Kiribati country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 26 January 2024

The 33 atolls that make up Kiribati - the former Gilbert Islands - occupy a vast area in the equatorial Pacific - nearly 4,000km from east to west and more than 2,000km from north to south.
Kiribati - pronounced Kiribass - won independence from the United Kingdom in 1979. Home to the South Pacific's largest marine reserve, many of the atolls are inhabited; most of them are very low-lying and at risk from rising sea levels as a result of global warming.
With the Fijian government's permission, Kiribati has bought land in Fiji for food security and as a possible refuge.
Kiribati's economy is weak and is largely dependent on exports of copra and coconuts. Fishing licences, foreign aid and remittances from workers abroad also contribute, as does a trust fund set up with revenues from phosphate mines on the island of Banaba, whose depletion in 1980 hit Kiribati hard.
See more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
REPUBLIC OF KIRIBATI: FACTS
Capital: South Tarawa
Population: 121,300
Area: 811 sq km
Languages: English, Gilbertese
Life expectancy: 65 years (men) 68 years (women)
LEADER
President: Taneti Maamau
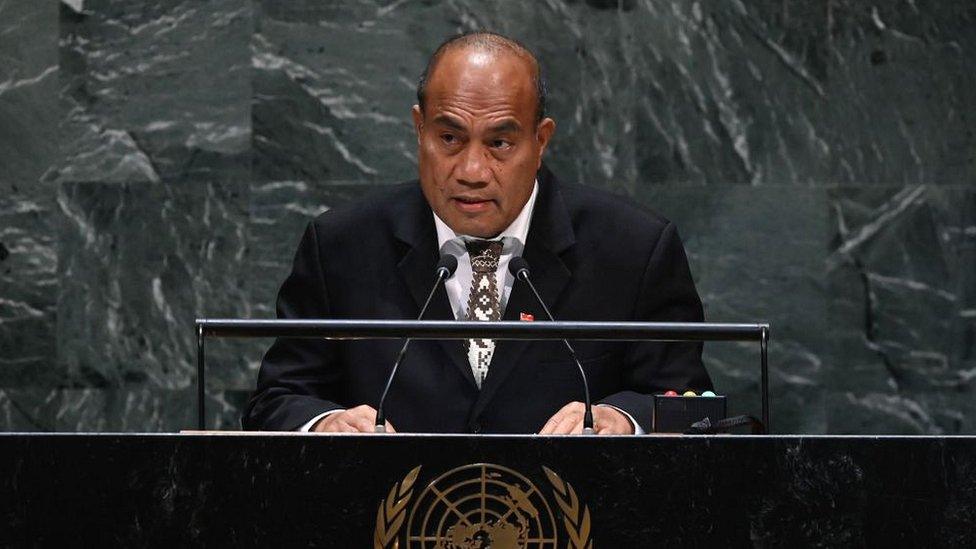

Taneti Maamau was elected as president in March 2016.
He succeeded Anote Tong who served three successive terms, the maximum allowed by the constitution.
MEDIA
Freedom of speech and of the media is generally respected. The government-run radio station and newspaper offer diverse views.
Protestant and Catholic churches publish newsletters and periodicals; these are important sources of information. There is no domestic TV service.
TIMELINE
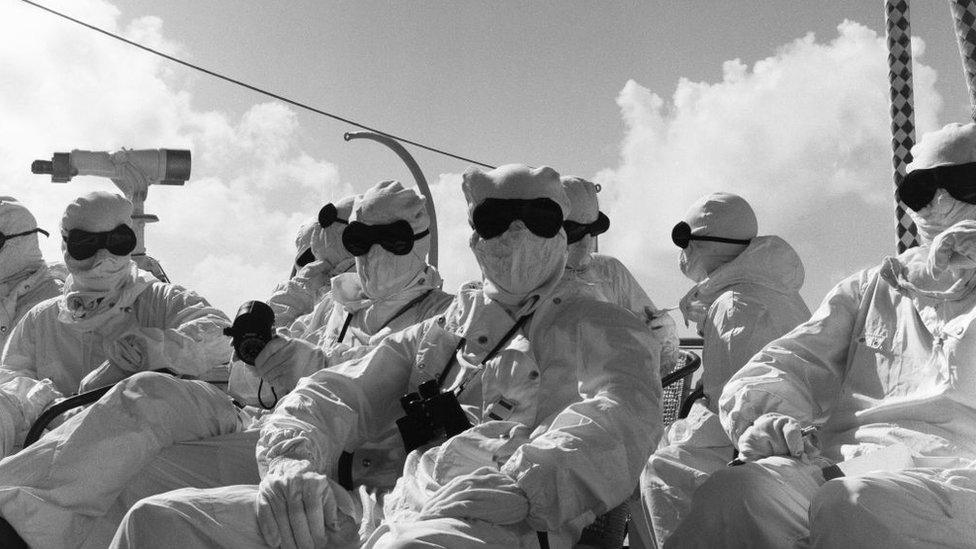

Christmas island, now Kiritimati island, was used for nuclear testing by Britain and the US
Key dates in the history of Kiribati:
11th-14th Centuries - Samoans migrate to the islands, Fijians and Tongans follow.
1820 - Named the Gilbert Islands, after British naval captain Thomas Gilbert, who visited on several of them when sailing from Australia to China in 1788.
1892 - Britain declares a protectorate over the Gilbert Islands and the neighbouring Ellice Islands (now Tuvalu), turning them both into The Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony in 1916.
1941-43 - After the attack on Pearl Harbor, during World War Two, Butaritari and Tarawa, are occupied by Japan.
1943 - Battle of Tarawa. The heavily-defended Tarawa Atoll sees some of the fiercest fighting in the Pacific when US marines invade to drive out the Japanese. Nearly 6,400 Japanese, Koreans, and Americans die in just four days of fighting, mostly on and around the small island of Betio, in the southwest of the atoll.
1945 - Environmental damage caused by phosphate mining forces many residents of Banaba island to leave and settle on Rabi Island in Fiji.
1957-58 - Britain detonates its first hydrogen bombs over Christmas Island in three separate tests.
1962 - The US uses Christmas Island to carry out 24 separate nuclear test explosions in one of the largest nuclear weapons testing programme carried out by the US. Most of these are conducted with free fall bombs dropped from B-52 bomber aircraft.
1975 - The colony is divided into two separate territories, the Gilbert Islands and the Ellice Islands.
1979 - The Gilbert Islands become an independent republic within the Commonwealth under the name of Kiribati - the Ellice Islands become independent as Tuvalu.
1995 - Kiribati unilaterally moves the international date line to the east so the country is no longer divided by it. The move means Kiribati becomes the first country to see the dawn of the third millennium.
1999 - Kiribati became a full member of the United Nations.
2008 - Kiribati asks Australia and New Zealand to accept Kiribati citizens as permanent refugees as a result of climate change leaving the islands eventually uninhabitable
2012 - Kiribati buys a 2,200-hectare estate on the second largest island of Fiji, Vanua Levu, reportedly as a potential destination for its future climate refugees.
2021 - Kiribati announces it will allow commercial fishing in its marine protected area - the largest in the world.
2023 - Kiribati confirms its intention to rejoin the Pacific Islands Forum, ending a bitter two-year split.
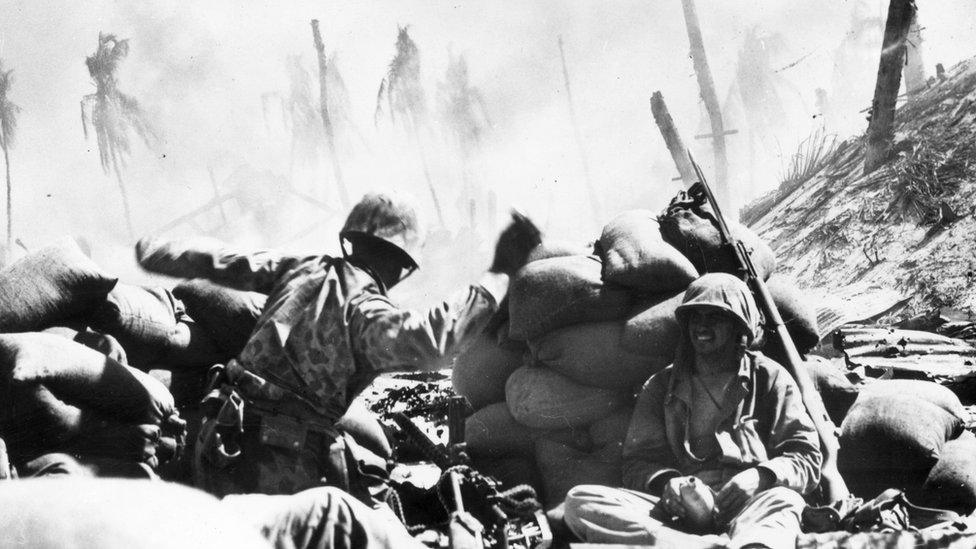

US marines fought a bitter battle to overcome Japanese forces on Tarawa Atoll in 1943
Related topics
- Published27 October 2023
- Published27 October 2023
- Published30 October 2023
- Published27 October 2023
- Published19 October 2015
- Published26 February 2024
