The Gambia country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 12 April 2023
The Gambia is one of Africa's smallest countries and, unlike many of its west African neighbours, has enjoyed long spells of stability since independence.
President Yahya Jammeh ruled the country with an iron fist after seizing power in a bloodless coup in 1994. His 22-year rule came to an end in 2016, when he was defeated in a shock election result by Adama Barrow. Mr Jammeh only left office after mediation by neighbouring countries and the threat of armed intervention.
Stability has not translated into prosperity. Despite the presence of the Gambia river, which runs through the middle of the country, only one-sixth of the land is arable, and poor soil quality has led to the predominance of one crop - peanuts.
Tourism is an important source of foreign exchange, as is the money sent home by Gambians living abroad. Most visitors are drawn to the resorts that occupy a stretch of the Atlantic coast.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
REPUBLIC OF THE GAMBIA: FACTS
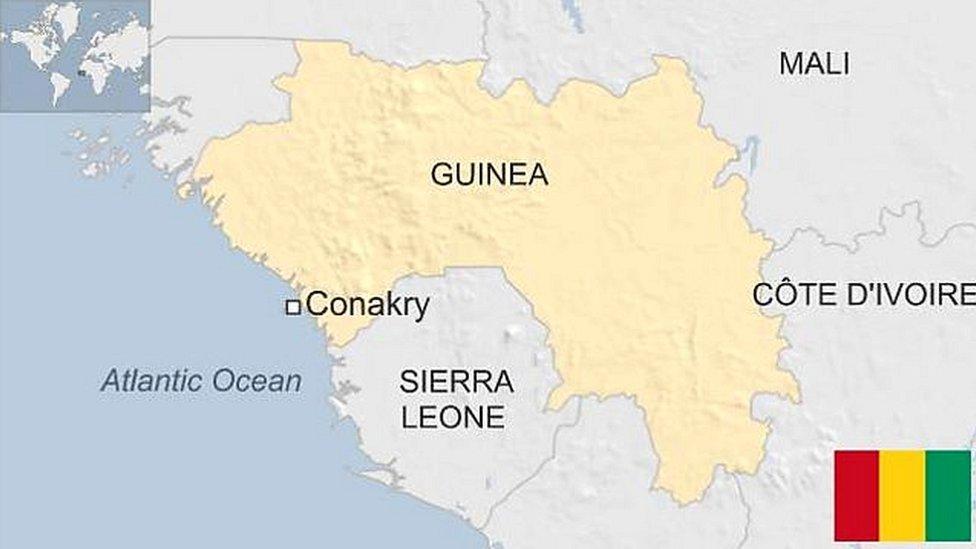
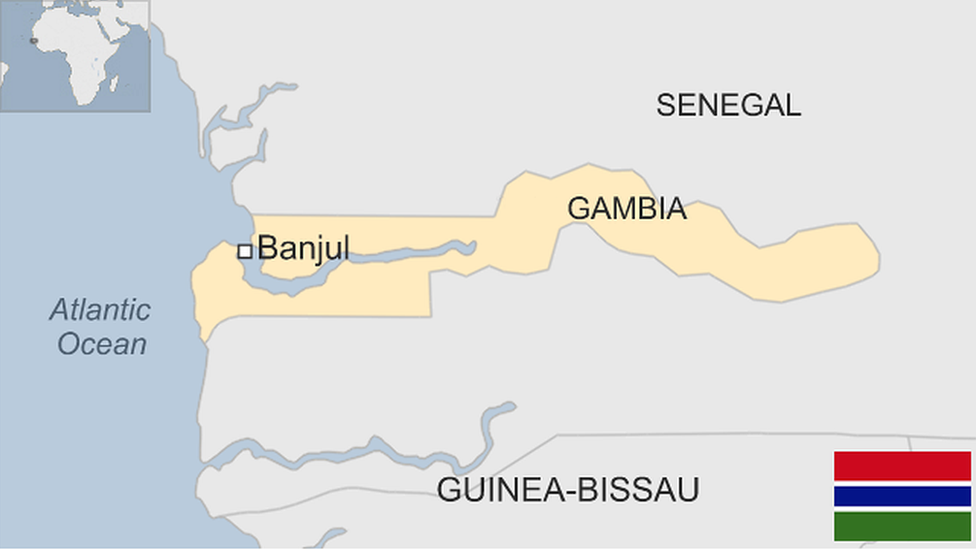
Capital: Banjul
Area: 11,300 sq km
Population: 2.4 million
Language: English
Life expectancy: 61 years (men) 64 years (women)
LEADER
President: Adama Barrow
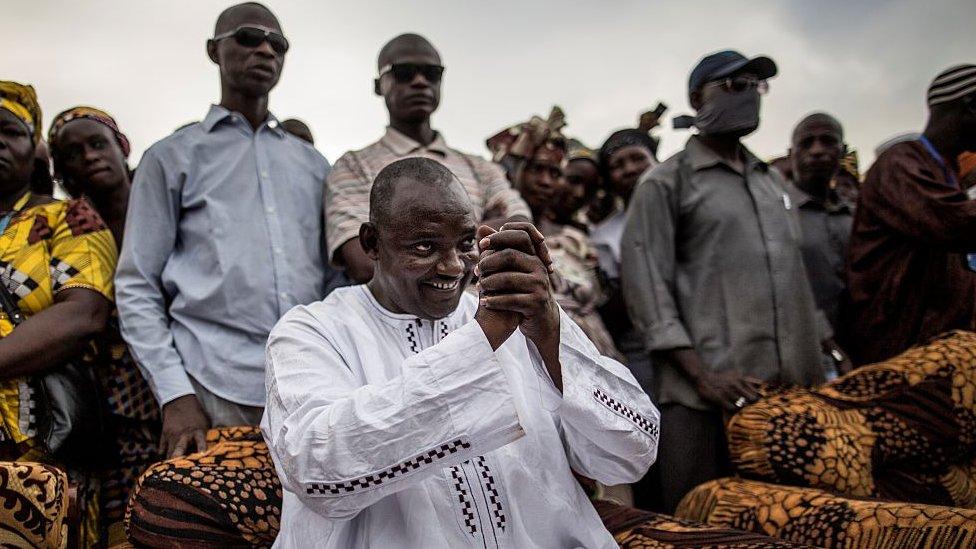

Adama Barrow defeated long-serving President Yahya Jammeh in a shock election victory in December 2016. A property developer, Barrow ended Yahya Jammeh's 22-year authoritarian rule by winning more than 45% of the vote.
Jammeh initially accepted the result, but later rejected the vote. Barrow temporarily fled to Senegal and was inaugurated at the Gambian embassy in Senegal in January 2017 before Jammeh was forced to leave the Gambia.
A member of the United Democratic Party, during his election campaign Mr Barrow pledged to revive the country's economy.
He was re-elected in the December 2021 presidential elections.
MEDIA
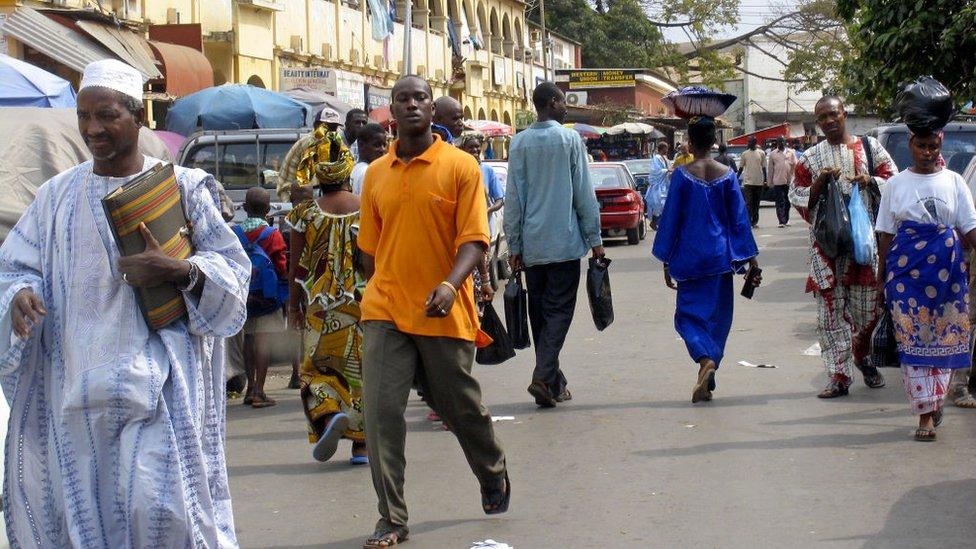

The country's media scene has changed since the end of President Jammeh's rule
Gambia's media scene has seen considerable progress in terms of press freedom since the end of Yahya Jammeh's authoritarian rule.
The crime of defamation was declared unconstitutional in 2018, attacks on reporters have dropped and new media outlets have been launched, says Reporters Without Borders (RSF).
The state-owned broadcaster has lost its monopoly and many radio and television networks have been set up.
TIMELINE
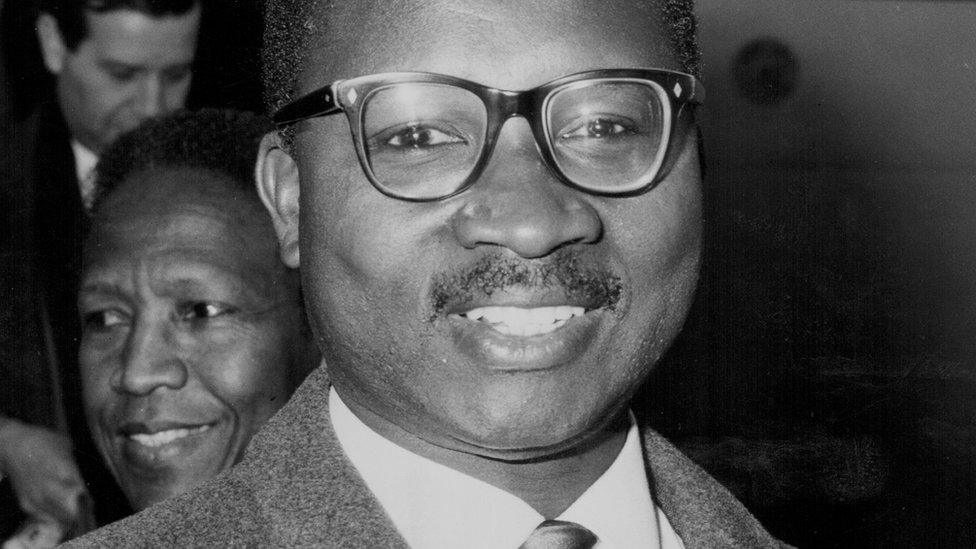

Sir Dauda Jawara was The Gambia's leader from independence in 1965 until he was ousted in 1994
Some key dates in The Gambia's history:
9th/10th Centuries - First written record by Arab traders; region is dominated by the trans-Saharan trade route.
13th Century - Part of the Mali Empire, which at its peak is the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region.
15th-16th Century - Part of the Songhai Empire, which subsequently dominates the western Sahel and east-west trade routes across Africa following the fall of the Mali Empire.
1455 - Portuguese explorers reach the mouth of the Gambia river, some Portuguese settle along the river.
1591 - Moroccan army invades and defeats the Songhai army at the Battle of Tondibi, leading to the collapse of the Songhai Empire, but Morocco is unable to exploit its battlefield victory.
1612 - French attempt to settle the area is defeated due to disease among the colonists.
17th Century - Various expeditions and attempts at settlement of exploitation of resources by the English, Dutch and Courlanders.
1661 - Following the restoration of Charles II, English traders re-establish a settlement at the mouth of the Gambia river.
1766 - The British crown takes control of the settlements and forts which become part of the Senegambia colony.
1783 - The region is handed back to British commercial control.
1807 - Britain abolishes slavery and subsequently makes efforts to suppress slave traders operating in the river Gambia.
1816-50s - Following the end of the Napoleonic wars, the British recolonise the area.
1850s - The French colony expands and virtually engulfs The Gambia. London and Paris hold various talks about ceding the Gambia for another part of West Africa but this arouses opposition in the UK.
1889 - Present boundaries of The Gambia set by agreement between Britain and France.
1895 - Becomes a British protectorate.
1965 - The Gambia becomes independent, with Queen Elizabeth II as head of state.
1970 - Country becomes a republic within the Commonwealth.
1982 - The Gambia and Senegal form a loose confederation called Senegambia following a 1981 coup attempt in which several hundred are killed. The coup is defeated with Senegalese military help. The confederation collapses in 1989.
1994 - Lieutenant Yahya Jammeh takes over in a coup. He is elected president two years later in a vote that three major political parties were barred from taking part in. He goes on to win three more elections and defeat several coup attempts.
2013 - Jammeh announces Gambia's withdrawal from the Commonwealth, describing it as a "neo-colonial institution". Critics say the move was prompted by wide-spread international condemnation over the government's human rights violations.
2015 - Jammeh declares the country an Islamic republic to break from the "colonial legacy".
2016 - Jammeh's 22-year-rule ends in a shock election defeat by Adama Barrow. He goes into exile in Equatorial Guinea following military pressure from neighbouring states to accept the result.
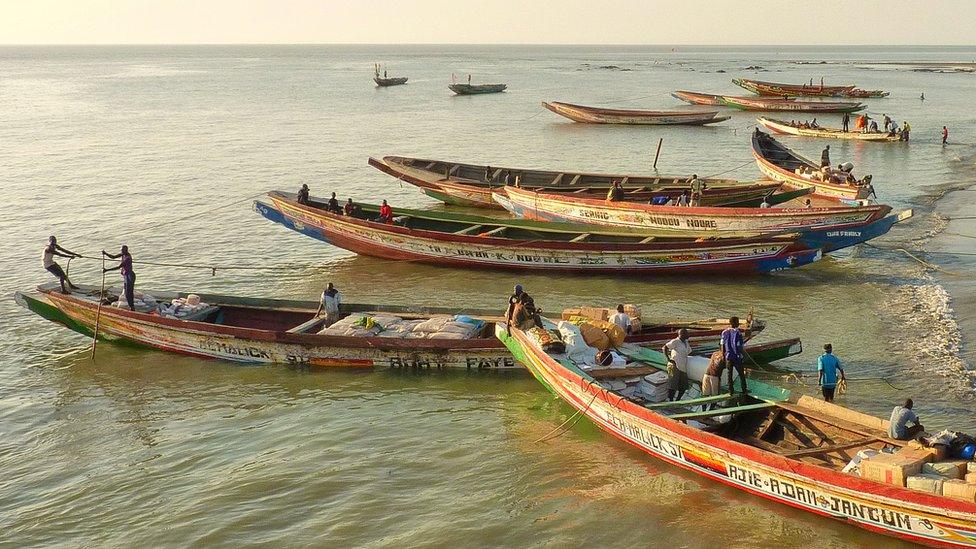

Tourism is a now an important part of The Gambia's economy
Related topics
- Published11 September 2023
- Published9 July 2024
- Published9 July 2024
- Published26 February 2024
- Published14 April 2023