Somalis with albinism: Pelted with stones and raw eggs
- Published
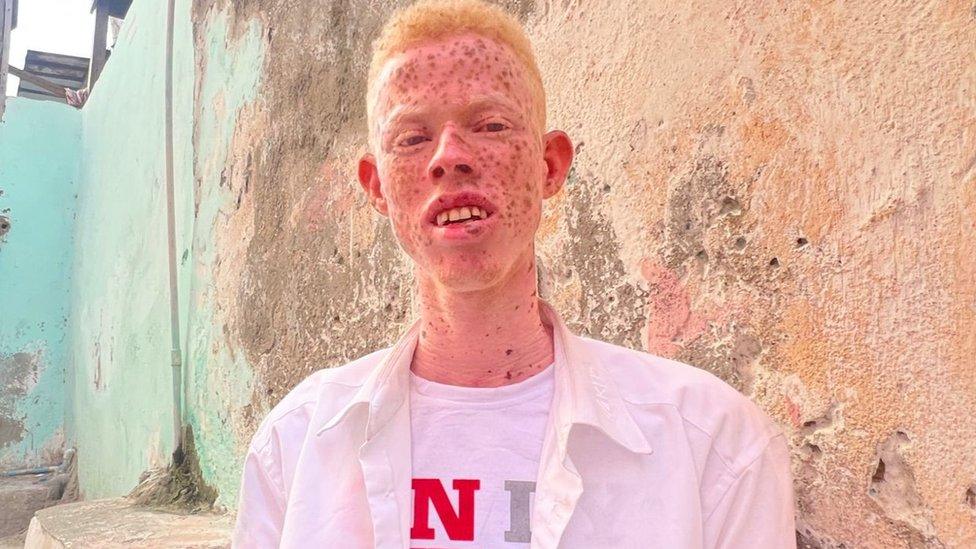

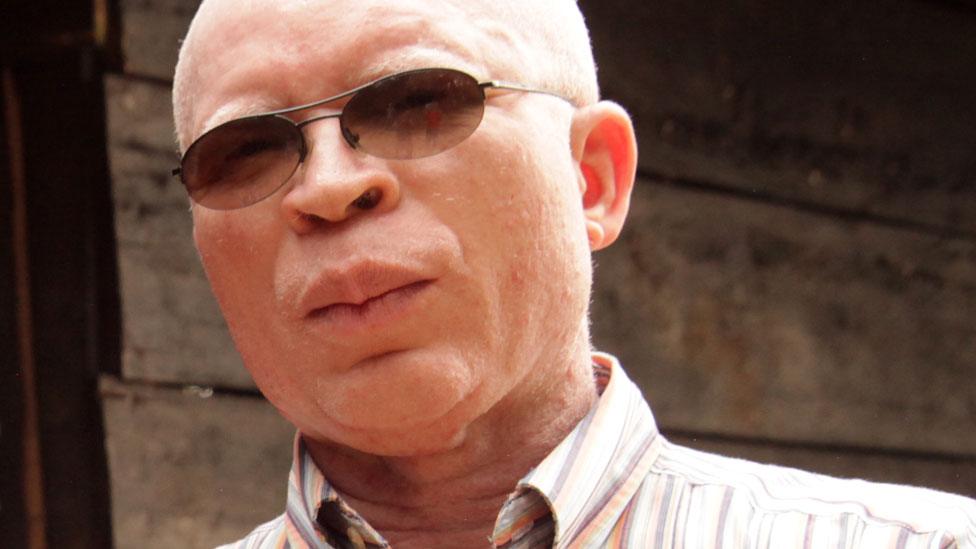
Referring to the stigma he faces in Somalia because he has albinism, 25 year-old Elmi Bile Mohamed says: "People tell me I am a cannibal and that I will eat their children. They are terrified of me."
Mr Mohamed struggled to find a place to live in the capital, Mogadishu, since leaving his rural home in the central region of Hiraan. His brothers also suffer from the condition.
"We were continuously insulted and tortured by our community. We were beaten up and mocked for the pale colour of our skin, hair and eyes," he says.
"I thought I would find a better life in Mogadishu but I was wrong."
Mr Mohamed searched and searched for a room in a shared house but was rejected at every turn.
He ended up paying $30 (£23) a month to live in a storage shed in Hamar Weyne district, the oldest part of the city.
"People think I am cursed," he says. "They often throw a mixture of salt water and raw eggs onto my doorstep because they believe this will protect them from me."
Mr Mohamed eventually found a job as a cleaner in a restaurant earning between $1.40 and $4 (£3) a day.
It didn't last long.
He was fired after customers stopped going to eat there, saying they feared he would infect them with albinism even though it is not a contagious disease, rather a genetic condition.
"I went from restaurant to restaurant looking for another job but nobody would employ me," he says. "I ended up begging on the streets, holding up a placard with my phone number on it so people could make donations via mobile payments."
The money he earned from begging was rarely enough to cover his meals and rent, let alone the sunblock and glasses he needs to protect his sensitive skin and eyes. People with albinism have little or no melanin, the pigment that colours eyes, hair and skin and offers protection from the sun.
Mr Mohamed's decision to move to Mogadishu paid off when the UN's International Organization for Migration (IOM) gave him a job in Mogadishu, as a field enumerator in communities at risk of displacement.
He has a particular responsibility to help fight the many misconceptions and negative stigmas associated with albinism in Somalia.
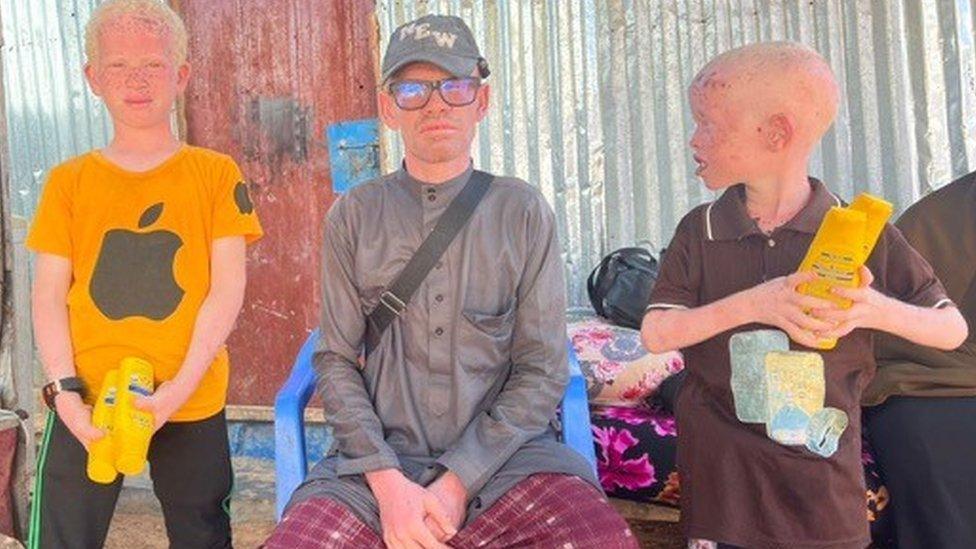

The head of Somalia's albino association, Mohamed Abukar Abdiqadir, with his children
It is not clear how many people with albinism live in Somalia as there is no data available. The country has been affected by conflict and instability for more than three decades so it is impossible to gather reliable information.
Earlier this year, about 80 families living with albinism in Mogadishu came together to form an association, Somali Albinos, which they hope will raise awareness about their plight and help reduce stigma.
So far, they have been sent 86 bottles of sun cream from Somali women living in the diaspora.
It is recommended that people with albinism wear high-factor sunscreen, protective clothing and sunglasses to reduce exposure to sunlight.
Their lack of melanin means they are at increased risk of getting sunburn and skin cancer. It also leads to eye problems as melanin is involved in the development of the retina, the thin layer of cells at the back of the eye.
"Other Somalis with disabilities have formed organisations which lobby for help from the government and international organisations," says the group's chairman, 40 year-old Mohamed Abukar Abdiqadir. "They now have rights. We don't."
"I was elected as the leader of our association because I am a hero and I never give up," says Mr Abdiqadir, who has six children. Like him, they all live with albinism.
He scrapes together a living by selling dried and tinned food from a trolley in Hamar Weyne market. He always wears a hat to protect himself from the harsh sun.
"The reason people hate and fear us is ignorance," he says.
"The evil and discrimination we face must not stop us from fighting for our rights and feeding our families. If Somalis learn about albinism, they will realise we are people just like them."
The people I love the most - my husband and my relatives - shun my children"

For now, prejudice against people with albinism is so severe that children with the condition rarely get an education.
"I took my children out of school because they were being stoned every day," says Asha Gele, whose two sons live with albinism.
"Their delicate skin was badly damaged by the stones people threw at them, so now I keep them inside all day, every day," she says. "They won't get an education, they won't learn how to play with other children, but at least they will be safe."
The family pays $40 a month to live in a makeshift two-roomed property in north Mogadishu's Huriwa district. Its walls and roof are constructed from old cloth and broken, rusted sheets of corrugated iron, not enough to stop the sunlight pouring in and burning the children's skin.
"I used to earn decent money selling vegetables in the market," Mrs Gele says. "I had to give up my business to stay at home with my children. Now we struggle to survive on the $4 to $6 my husband earns daily as a rickshaw driver."
Mrs Gele says her marriage is falling apart because her husband blames her for giving birth to children with albinism. He accuses her of bringing bad luck to the family.
"The people I love the most - my husband and my relatives - shun my children. My own brother keeps his distance because he believes they will infect him with albinism," she says.
"But I will always stand by and defend them no matter what. I will be patient and I will never neglect them. They did not choose to live like this."
Naima Said Salah is a journalist with Somalia's only all-women media house, Bilan Media.
Update 19 September: We have updated this article to reflect that Elmi Bile Mohamed now works with the IOM.
Related topics
- Published20 April 2022

- Published25 April 2019

- Published8 July 2019
- Published21 February 2017
- Published4 June 2016

- Published16 May 2016
