Europe's slow start: How many people have had the Covid vaccine?
- Published
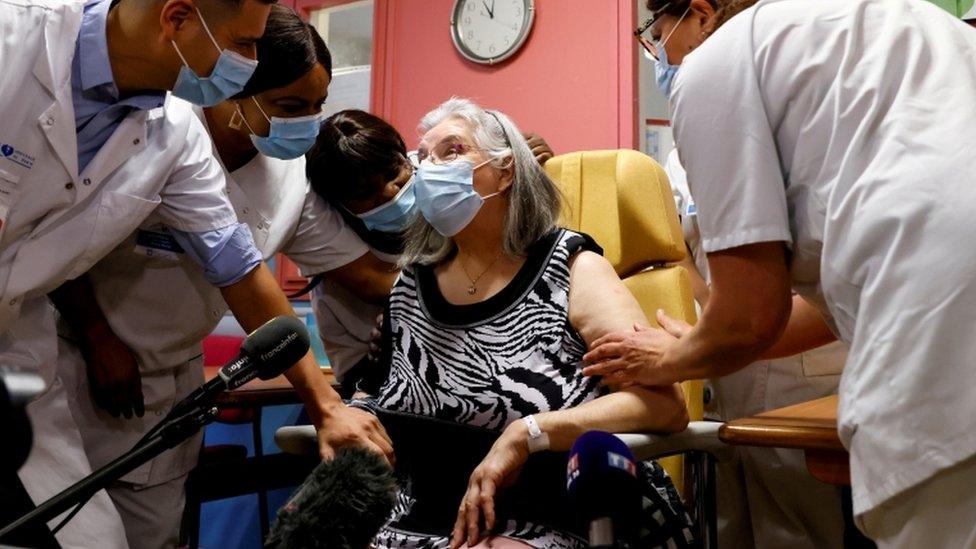
A 78-year-old French woman received the first dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in France
A global race is on to vaccinate people against Covid-19 - and with infections soaring in Europe many have complained that the roll-out is too slow in the EU.
Member states decide individually who to vaccinate, when and where, but the EU is coordinating strategy and buying vaccines in bulk. On Friday, the EU Commission agreed to buy an extra 300 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine - that would give the EU nearly half of the firm's global output for 2021.
BBC reporters in seven European capitals explain how the vaccinations are going on their patch.

In an election year, the vaccine has become a political battleground, writes Jenny Hill, in Berlin.
The fact it was German scientists who developed the first effective Covid vaccine has been the source of great national pride. And, by and large, Germans appear to be reasonably comfortable with the idea of immunisation.
A recent survey found 65% were prepared to have the vaccine. Other research indicates that less than a quarter of those surveyed would not. But politically - and perhaps unsurprisingly, given this is an election year - Germany's vaccination programme has become a battleground.
Vaccinations began here just under two weeks ago and prioritise the over 80s and care home workers. By Thursday evening, more than 477,000 first doses had been administered.
Germany's share of the EU order amounts to 56 million doses. So far, 1.3 million doses have been delivered.
But some of the hundreds of specially prepared vaccination centres are still not in use and even the government has admitted there simply isn't enough to go around. Angela Merkel and her health minister Jens Spahn have been accused of failing to secure enough doses.
Much of the criticism has come from Mrs Merkel's own coalition partners but some within the scientific community have echoed their concerns - that Germany put European interests above its own by insisting on a joint EU procurement process. The scientists who developed the vaccine have said publicly that the EU originally turned down an offer for a further order.
Germany's share of the EU order amounts to 56 million doses. So far, 1.3 million doses have been delivered and it's thought that by the end of the month a further 2.68 million will have followed.
Mr Spahn, whose assured performance through the pandemic led some to wonder whether he might be a potential successor to Mrs Merkel, has blamed the shortage on the inability of the manufacturers of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to meet global demand.
Germany has now ordered an extra 30 million doses and, following the recent European approval of the Moderna vaccine, expects to start rolling that out next week. The government is sticking to its pledge that the vaccination programme will be complete by the end of the summer.

The Czech prime minister has hit out at apparent delays in distributing the vaccine, writes Rob Cameron, in Prague.
The Czech vaccination effort began on 27 December, when the prime minister, Andrej Babis, became the first person in the country to receive the jab. Mr Babis, who is 66, had previously questioned whether he would be eligible, as he'd had his spleen removed as a teenager.
But the country's programme has got off to a sluggish start. Mr Babis - a billionaire businessman who has been dogged by both European and Czech investigations into alleged misuse of EU funds - has lost no time venting his (figurative) spleen at the European Commission over the delay. "We believed when we contributed €12m to the European fund in November that we'd receive the vaccine," he told a newspaper this week.
The health minister conceded this week that immunising the higher-risk groups will take months.
The country has received 30,000 doses of the Pfizer vaccine. So far, it has managed to administer it to 19,918 people. The government says it is ready to roll out the jab en masse as soon as supplies arrive from the manufacturers.
It has also published a strategy, which envisages a three-stage process. The first will see targeted vaccination of high-risk groups. This will gradually give way to mass vaccination in 31 centres, using an online reservation system that will be open to all from 1 February. And the final stage will see the country's GPs deployed, hopefully to administer the Oxford-AstraZeneca and other jabs, which unlike the previous two can be stored and transported at fridge temperature.
However, the timing in the original strategy document now appears optimistic. The health minister conceded this week that immunising the higher-risk groups - all health and social care staff, teachers, everyone over 65, all those with serious health conditions - will take months. GPs may not begin vaccinating young, healthy members of society until late spring, or summer.

A sluggish start is being blamed on bureaucracy and vaccine scepticism, writes Hugh Schofield, in Paris.
France's boast of a big, effective state apparatus has been badly exposed by the sluggish start to the Covid vaccination programme. After the first week, when neighbouring Germany had inoculated around 250,000 people, France was on a mere 530. By Friday, the figure had gone up to 45,500 - still so small as to be statistically meaningless.
So why has it taken so long for France to put the plan into action? It is not as if the authorities did not have time to prepare. And it is certainly not a question of a lack of vaccine. In fact, more than a million Pfizer doses are already in cold storage, waiting to be used.
Polls suggest as many as 58% of the public do not want to be given the jab.
The primary reason for the delay seems to be the cumbersome, over-centralised nature of France's health bureaucracy. A 45-page dossier of instructions issued by the ministry in Paris had to be read and understood by staff at old people's homes.
Each recipient then had to give informed consent in a consultation with a doctor, held no less than five days before injection. The lengthy procedure is in theory to save lives - those of patients who might have an adverse reaction. But as the critics have been arguing, delay in inoculating the population is also costing lives.
Another problem in France is the high level of scepticism towards vaccination - product of a more general suspicion of government. Polls suggest as many as 58% of the public do not want to be given the jab. The effect - critics say - has been to make the government unduly cautious. When urgency was required, the authorities were reluctant to move fast for fear of galvanising the anti-vaxxers.
After President Emmanuel Macron communicated his anger at the delays at the weekend, the pace is picking up. The procedure for consent is being simplified. By the end of January, the plan is to have 500-600 vaccination centres open across the country - either in hospitals or other big public buildings.
Politically a lot is at stake. The government has already come under fire for failings in providing masks and tests. With opposition voices calling the vaccine delay a "state scandal", President Macron needs a roll-out that is fast and problem-free.

National pride accelerated Russia's rollout, but one man is conspicuously absent from the list of people vaccinated, writes Sarah Rainsford, in Moscow.
Russia registered its main Covid vaccine for domestic use way back in August, before mass safety and efficacy trials had even begun. In December, with those trials still underway, it began rolling out Sputnik V to the public ahead of mass vaccination launches everywhere else in Europe. The rush was driven by national pride as well as medical necessity.
Sputnik was initially offered to front line health and education workers but early take-up of the two-dose vaccination was slow and the list of those eligible soon expanded.
A poll by the Levada Centre in late December showed only 38% of respondents were willing to get the jab: wary of domestic healthcare and medicines, Russians were sceptical of bold early claims made for the vaccine and nervous about possible adverse reactions. Even so, and despite similar delays scaling-up production as in other countries, Sputnik's backers announced this week that more than a million people had been vaccinated.
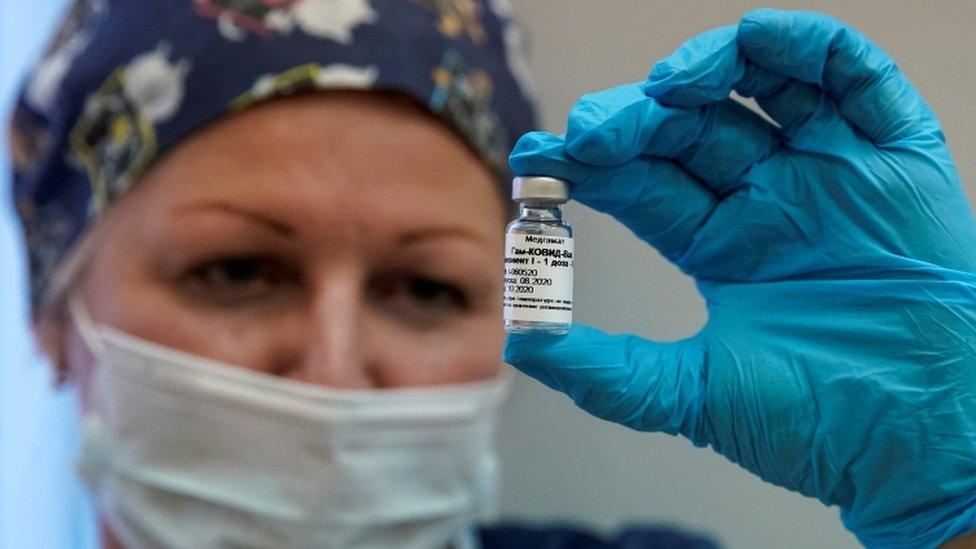
Russia began rolling out its Sputnik V vaccine in December
But one man still conspicuously absent from the list of the vaccinated is Vladimir Putin, despite the Kremlin saying he will - eventually - get the jab. In the meantime, those who meet him in person are obliged to test for Covid first and even quarantine. The president may need to lead by example, though. Mr Putin has said repeatedly that protecting the economy is his priority so he's banking on mass vaccination to avoid a return to national lockdown.
Russia has built giant, temporary hospitals since the start of the pandemic and the health minister said this week that 25% of Covid beds remain free. There's also been a fall in the number of new daily cases reported - around 25,000 for the past 5 days. But that's not down to the vaccine yet. The country is nearing the end of a 10-day New Year holiday period and the number of Covid tests has also dropped.

As infection rates grow in a country praised by many for its no-lockdown approach, a successful vaccine programme is crucial writes Maddy Savage, in Stockholm.
Almost two weeks since 91-year-old care home resident Gun-Britt Johnsson became the first Swede to get the initial dose of a Pfizer jab, there is still no official tally of how many others have received the vaccination.
The Public Health Agency of Sweden says it's in the process of compiling data from the country's 21 regional health authorities tasked with vaccinating the entire adult population - around eight million people - by 26 June. The date isn't arbitrary, it's the biggest public holiday weekend of the year, when Swedes traditionally hold Midsummer celebrations. Karin Tegmark, a senior manager at the agency, says the date remains "feasible". But she says it depends on the delivery of vaccines to the country.
After months of high trust levels in the country's no-lockdown approach, support for the health agency has dwindled.
Alongside 4.5 million doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, Sweden has ordered 3.6 million jabs from Moderna, the first of which are expected to arrive next week. The country also plans to roll-out the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine as soon as possible after it is approved by the EU - ideally by February.
Swedes initially appeared lukewarm to the idea of taking a speedily-developed coronavirus vaccine, although a poll at the end of December found 71% would take one. A key driver of the initial scepticism is thought to be the failure of a voluntary mass vaccination programme for swine flu in 2009. Hundreds of Swedish children and young adults under 30 developed the sleeping disorder narcolepsy, which was found to be a side effect of the Pandemrix vaccine.
A successful vaccination programme will be crucial, not least because it comes at a time when Swedish authorities are struggling to maintain public confidence. After months of high trust levels in the country's no-lockdown approach, support for the health agency has dwindled as Sweden has struggled with the second wave of coronavirus.
Meanwhile, several high profile officials have faced heavy criticism for breaching their own recommendations - including the head of the civil contingencies agency (pictured), who resigned after spending Christmas with his daughter in the Canary Islands.

A new government in Belgium seems unified on the vaccine rollout - for now at least, writes Nick Beake, in Brussels.
It seemed fitting that the first person in Belgium to receive a Covid jab lives in the place where the world's first approved Covid vaccine is being produced. Jos Hermans, a 96-year-old from the municipality of Puurs, was given the injection on 28 December, in his care home. A further 700 elderly residents were also administered a dose in what was a small, initial trial.
The mass vaccination programme in Belgium began on 5 January, but has been criticised for starting slowly. Federal Health Minister Frank Vandenbroucke had promised in November that the rollout would be "seamless and fast", tweeting: "If that does not work, shoot me."
The first phase looks to vaccinate up to 200,000 nursing home residents by the end of this month, or early February. Healthcare professionals will be next in line and the aim was for the whole population to be inoculated by the end of September.
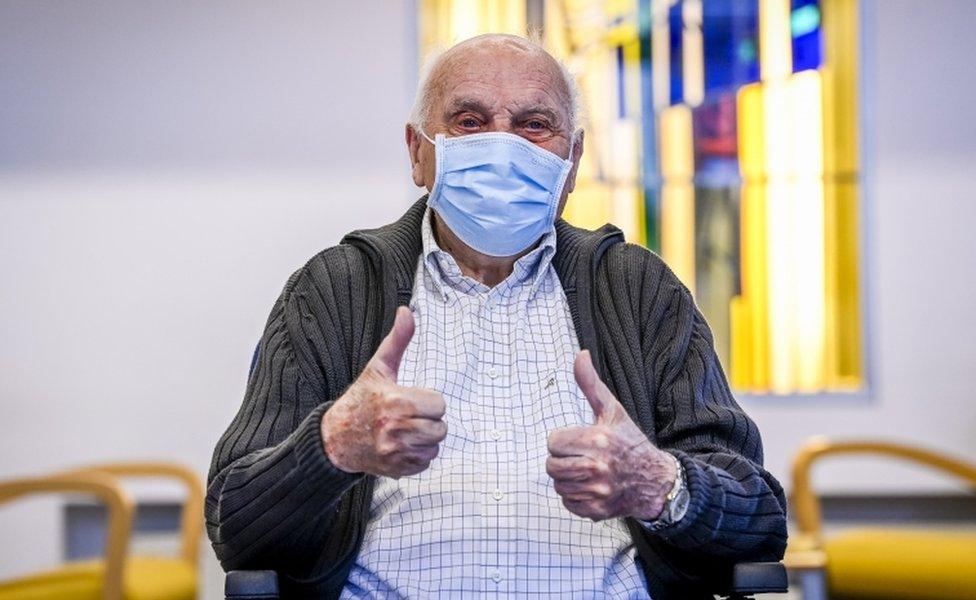

Jos Hermans, a 96-year-old from Puurs, was given the injection on 28 December
You may think the country would be at an advantage being the epicentre of the Pfizer-BioNTech production. While this clearly helps with distribution, Belgium cannot receive more doses - relative to its population - than other EU countries under strict Commission rules. That didn't stop the minister-president of the Flanders region, who admitted this week that he had contacted Pfizer directly in the hope of procuring more doses, only to be rebuffed.
After getting a guarantee from Pfizer over supply of the jab, the federal Belgian authorities have adapted their strategy: they now propose giving as many available doses to as many people as they can - and no longer reserving vials for patients' second dose, given three weeks after the first. In general, the federal government, rather than the European Commission has faced any criticism for a delay and has defended its "careful" approach.
And there appears to be an interesting regional or cultural discrepancy when it comes to whether people are willing to take the vaccine. Of the Flemish population interviewed in a poll, half have said they wanted the vaccine as soon as possible. Among French speakers - it was 20% fewer, which chimes with the deeper scepticism over the border in France.
In a country where politics are notoriously complicated and fractious - they've only recently agreed a government, after a 500-day vacuum - the Federal Coalition appears unified on its Covid vaccine strategy. For now, at least.

Regional variances and political rows have marked the beginning of Spain's vaccination programme writes Guy Hedgecoe, in Madrid.
Spain started administering the vaccine on 27 December. So far, 743,925 doses have been distributed to regional administrations, with 277,976 people vaccinated, according to the health ministry. The objective of the coalition government is to immunise 2.3 million people within 12 weeks. Priority is being given to elderly residents of care homes, those who look after them, and healthcare personnel.
Each of the country's 17 regions has a high degree of control over healthcare and should receive the number of doses that corresponds to their populations. However, already there has been substantial geographical disparity.
Government data showed, for example, that while the northern region of Asturias had used 55% of the doses it had received by 3 January, the Madrid region had only administered 5% by the same date. Some regions are holding back doses to administer a second follow-up jab to the same person in several weeks' time, and some have been vaccinating on national holidays while others have not.
The pandemic has been the cause of constant political conflict, with the right-wing opposition accusing the leftist government of incompetence.
Although vaccination is voluntary, the government has said it is making a register of those who do not wish to be inoculated. That initiative has generated controversy, although the government has insisted the register will merely seek to clarify why people refuse the vaccination.
However, the pandemic has been the cause of constant political conflict, with the right-wing opposition accusing the leftist government of Pedro Sánchez of incompetence, lack of transparency and using coronavirus to accumulate power.
The arrival of a vaccine has not stopped the rancour. Alberto Núñez Feijóo, the conservative Popular Party (PP) president of Galicia, warned the number of doses being distributed to each region was being dictated by "political affiliations or parliamentary needs", a claim the central government has rejected.
Figures correct as of 17:00 GMT.
- Published4 March 2022

- Published28 May 2021
- Published8 December 2020
