Lithuania country profile
- Published
This page is no longer being updated. It was last updated on 25 November 2024
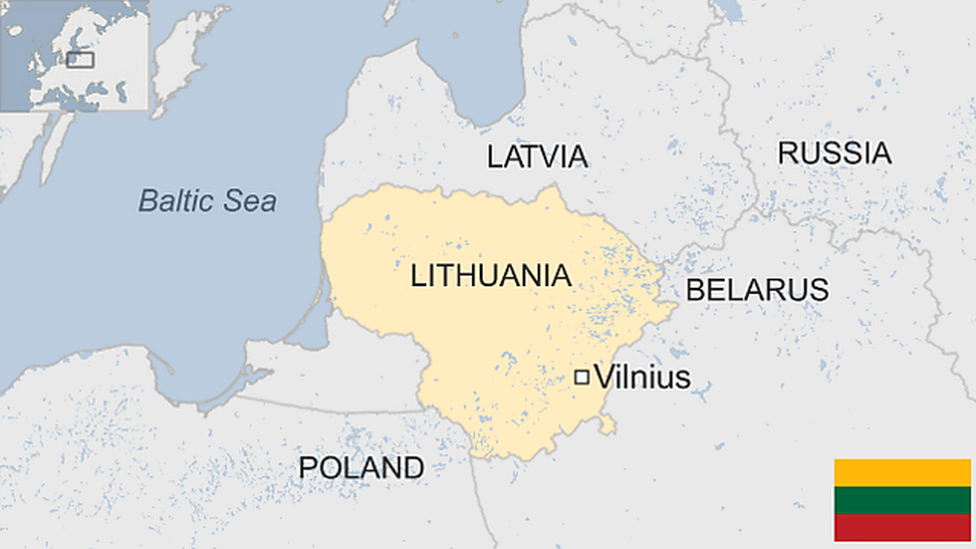
Lithuania is the largest and most southerly of the three Baltic republics.
Not much more than a decade after it regained its independence during the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1990, Lithuania joined Nato and then the EU in 2004.
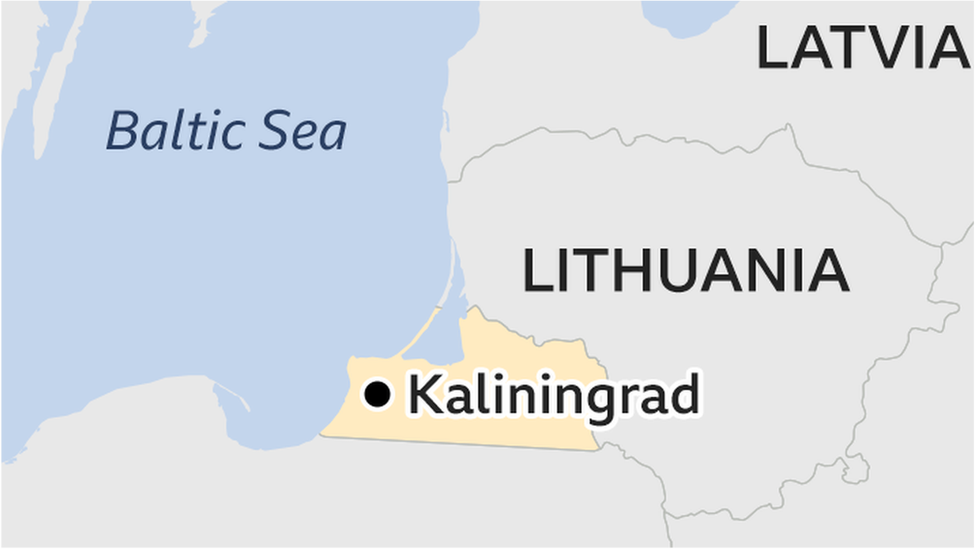
Russia's Kaliningrad exclave hosts the headquarters of the Russian Navy's Baltic Fleet, and shares a major border with Lithuania.
Read more country profiles, external - Profiles by BBC Monitoring, external
REPUBLIC OF LITHUANIA: FACTS
Capital: Vilnius
Area: 65,300 sq km
Population: 2.8 million
Languages: Lithuanian
Life expectancy: 70 years (men) 80 years (women)
LEADERS
President: Gitanas Nausėda

Incumbent Gitanas Nausėda was re-elected president in the May 2024 election in a second-round landslide with 76% of the votes. He had won the previous 2019 presidential election.
A second round was held as no candidate received an absolute majority in the first round. This saw Nausėda and Prime Minister Ingrida Šimonytė facing each other in the runoff, a rematch of 2019 in which Nausėda also defeated Šimonytė.
The Lithuanian president has somewhat more executive authority than in neighbouring Estonia and Latvia. Though Lithuania does not have a fully presidential system, the president generally has the most authority in foreign affairs.
Prime Minister: Gintautas Paluckas

Lithuania's parliament approved Gintautas Paluckas, deputy leader of the Social Democrats (LSDP) as prime minister in November 2024 after the LSDP won the October 2024 elections, defeating incumbent Ingrida Šimonytė and her conservative Homeland Union - Lithuanian Christian Democrats (TS-LKD).
Paluckas, a former head of the LSDP, had been expected to become premier after the party's leader, Vilija Blinkevičiūtė, decided she would rather remain a member of the European Parliament than become prime minister.
The centre-left LSDP secured a decisive 52-seat majority, positioning it to lead the government.
Lithuania has been one of the EU's strongest supporters of Kyiv and fiercest critics of Moscow under its outgoing conservative-led government, and Blinkevičiūtė had promised that would not change.
MEDIA
Lithuania's private TV and radio stations compete with public networks run by Lithuanian National Radio and Television (LRT).
The media are free and operate independently of the state. There are no government-owned newspapers.
Read full media profile
TIMELINE
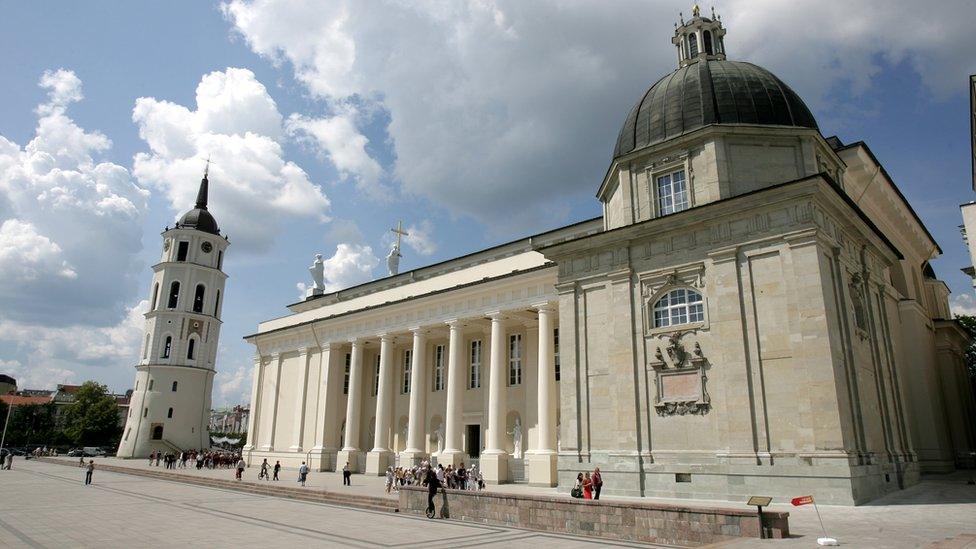

A view of Vilnius cathedral
Some key dates in Lithuania's modern history:
1915 - Lithuania, under Russian rule since the late 18th Century, is occupied by German troops during World War One.
1918 - Lithuania declares independence.
1920 - Soviet Russia recognises Lithuania's independence.
1939 - The Soviet Union compels Lithuania to accept Soviet military bases.
1940 - Soviet Army invades. President Antanas Smetona flees. Lithuania incorporated into Soviet Union.
1941 - Thousands of Lithuanians are deported to Siberia. Nazi Germany invades Soviet Union and occupies Lithuania.
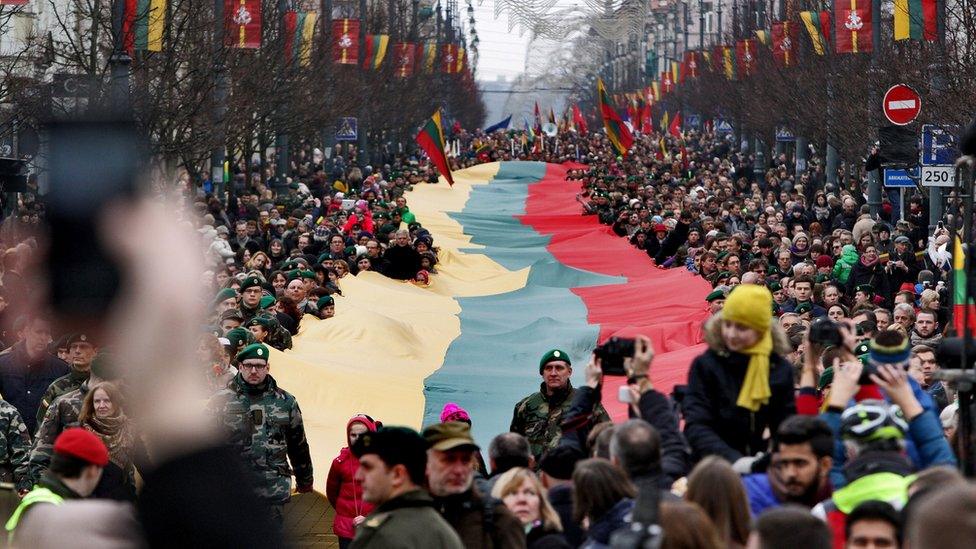

Parade to mark the 25th anniversary of the restoration of independence held in Vilnius in 2015
1944 - Soviet Army returns, presaging further deportations and repression of resistance.
1989 - Parliament approves declaration of Lithuanian sovereignty, stating that Lithuanian laws take precedence over Soviet ones.
1991 - Soviet troops fire on civilians outside television tower in Vilnius, killing 13 and injuring several hundred. Referendum sees overwhelming vote in favour of independence. Following a failed coup in Moscow, the Soviet Union recognises Lithuania's independence. Lithuania joins the UN.
1992 - New constitution introduces presidency.
2004 - Lithuania joins Nato and the EU.
2014 April - Nato steps up military presence in the Baltic states in response to tensions with Russia over Ukraine.
2015 - Lithuania adopts the euro. Government says it plans to restart military conscription, which ended in 2008, amid concerns about Russian assertiveness in the Baltic region.
2022 - Lithuania declares state of emergency along its border with Russia and Belarus following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.

Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania, in winter
- Published29 March 2023
- Published13 February 2024
- Published23 July 2024
- Published22 August 2023
- Published25 March 2024
- Published27 January
- Published20 January
- Published22 August 2023