Morocco country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 28 October 2024
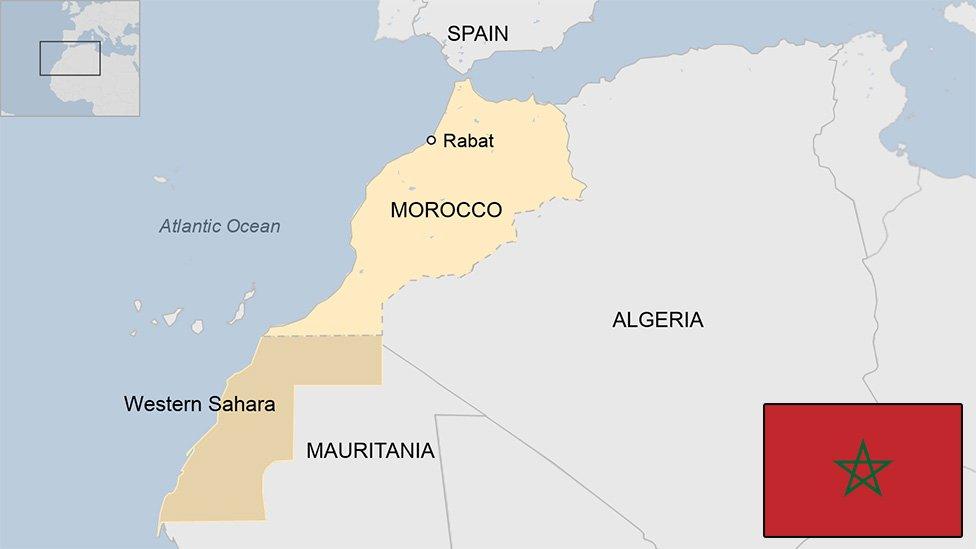
The Kingdom of Morocco is the most westerly of the North African countries known as the Maghreb - "the West". It has Atlantic and Mediterranean coastlines, a rugged mountain interior and a history of independence not shared by its neighbours.
Its culture is a blend of Arab, Berber, European and African influences.
Morocco was a French protectorate between 1912 and 1956. Since independence, Morocco has remained relatively stable and wields significant influence in both Africa and the Arab world.
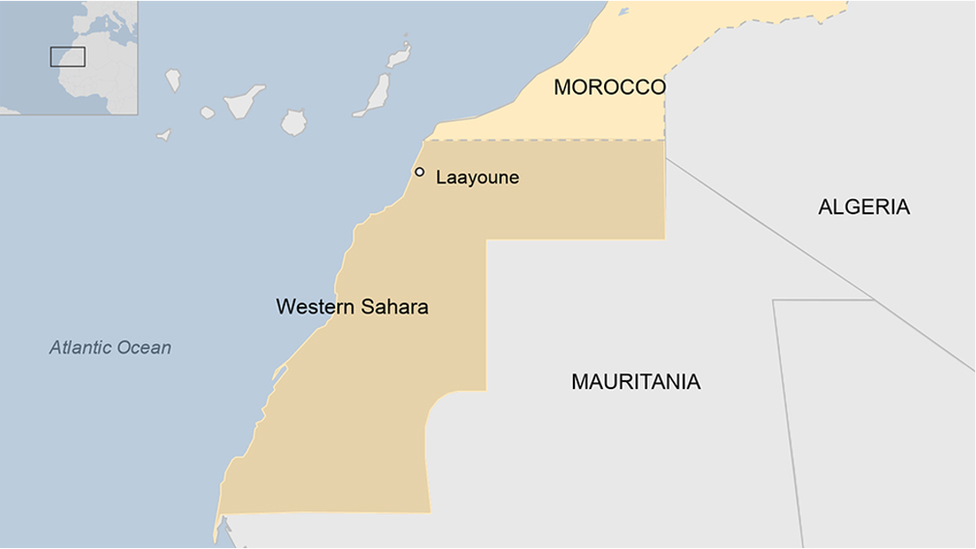
In 1975, Morocco annexed the former Spanish colony of Western Sahara. Since then it has been the subject of a long-running territorial dispute between Morocco and its indigenous Sahrawi people, led by the Polisario Front.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
KINGDOM OF MOROCCO: FACTS
Capital: Rabat
Area: 446,300 sq km
Population: 38.1 million
Languages: Arabic, Tamazight
Life expectancy: 72 years (men) 76 years (women)
LEADERS
King: Mohammed VI
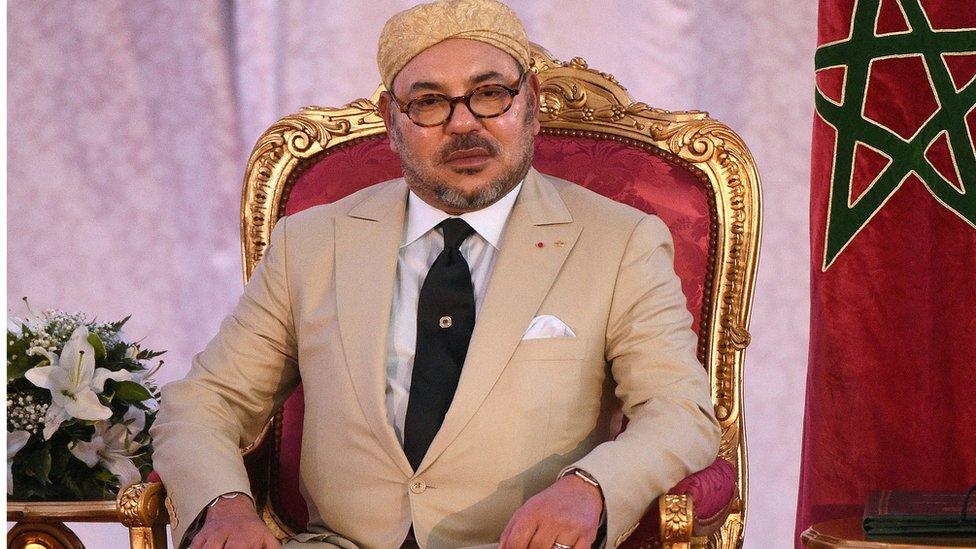

Mohammed VI became king in 1999. He initiated political and economic changes and an investigation into human rights abuses during his father's rule.
A key reform was the Mudawana, a law which grants more rights to women. The king has said it is in line with Koranic principles, but religious conservatives have opposed it.
Following pressure for reform inspired by the "Arab Spring" of 2010 onwards, a new constitution was introduced, expanding the powers of parliament and the prime minister, but leaving the king with broad authority over all branches of government.
In 2020, Morocco and Israel signed a normalisation agreement, but since Hamas's 2023 attack on Israel - the worst in Israel's history - and Israel's invasion of the Palestinian territory of Gaza, there have been anti-normalisation rallies across Morocco in solidarity with Palestinians.
Prime minister: Aziz Akhannouch
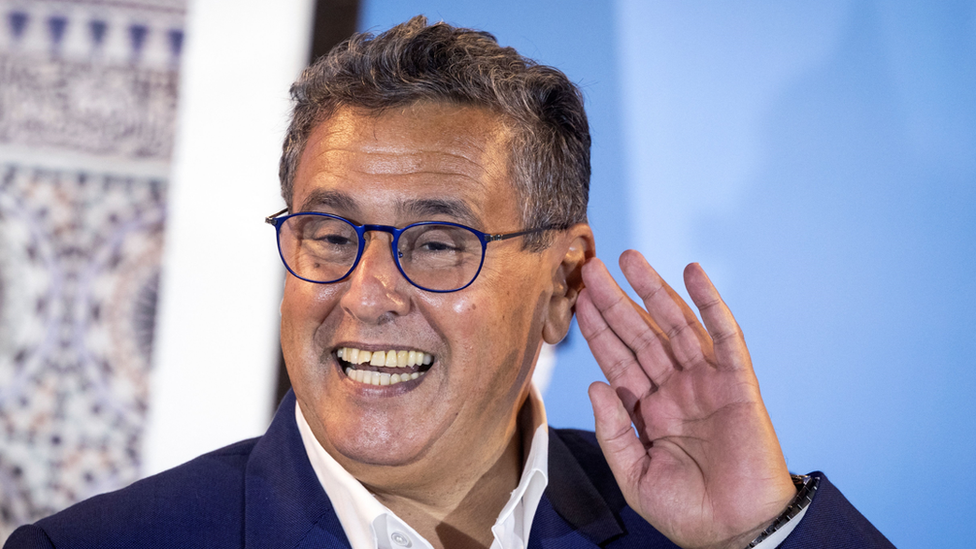

The liberal National Rally of Independents party led by oil and gas billionaire Aziz Akhannouch narrowly won the September 2021 election, ousting the conservative Islamist PDJ party that had led governments for a decade.
Moroccan political analysts said a flagging economy undermined support for the PDJ. Mr Akhannouch held office in PDJ-led coalitions as agriculture minister from 2007 until he took over as prime minister.
MEDIA

The broadcast media are either dominated by the state or reflect the official line.
Paris-based Reporters Without Borders notes that "religion, the king and the monarchy in general, the country and territorial integrity cannot be questioned."
The government owns, or has a stake in, RTM and 2M, Morocco's main TV networks. Satellite dishes are widely used, giving access to French and pan-Arab stations.
Read full media profile
TIMELINE

A market in Marrakech
Some key dates in Morocco's history:
7th-8th Centuries - Arab invasion; Idris founds the first major Muslim dynasty.
11th-12th Centuries - Under first the Almoravid and then Almohad dynasties, Morocco dominates the Maghreb and much of Spain.
1549-1649 - Saadi dynasty rule Morocco and parts of west Africa.
1666 onwards - Alawi dynasty rule as Sultans of Morocco
1884 - Spain creates a protectorate in coastal areas of Morocco.
1904 - France and Spain carve out zones of influence.
1912 - Morocco becomes a French protectorate under the Treaty of Fez.
1921-26 - Tribal rebellion in Rif mountains is suppressed by French and Spanish troops.
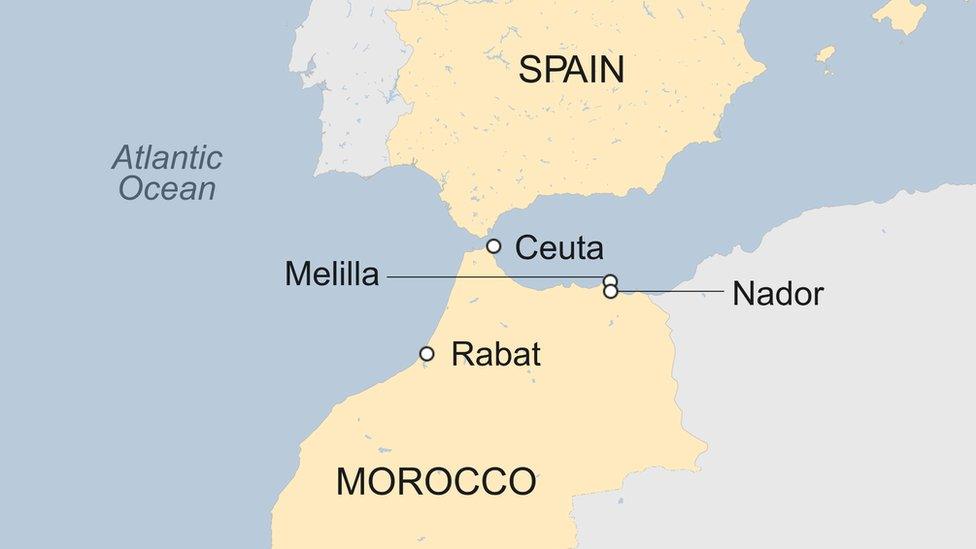
1956 - End of French protectorate after unrest and strong nationalist sentiment. Spain keeps its two coastal enclaves of Ceuta and Melilla.
1961 - Death of King Mohammed; King Hassan II comes to power.
1971 - Failed attempt to depose king and establish republic.
1973 - Polisario movement formed, aims to establish an independent state in Spanish Sahara, a territory south of Morocco controlled by Spain.
1975 - The Green March: King Hassan orders 350,000 civilian volunteers to cross into Spanish Sahara. Spain agrees to leave and transfer it to joint Moroccan-Mauritanian control. Algeria objects and threatens military intervention. Moroccan forces occupy the territory.
1975-91 - The Polisario Front fights a 16-year-long guerrilla war against Moroccan forces. This ends with a UN-brokered cease-fire which sees the Polisario controlling about 20% of the territory, the rest being controlled by Morocco.
1991 - UN-monitored ceasefire begins in Western Sahara, but the region's status remains undecided.
2011 - Thousands of people rally in Rabat and other cities calling for political reform and a new constitution curbing the powers of the king.
2020 - US announces it will recognize full Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara in exchange for Morocco establishing relations with Israel.
2021 - Morocco proposes autonomy for Western Sahara under the sovereignty of the King of Morocco.
2022 - Spain accepts Morocco's proposal as "the most serious, realistic and credible basis" for ending the dispute over Western Sahara. Saharawi political parties reject the proposal.
2023 - Israel recognizes Morocco's claims over Western Sahara.
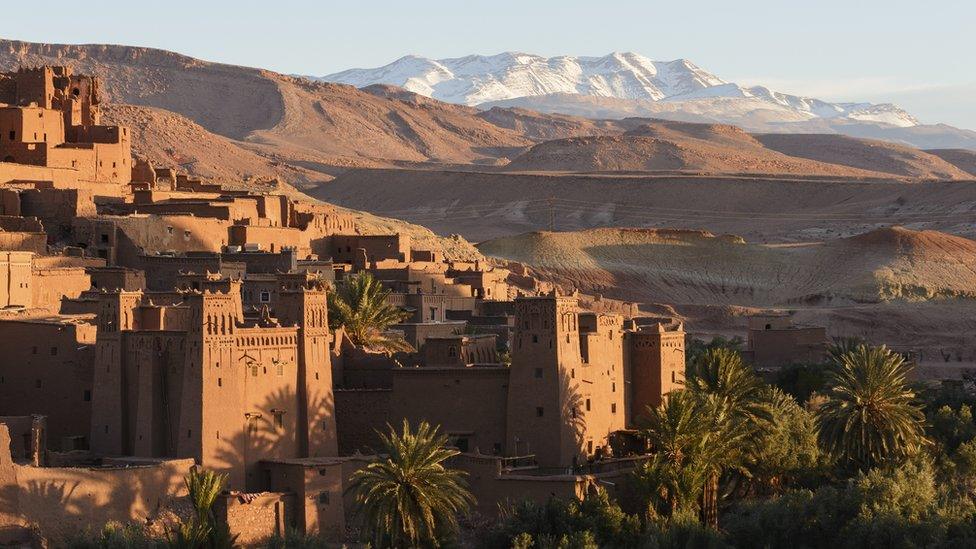

The Aït Benhaddou is a ksar, or fortified village, along the former caravan route between the Sahara and Marrakesh
- Published22 March 2024
- Published21 August 2023

- Published19 May 2023
- Published18 May 2023
- Published9 September 2024
- Published9 July 2024
- Published28 October 2024