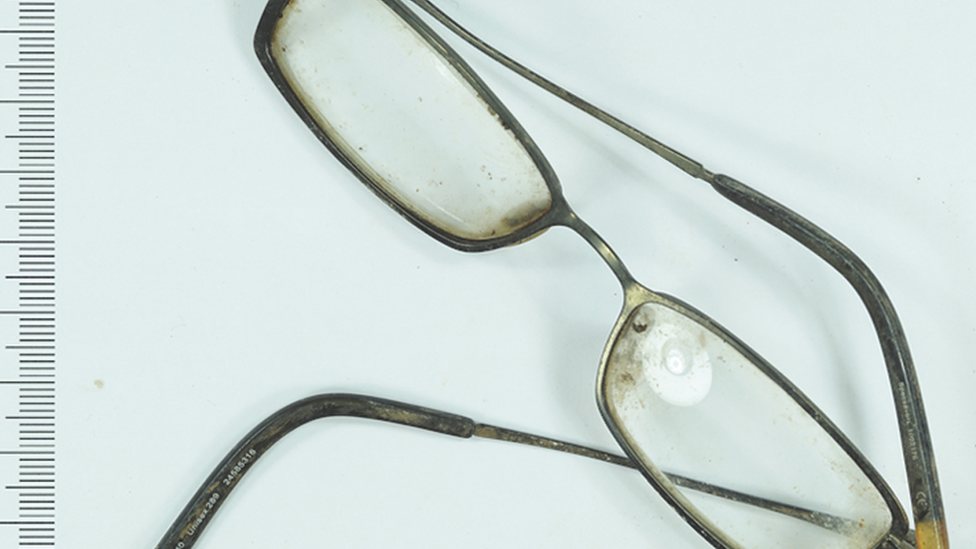
A pair of child's spectacles
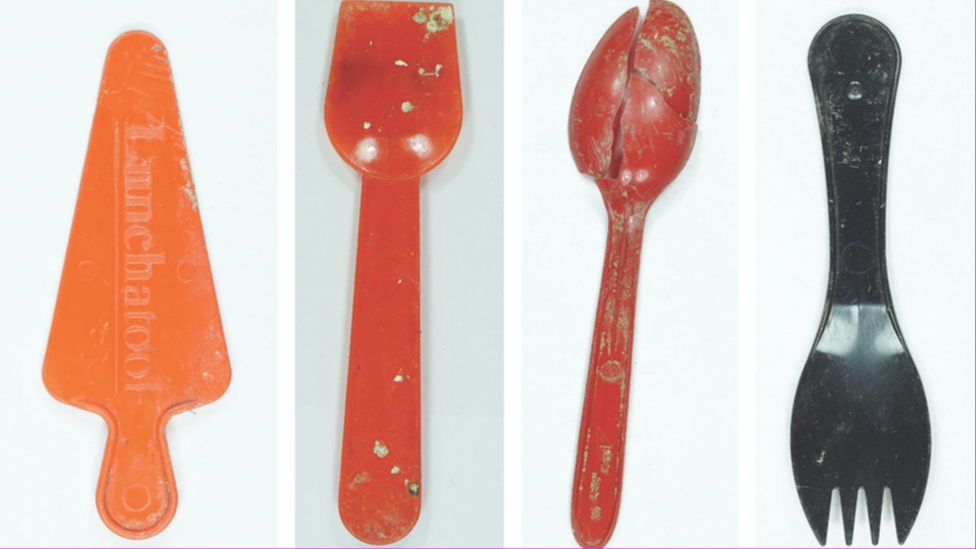

Prof Mytum said enough plastic had been "trodden into the earth" to dominate the archaeological records of these reconstructed houses, which were built from records of houses that used to stand on the hillfort site.
The researchers concluded it provided some "incontrovertible evidence to support the use of the term the 'Plastic Age' for the late twentieth and early twenty-first century".
"Schools and families need to think about how they can make pack lunches that are more environmentally friendly," said the professor.
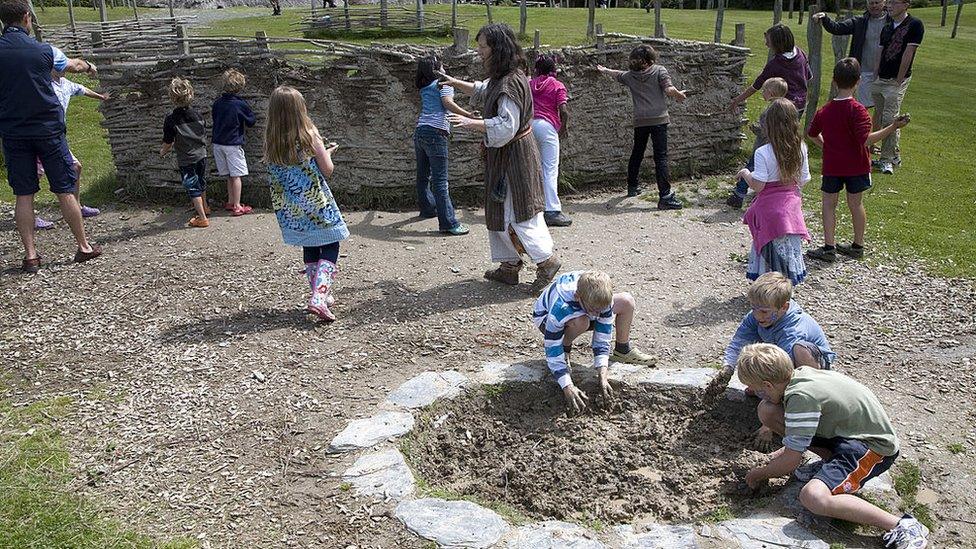

The researchers hope their finds will help parents and schools rethink packed lunches for educational trips to locations such as Castell Henllys
The team said the discoveries would help uncover how and where plastic waste accumulates, to reduce the amount incorporated in the ground.
They are also working with Pembrokeshire Coast National Park to help educate the public and raise awareness over environmental concerns that might be raised by something so simple as a school packed lunch.
But Prof Mytum also said he hoped the Plastic Age did not last millennia, like the Iron Age.
"With many initiatives now pushing to switch from disposable plastic and plasticised items, this may be a narrow, but archaeologically distinctive chronological horizon," he added.
- Published3 January 2021

- Published4 September 2020

- Published31 August 2020

- Published23 July 2020

- Published1 March 2020
