Coronavirus: Ten African innovations to help tackle Covid-19
- Published
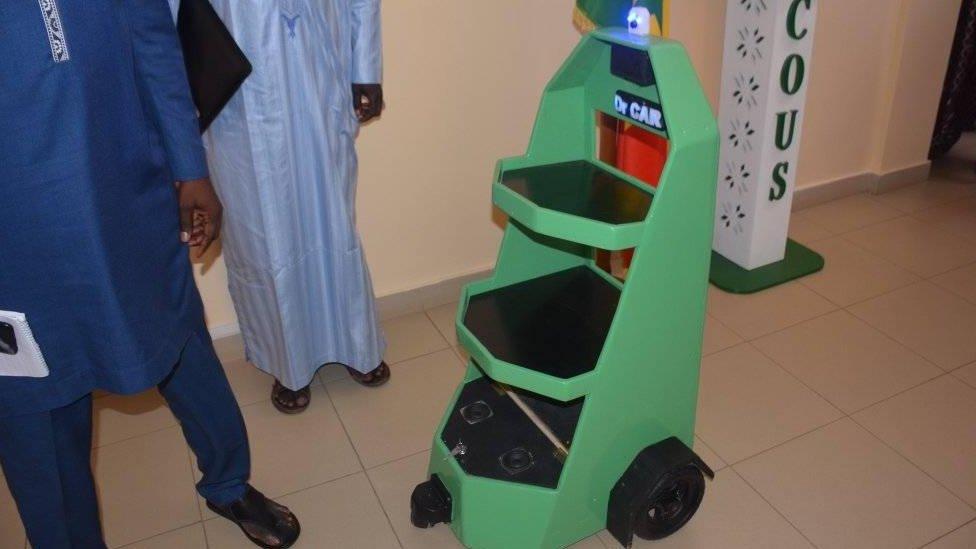

The Doctor Car robot
As Africa passes more than a million confirmed Covid-19 cases, innovators on the continent have responded to the challenges of the pandemic with a wide range of creative inventions. Here are 10 we've picked out.
1. 'Doctor Car' robot
Students from the Dakar Polytechnic School in Senegal have built a multifunctional robot designed to lower the risk of Covid-19 contamination from patients to caregivers.
The device is equipped with cameras and is remotely controlled via an app. The designers say it can move around the rooms of quarantined patients to take their temperatures and deliver drugs and food.
2. Automatic hand-washing machine
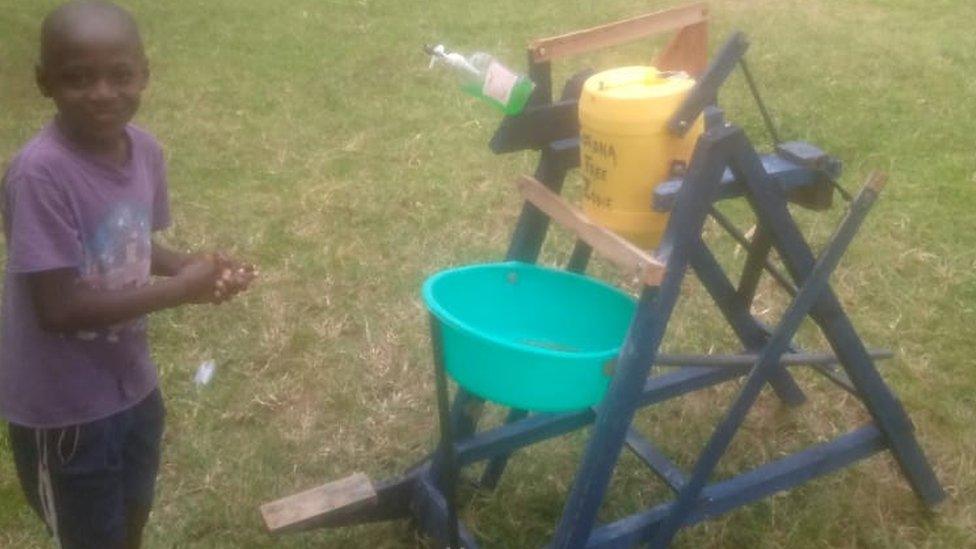

Stephen received a presidential award for his invention
Nine-year-old Kenyan schoolboy Stephen Wamukota invented a wooden hand-washing machine to help curb the spread of coronavirus.
The machine allows users to tip a bucket of water to wash their hands by using a foot pedal. This helps users avoid touching surfaces to reduce the risk of infection.
Stephen was given a presidential award in June.
3. The Respire-19 portable ventilator
Amid a shortage of ventilators on Covid-19 wards in Nigeria, 20-year-old engineering student Usman Dalhatu attempted to help meet the shortfall.
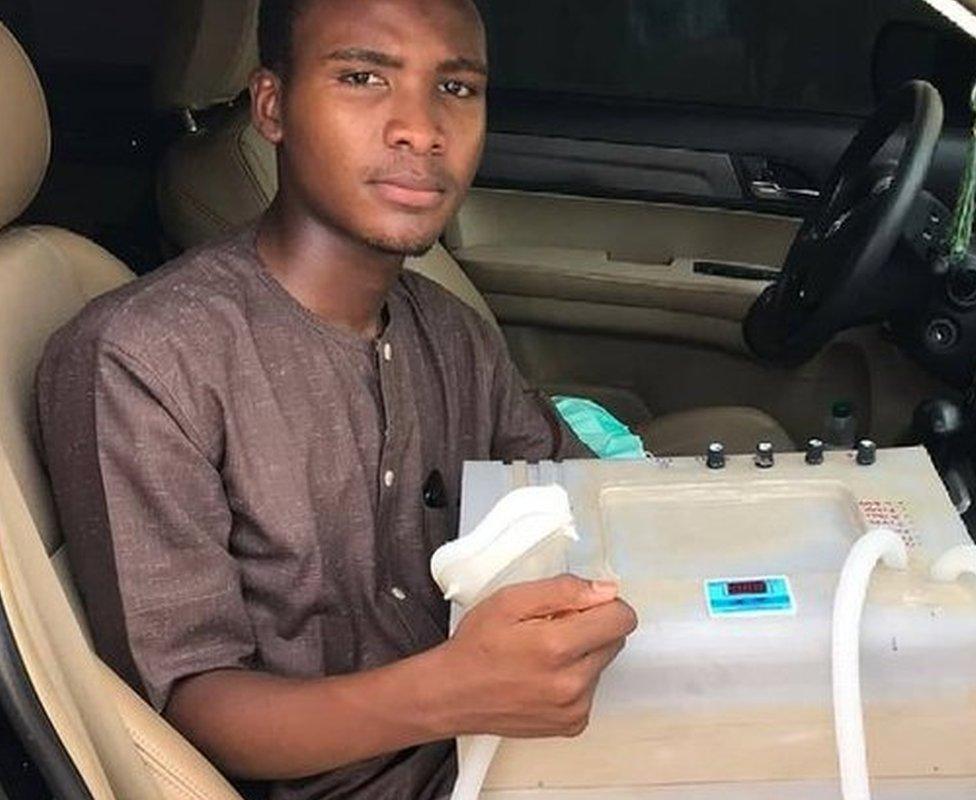

Usman Dalhatu says he's awaiting approval for his ventilator
Dalhatu built the portable automatic ventilator to help people with respiratory problems - often a symptom of a severe coronavirus infection. He now plans to build up to 20 ventilators.
4. 3D mask printing
Natalie Raphil is the founder of Artificial Intelligence company Robots Can Think South Africa.
She's using 3D printers to produce 100 masks a day, external for use in some of Johannesburg's major hospitals. South Africa accounts for around half of all reported coronavirus cases in Africa.
5. Solar-powered hand-washing sink
Amid a lockdown in Ghana aimed at curbing the spread of Covid-19, shoemaker Richard Kwarteng and his brother Jude Osei decided to design a solar-powered hand-washing basin, external.
When hands come into contact with a sensor on the device, soapy water is automatically released. An alarm goes off after 25 seconds of hand-washing - within the timescale recommended by the World Health Organization.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

6. Web-based X-ray lung scans
Engineers in Tunisia have created an online platform that scans lung X-rays, external to try to determine if a person could be suffering from coronavirus.
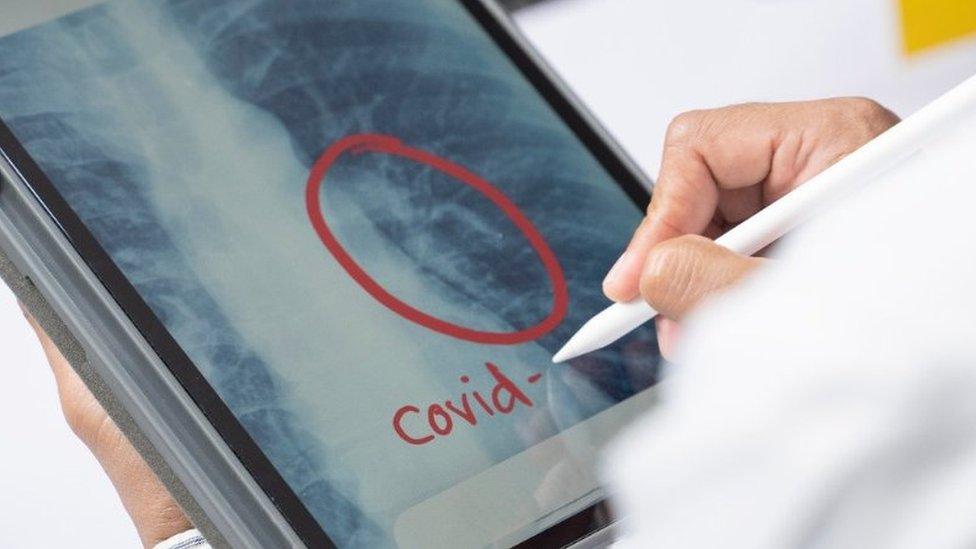
When an X-ray is uploaded onto the platform, it runs a test to detect signs of a possible coronavirus infection. Researchers at the National Institute of Applied Science and Technology in Tunis say the tool is 90% effective in indicating the probability of infection.
The platform is still in development, but thousands of lung X-rays have been fed into the system to enable it to recognise the impact of Covid-19 on lungs.
7. Police robots on lockdown patrol
Authorities in Tunisia deployed police robots on the streets of the capital Tunis in April to enforce lockdown measures.
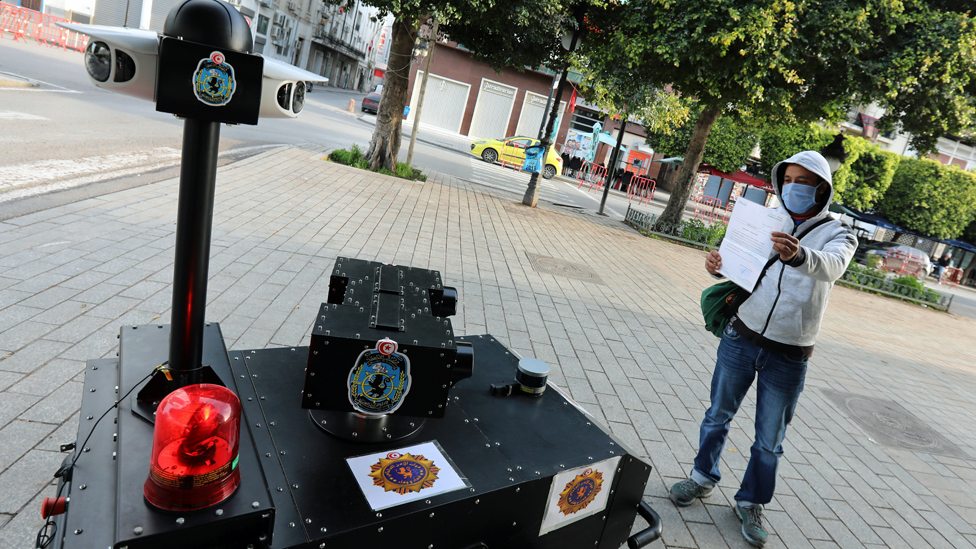

The surveillance robots, called PGuards, spied on people walking on the street and approached them to ask why they were out.
Offenders then had to show their ID and other documents to the cameras attached to the robots. The four-wheeled devices are equipped with thermal-imaging cameras and light detection and ranging technology.

More about coronavirus in Africa:
Professor Ndeye Coumba Touré Kane is advocating for a greater use of face masks in Senegal.

8. Wooden money sanitiser
Kenyan mobile money agent Danson Wanjohi has built a wooden device, external that sanitises cash notes that are passed through a slot in the machine.
Wanjohi constructed the mechanism using a motor, a rubber band and gears which enable notes to pass through the machine.
As the notes pass through the device, they are cleaned with a sanitising solution.
9. Rapid 65-minute Covid-19 testing kit
South African tech entrepreneurs Daniel Ndima and Dineo Lioma have created a Covid-19 testing kit, external which provides results in just 65 minutes.
Typically, it can take up to three days for Covid-19 tests to produce results.
The testing kit is known as qPCR, and features a technology used to measure DNA. The testing kit needs to undergo regulatory approval before it can be rolled out.
10. Socially distanced haircuts
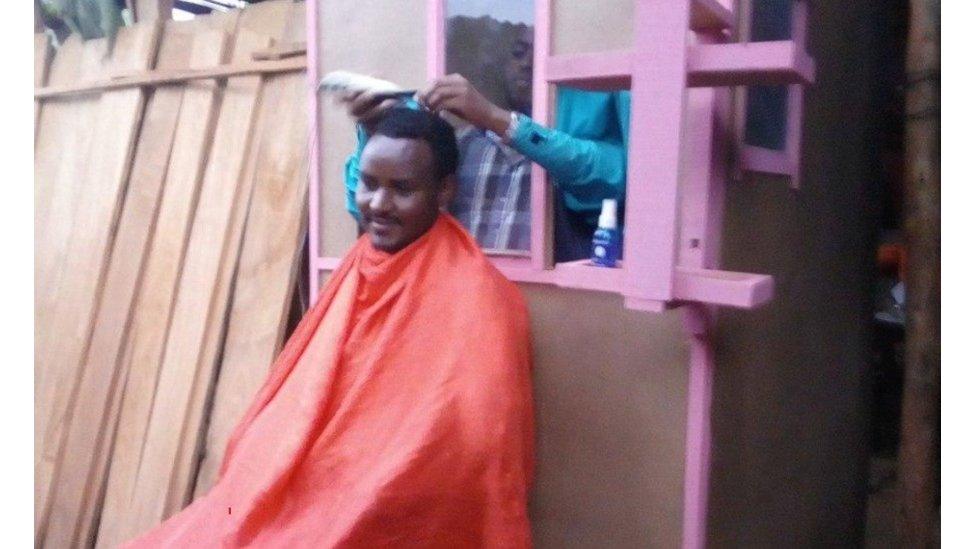

In Ethiopia, barbers have come up with a way to continue cutting hair for clients while minimising the risk of Covid-19 transmission.
The barbers stand in a specially constructed booth which acts as a partition separating them from clients, minimising person-to-person contact.
- Published16 July 2021
- Published14 August 2020

- Published14 August 2020

- Published10 August 2020
