Seven things banned under Ethiopia's state of emergency
- Published

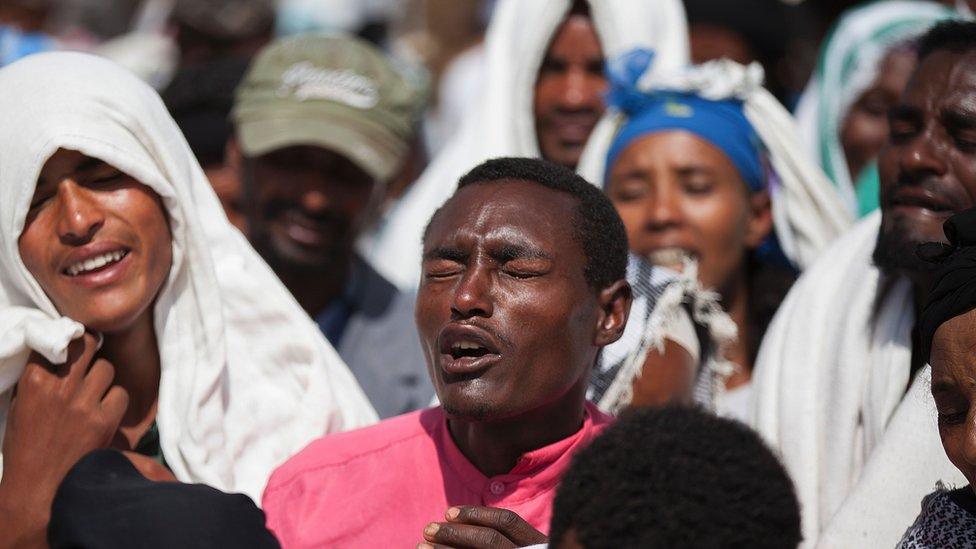
The most recent protests were sparked by the deaths of at least 55 people at an Oromo religious festival
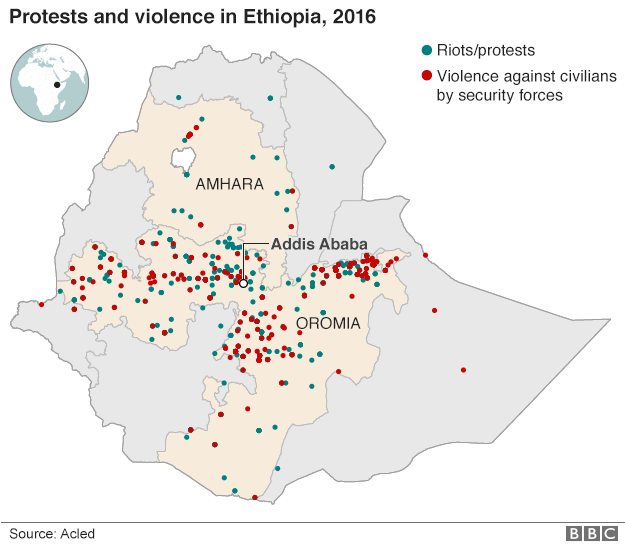
Ethiopia's government has declared a six-month state of emergency in the face of an unprecedented wave of violent protests.
Activists in the country's Oromia region have been holding demonstrations since last November, and protesters from the Amhara region have also joined in.
The deaths of at least 55 people at an Oromo religious festival on 2 October triggered fresh unrest, including the targeting of some foreign-owned businesses.
Rights groups say that at least 500 people have died during the protests overall and last week Prime Minister Hailemariam Desalegn said that could be an accurate estimate.
The emergency was announced earlier this month but the government has now made clear what this means in practical terms.
Here are some of the things that are restricted:

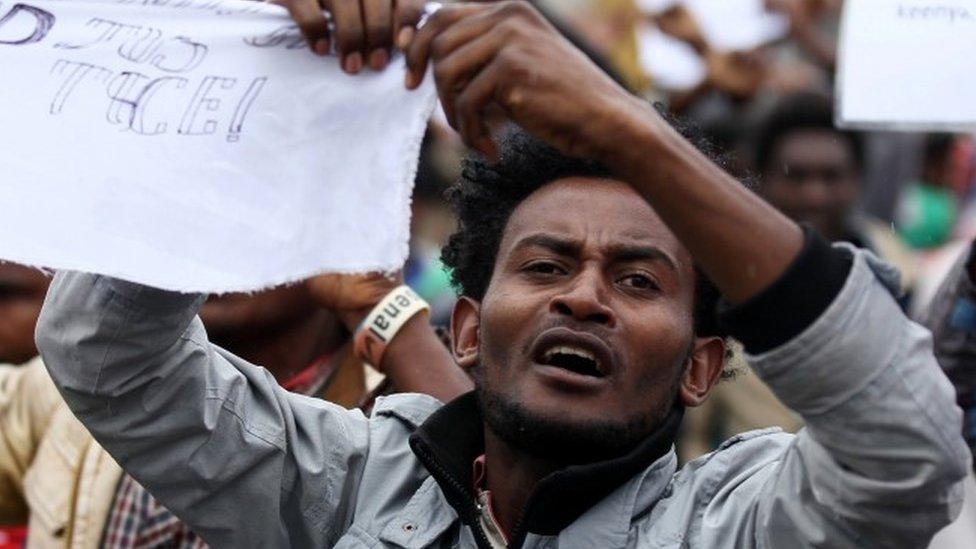
1. Social media

Activists have used their mobile phones to spread news about their protests
You cannot use social media, such as Facebook and Twitter, to contact what are called "outside forces". In fact, any attempt to communicate with "terrorist organisations and anti-peace groups designated as terrorist" is banned.
Protesters have been posting messages and mobile phone footage to social media and websites run by Ethiopian dissidents living abroad.
The government has accused Eritrea and Egypt of fomenting the protests.

2. Broadcast Media
You cannot watch the TV channels Esat and OMN, which are both based outside the country. The government has described them as "belonging to terrorist organisations".
These broadcasters have become some of the major sources for people wanting to know more about the protests.

3. Protests

Protests have been frequent in Ethiopia in recent months
You cannot organise a demonstration at your school or university, neither can you be involved in a political campaign that is "likely to cause disturbances, violence, hatred and distrust among the people".
University campuses were among the first places to be hit by the wave of anti-government protests.

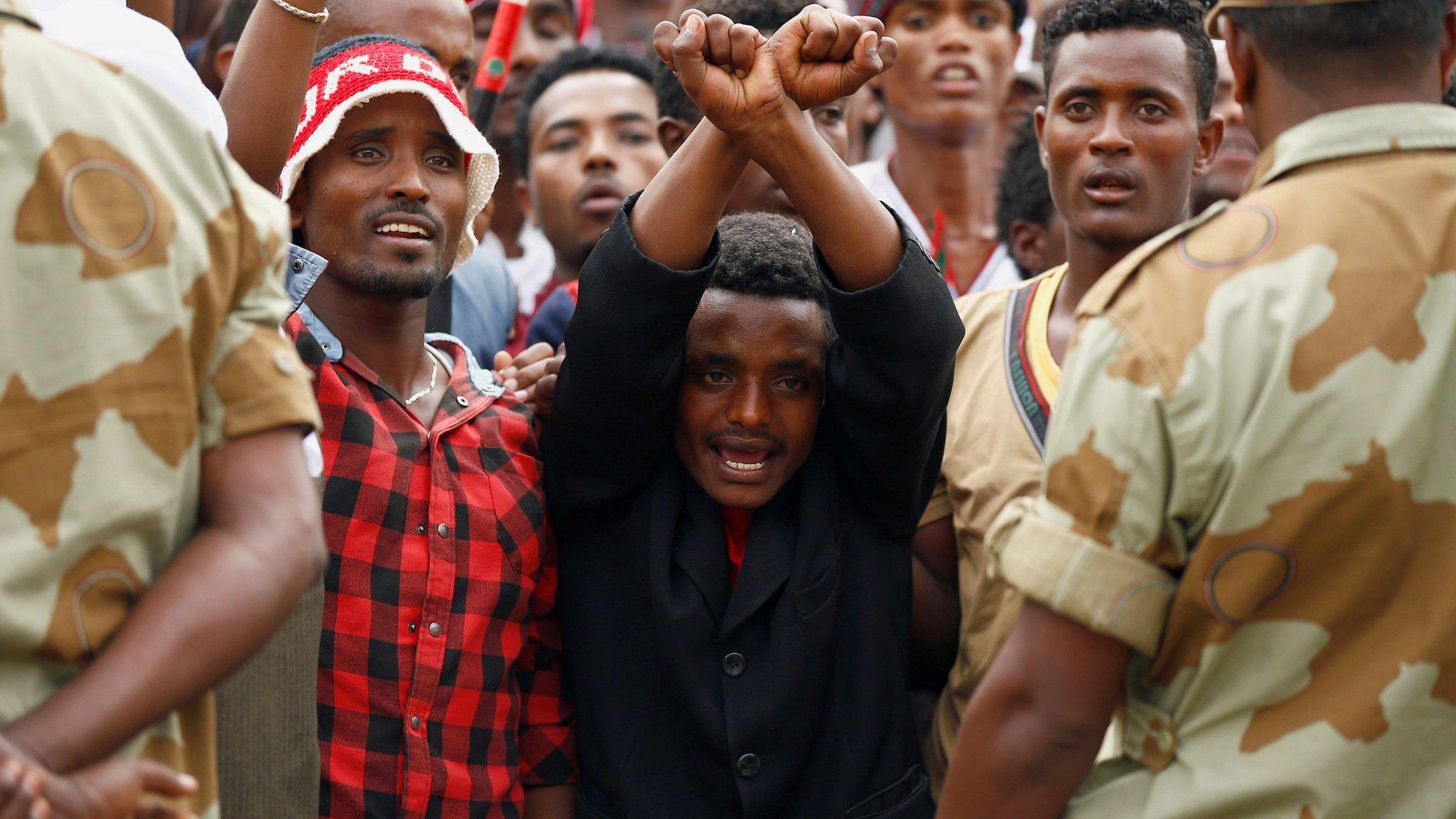
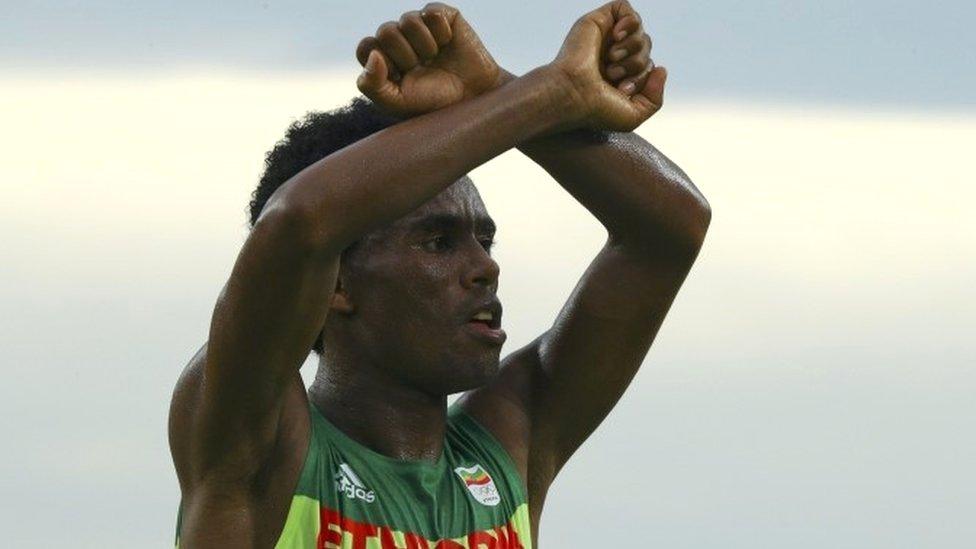
4. Gestures

Ethiopian Olympic marathon runner Feyisa Lilesa made the crossed arms Oromo protest symbol well known around the world
You cannot make a political gesture, such as crossing your arms above your head, or communicate a political message to the public "without permission".
The crossing-arms gesture has been seen widely at the protests in Oromia, and even made it to the Olympics when marathon runner Feyisa Lilesa used it as he crossed the line in second place in Rio in August.

5. Curfew

Factories have been targeted in arson attacks
You cannot visit a factory, farm or governmental institution between 6pm and 6am the next day. If you violate the curfew than "law enforcement bodies have been authorised to take the necessary action".
Government buildings and private businesses, some of them foreign owned, have been deliberately targeted by some of the protesters.

6. Diplomats

If you are a diplomat you are not allowed to travel more than 40km (25 miles) from the capital, Addis Ababa, without permission. The government says that this is for your own safety.
In general, the diplomatic reaction to the protests and the state of emergency has been muted. The US has said, external that it is "troubled" by any restrictions on the freedom of expression in the state of emergency, but, like other western powers has called for peaceful dialogue to solve the country's problems.
Ethiopia is a close ally of the US against Islamist militancy in neighbouring Somalia.

7. Guns
If you have a gun, you cannot take it within 25km of the country's main roads out of Addis Ababa, and within 50km of the country's borders, even if you have a permit to carry it.

More about the protests in Ethiopia
- Published7 October 2016

- Published22 August 2016

- Published26 August 2016

- Published9 March 2016

- Published18 January 2016
