Brics: What is the group and which countries have joined?
- Published

Russian President Vladimir Putin will host the 2024 Brics summit
Saudi Arabia has joined Brics, the alliance of major developing countries, along with four other nations.
The Saudi membership was due to start on 1 January, but there was a delay before it was confirmed.
The Brics group wants emerging economies to have more influence in international politics.
What does Brics mean and who are the new members?
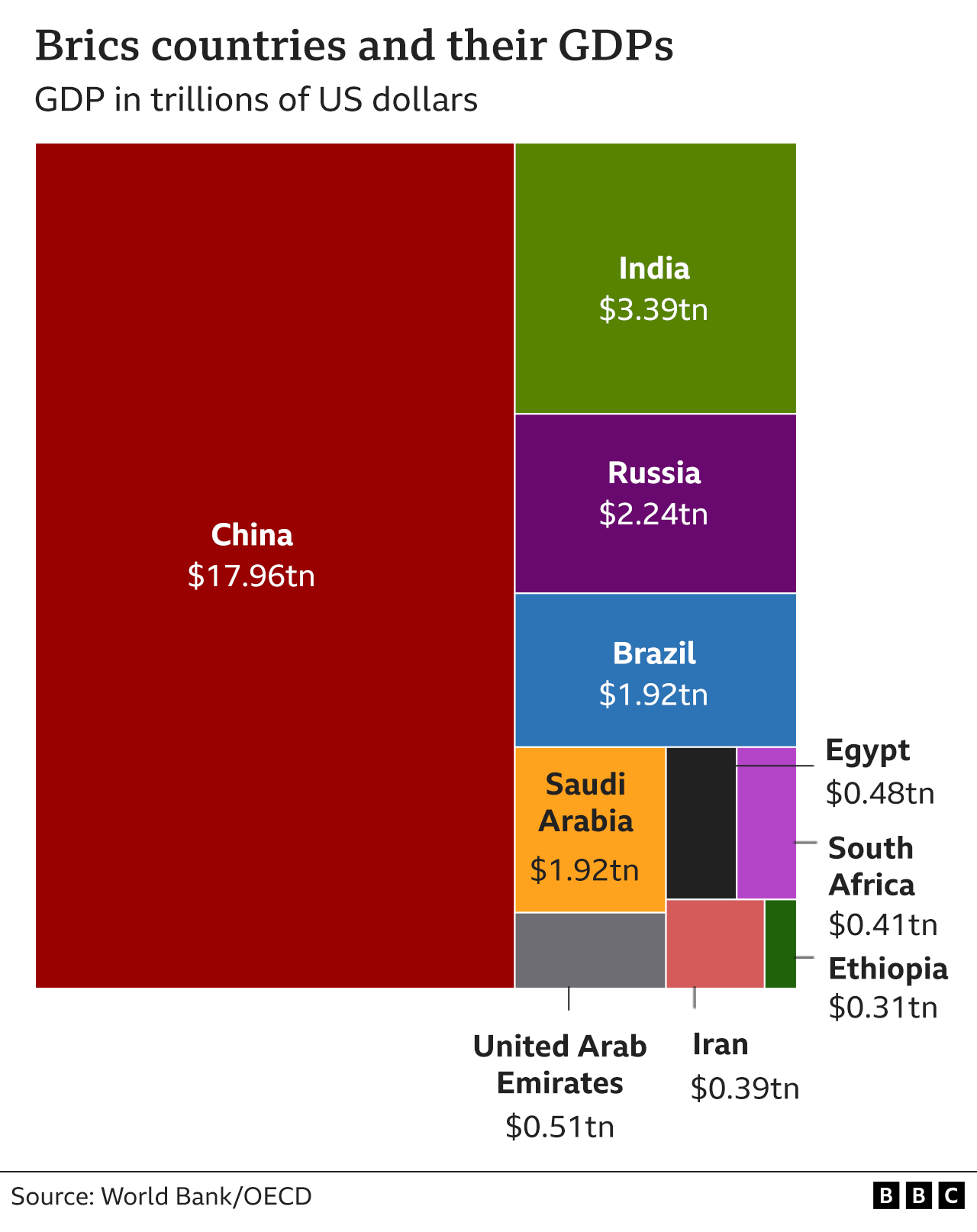
In 2006, Brazil, Russia, India and China created the "Bric" group. South Africa joined in 2010, making it "Brics".
The group was designed to bring together the world's most important developing countries, to challenge the political and economic power of the wealthier nations of North America and Western Europe.
Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) were invited to become members with effect from 1 January 2024.
A Saudi Arabian government minister said in mid January it had not joined, external.
But South Africa's government since confirmed its membership status, external.

Saudi Arabia's King Salman bin Abdulaziz (L) pictured with Chinese President Xi Jinping (R) in Beijing
Argentina was also invited to join, but President Javier Milei pulled out in December 2023, shortly after taking office.
The group sets priorities and makes decisions at an annual summit. Members take it in turns to serve as president for a year.
The name for the expanded group has not yet been announced, but may be "Brics +".
Why does Brics matter?
Brics countries include major world powers, such as China and Russia, and countries which are influential on their continent, such as South Africa and Brazil.
The expanded group has a combined population of about 3.5 billion, external, or 45% of the world's inhabitants.
Combined, members' economies are worth more than $28.5tn, external - about 28% of the global economy.
With Iran, Saudi Arabia and UAE as members, Brics countries produce about 44% of the world's crude oil, external.
However, the group argues that Western nations dominate important global bodies such as the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, which lend money to governments.
It wants to see a "greater voice and representation", external for emerging economies.
In 2014, the Brics nations set up the New Development Bank to lend money to boost infrastructure.
By the end of 2022, it had provided nearly $32bn to emerging nations, external for new roads, bridges, railways and water supply projects.
This is China's main aim for Brics, according to Prof Padraig Carmody from Trinity College Dublin.
"Through Brics, China is trying to grow its power and influence - especially in Africa," he says. "It wants to be be the leading voice for the global south."
The other major world power in the group has a different purpose:
"Russia sees [Brics] as part of its fight against the West, helping it to overcome the sanctions imposed after the invasion of Ukraine," says Creon Butler of the London-based think tank Chatham House.
Iran's membership could increase the anti-Western nature of Brics, he adds.
Will a Brics currency replace the dollar?
Nations often use the US dollar to trade between themselves.
Leading politicians in Brazil and Russia have suggested creating a Brics currency, to reduce the dollar's dominance. However, this was not discussed at the group's 2023 summit.
It would be impractical for Brics nations to create a common currency because their economies are so different, says Professor Carmody.
However, he says it is possible that "they may consider in the future creating some new currency to be used for international trade payments, or a cryptocurrency for international trade".
Is Brics a rival to the G20?
The G20 group was set up in 1999 for developed and developing nations to discuss global issues.
However, the Brics group also contains many of the countries which are in the G20.
In future, they may work in tandem, says Dr Irene Mia from the International Institute for Strategic Studies think tank.
"Together, they might push for more money for developing nations to tackle climate change," she says.
How will Russia use its 2024 Brics presidency?
Russia will host the 20024 Brics summit in Kazan in October.
President Vladimir Putin has said he wants to, external:
increase the role of Brics in the international financial system
develop cooperation between banks, and expand the use of Brics currencies
promote collaboration between tax and customs authorities
"With Brics, Russia will want to show the West that it still has friends and allies in the rest of the world, despite its invasion of Ukraine," says Dr Mia.