Japan crisis sparks review of Europe nuclear projects
- Published

Tens of thousands of anti-nuclear protesters demonstrated in Germany on Saturday
Nuclear projects in Europe are being reviewed in light of the emergency in Japan, sparked by a massive earthquake and tsunami.
The German and the Swiss governments have suspended decisions on their nuclear programmes, and the European Commission is holding a meeting of ministers and experts on Tuesday.
Thousands of anti-nuclear activists rallied on Saturday in Germany.
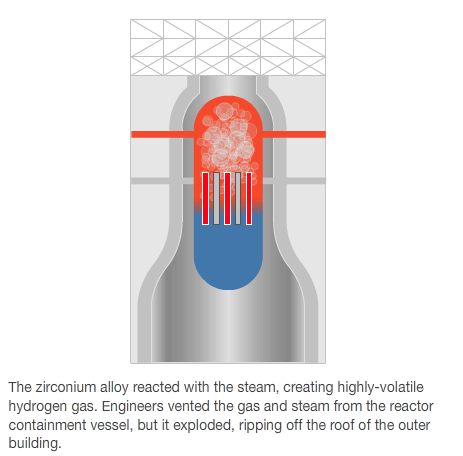
A nuclear plant in Fukushima has been hit by a third explosion in four days.
The blast occurred at reactor 2 at the Fukushima Daiichi plant - 250km (155 miles) north-east of Tokyo - which engineers had been trying to stabilise after two other reactors exploded.
Thousands of people are believed to have died following Friday's 9.0-magnitude quake and tsunami. Millions are spending a fourth night without water, food, electricity or gas and more than 500,000 people have been left homeless.
BBC Europe correspondent Chris Morris, in Brussels, said some of the decisions now being made in Europe were motivated by politics.
In Germany, where Chancellor Angela Merkel has suspended an agreement to extend the life of Germany's nuclear power stations, there are important state elections looming.
Tens of thousands of anti-nuclear activists demonstrated at the weekend against plans to extend the life of Germany's reactors.
Protesters in Stuttgart formed a human chain reaching 45km (27 miles) for the event, which had been planned before the current nuclear crisis in Japan because it was already a key election issue.
'No favours'
Meanwhile the Swiss government has delayed decisions on new nuclear plants there, and an Austrian minister has called for new safety tests on nuclear reactors across the continent.
Anti-nuclear Austria also has long-standing concerns about the safety of nuclear plants in former communist countries on its borders, said our correspondent.
"But there is also real concern about the lessons from the Japanese earthquake".
Mrs Merkel had conceded that, following events in Japan, it was not possible to "go back to business as usual", he said.
"The reaction may be a temporary one - much will depend on how the crisis in Japan is resolved.
"But - as Europe seeks to remove carbon based fuels from its economy - there is a long term debate about finding the right mix between nuclear energy and energy generated from renewable sources.
"There's no doubt that the events of the last few days haven't done the nuclear industry any favours," he added.
On Tuesday the European Commission will host a meeting of energy ministers and nuclear experts in Brussels, to assess nuclear safety issues.
The commission said responsibility for the safety of nuclear power lay primarily with individual member states.
But with nearly 150 nuclear reactors across the continent, it wanted to take stock of events in Japan, and review safety measures.
Many governments are cautious about immediate decisions, pointing out at that most of Europe is far less seismically active than Japan, said Chris Morris.
UK Energy Secretary Chris Huhne said lessons needed to be learned that were based on the facts.
That could include employing much more caution on where nuclear plants are sited.
"Frankly there are enormous differences but we have to learn everything we can from the Japanese experience to make sure if there was any human error, if there was any regulatory slip up, if there was anything we can learn we will learn it because safety is our number one concern," he told the BBC.
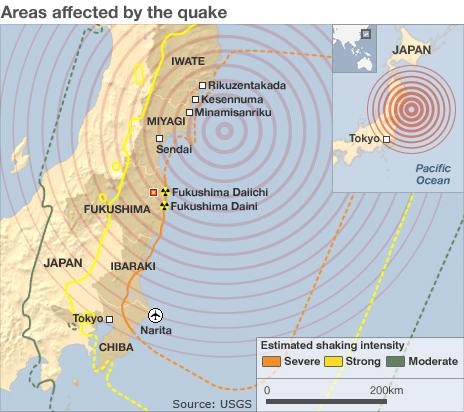
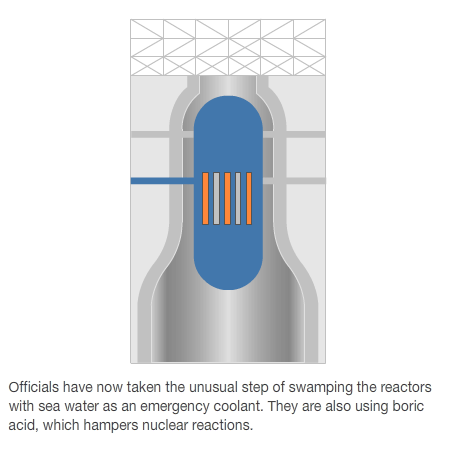
Following the latest explosion in Japan there were fears of a meltdown.
Radiation levels near the plant rose, and staff working at the reactor 2 were evacuated.
On Monday, a hydrogen blast at the Fukushima Daiichi's reactor 3 injured 11 people and destroyed the building surrounding it. It followed a blast at reactor 1 on Saturday.
Meanwhile, the relief operation is continuing in the north-east.
About 2,000 bodies were found washed ashore on beaches in Miyagi prefecture on Monday, in which officials estimate that 10,000 people have died.
About 1,000 were found on the Ojika peninsula and another 1,000 in the town of Minamisanriku, which was flattened by the tsunami.
Thousands are still unaccounted for - including hundreds of tourists - while many remote towns and villages remain cut off.

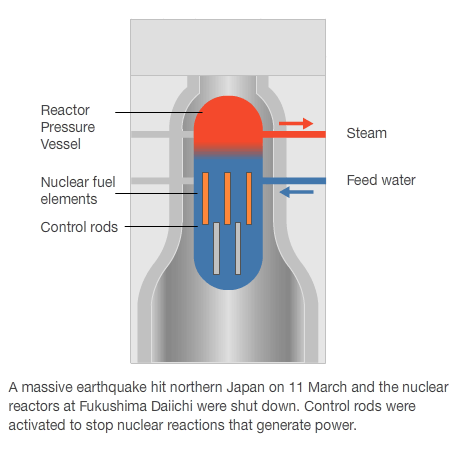
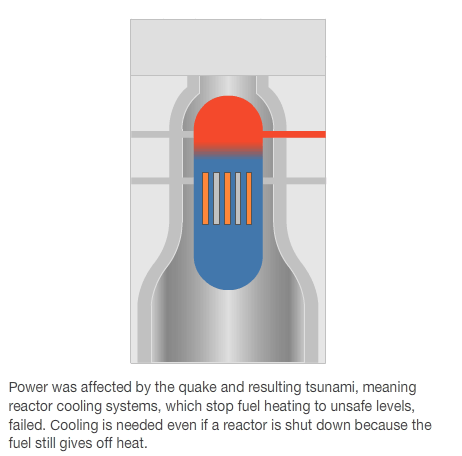
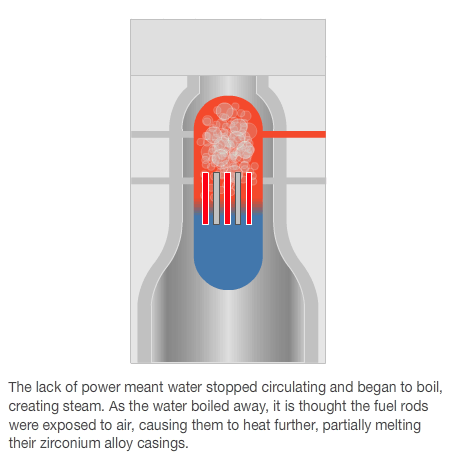
- Published15 March 2011
- Published12 March 2011