France fuel protest: One dead in 'yellow vest' blockades
- Published
Thousands march in France over diesel tax
One protester has died and more than 200 were injured as more than a quarter of a million people took to the streets of France, angry at rising fuel prices.
The female protester who died was struck after a driver surrounded by demonstrators panicked and accelerated.
The "yellow vests", so-called after the high-visibility jackets they are required to carry in their cars, blocked motorways and roundabouts.
They accuse President Emmanuel Macron of abandoning "the little people".
Mr Macron has not so far commented on the protests, some of which have seen demonstrators call for him to resign.
But he admitted earlier in the week that he had not "really managed to reconcile the French people with their leaders".
Nonetheless, he accused his political opponents of hijacking the movement in order to block his reform programme.
What has happened so far?
Some 280,000 people took part in protests across France, the interior ministry said in its latest update.
It said 227 people were injured during the day, seven seriously, with 52 people arrested.
Most of the protests have been taking place without incident although several of the injuries came when drivers tried to force their way through protesters.
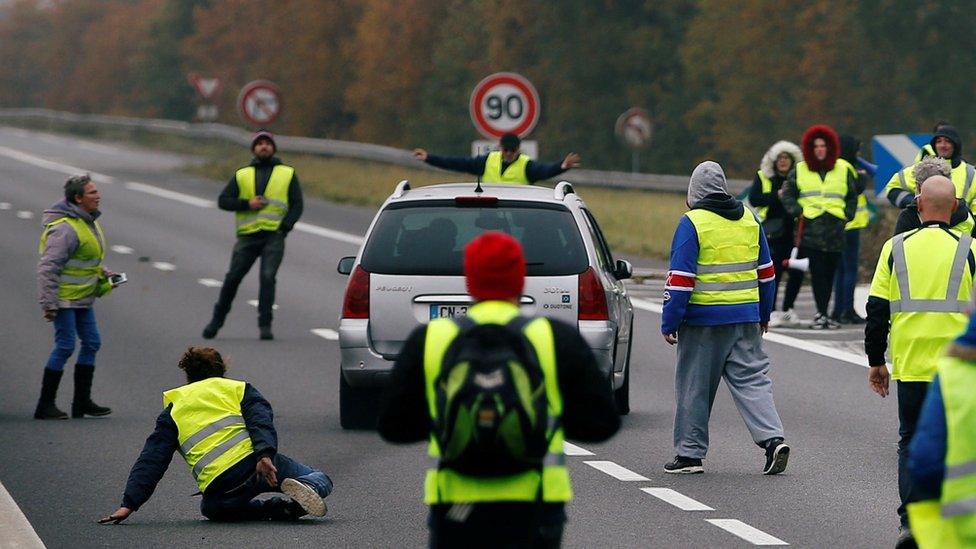

A driver forces a car through a group of protesters in Donges, western France
Chantal Mazet, 63, was killed in the south-eastern Savoy region when a driver who was taking her daughter to hospital panicked at being blocked by about 50 demonstrators, who were striking the roof of her vehicle, and drove into them.
The driver has been taken into police custody in a state of shock.
In Paris protesters approaching the Élysée Palace, the president's official residence, were repelled with tear gas.
Why are drivers on the warpath?
The price of diesel, the most commonly used fuel in French cars, has risen by around 23% over the past 12 months to an average of €1.51 (£1.32; $1.71) per litre, its highest point since the early 2000s, AFP news agency reports.
World oil prices did rise before falling back again but the Macron government raised its hydrocarbon tax this year by 7.6 cents per litre on diesel and 3.9 cents on petrol, as part of a campaign for cleaner cars and fuel.
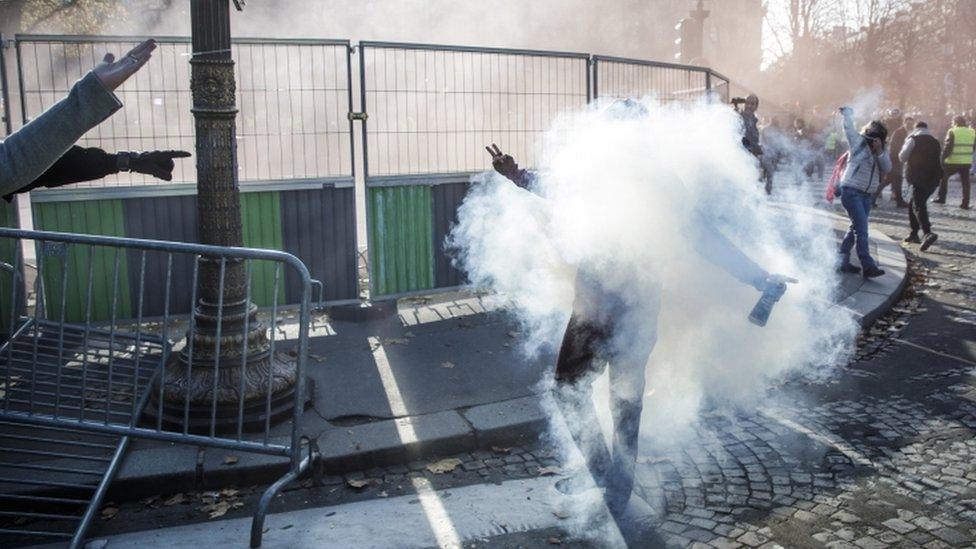
Tear gas was used to disperse protesters in Paris
The decision to impose a further increase of 6.5 cents on diesel and 2.9 cents on petrol on 1 January 2019 was seen as the final straw.
Speaking on Wednesday, the president blamed world oil prices for three-quarters of the price rise. He also said more tax on fossil fuels was needed to fund renewable energy investments.
How big is the movement?
It has broad support. Nearly three-quarters of respondents to a poll by the Elabe institute backed the Yellow Vests and 70% wanted the government to reverse the fuel tax hikes.
More than half of French people who voted for Mr Macron support the protests, Elabe's Vincent Thibault told AFP.
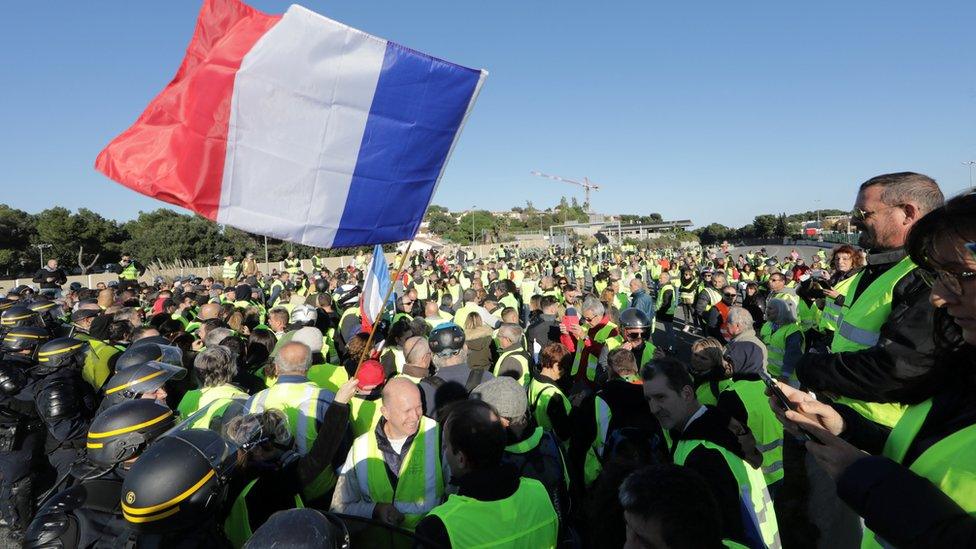

Police attend as protesters block a motorway in Antibes
"The expectations and discontent over spending power are fairly broad, it's not just something that concerns rural France or the lower classes," he said.
The BBC's Lucy Williamson in Paris says the movement has grown via social media into a broad and public criticism of Mr Macron's economic policies.
Are opposition politicians involved?
They have certainly tried to tap into it. Far-right leader Marine Le Pen, who was defeated by Mr Macron in the second round of the presidential election, has been encouraging it on Twitter.
She said: "The government shouldn't be afraid of French people who come to express their revolt and do it in a peaceful fashion."
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

Laurent Wauquiez, leader of the centre-right Republicans, called on the Macron government to scrap the next planned increase in carbon tax on fossil fuels in January to offset rising vehicle fuel prices.
Mr Castaner has described Saturday's action as a "political protest with the Republicans behind it".
Olivier Faure, leader of the left-wing Socialist Party said the movement - which has no single leader and is not linked to any trade union - had been "born outside political parties".
"People want politicians to listen to them and respond. Their demand is to have purchasing power and financial justice," he said.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

Is there any room for compromise?
On Wednesday, the government announced action to help poor families pay their energy and transport bills.
Prime Minister Edouard Philippe announced that 5.6 million households would receive energy subsidies. Currently 3.6 million receive them.
A state scrappage bonus on polluting vehicles would also be doubled for France's poorest families, he said, and fuel tax credits would be brought in for people who depend on their cars for work.
Protesters have mocked the president relentlessly as "Micron" or "Macaron" (Macaroon) or simply Manu, the short form of Emmanuel, which he famously scolded a student for using.
Allow X content?
This article contains content provided by X. We ask for your permission before anything is loaded, as they may be using cookies and other technologies. You may want to read X’s cookie policy, external and privacy policy, external before accepting. To view this content choose ‘accept and continue’.

- Published6 November 2018

- Published18 September 2018

- Published30 August 2018
