Spectre of violence still hangs over France
- Published

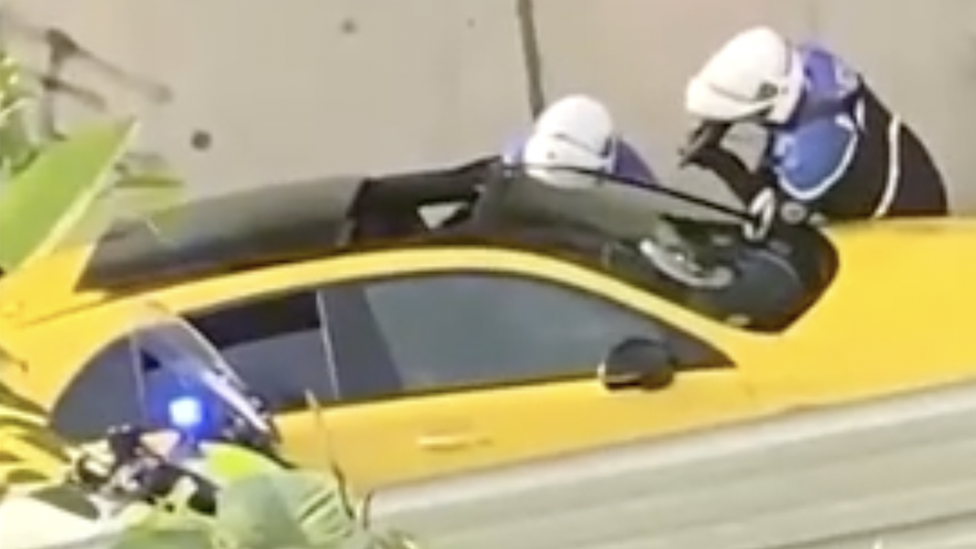
There has been a tight police presence around the Champs Elysée
"Could you just go home?"
It was a weary-sounding question, directed by a middle-aged French woman at a gang of youths pushing past her, as a mass of defence shield-wielding riot-police chased after them.
It was the early hours of Sunday morning on the Champs Elysées - the tourist shoppers' paradise in central Paris. The air was acrid with tear gas. Night number five of the street riots that have engulfed France since the killing of Nahel, a French Algerian teen, by a policeman on a Parisian housing estate.
My colleagues and I were filming the chaos all around when it struck me just how many people in France have posed the same question as the irritated lady.
The acts of violence across France dropped considerably overnight, the rioters shamed perhaps by Nahel's grandma, who took to French TV to appeal to the youngsters to calm down.
I spoke to another family member who asked to remain anonymous because tensions are still running so high. Visibly agitated, she told me they ache for the rioters to stay home.
Nahel's relatives never called for acts of hate or theft or destruction in his name, she insists. In fact, they all worry the violence could distract from what they do want: justice. For them, that means the police officer who killed Nahel, sentenced and imprisoned.
Emmanuel Macron is fervently hoping the protesters - and tag-along vandals - stay home. For so many reasons.
His second term as French president has been peppered by civil unrest - over pension reform and now, Nahel's death. It's not exactly improving his popularity ratings.
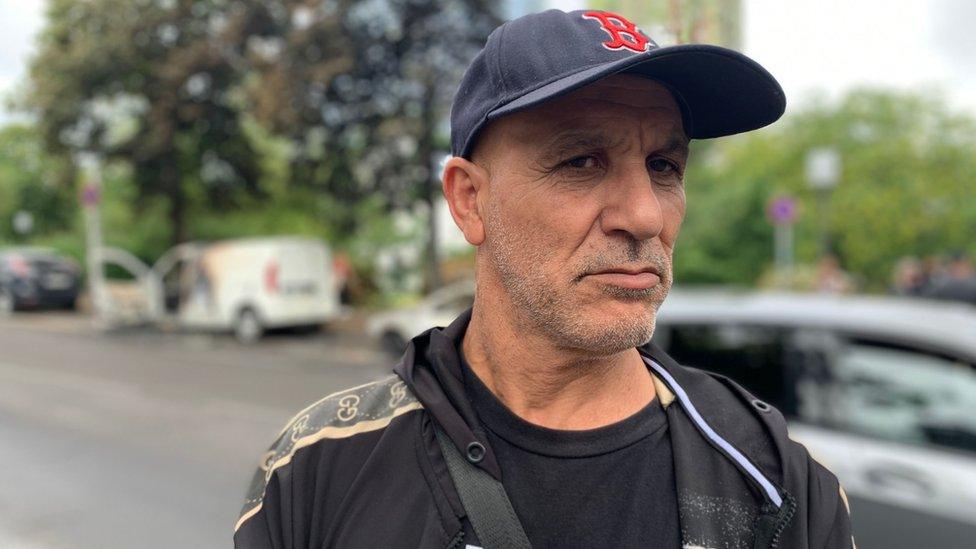

Abdul blames President Macron for the unrest
Teacher Abdul - who lives on the same estate as Nahel, told me Mr Macron was fully to blame. His economic reforms are a disaster. France is crumbling - he told me - along with its education system.
Abdul was convinced disgruntled, unemployed young men from disadvantaged neighbourhoods were at least partly responsible for the street violence. They're behind the scenes, pushing these teenagers, he said.
Abdul's neighbours bring out their mobile phones each morning to photograph the smouldering remains of the latest riot-devastation. They also told us they wished the youngsters would stop. Student Celia said she worries the violence could end in a backlash against their whole community.
On Sunday night, the mums in Aulney, a working-class area near Paris, took to the streets themselves, waving banners calling for an end to the violence. President Macron appealed to the "mamans et papas" (the mums and dads) of the rioters last week to keep them at home and off social media, which, he said, allow "inflammatory material" to circulate.
The crisis is also weakening Macron politically, under fire from the political left and right over what best to do next. The left accuses him of neglecting the poor and the marginalised. The right demands he crack down harder on the violence, imposing a nationwide state of emergency.
But the optics would be tricky for the French president. He'd worry a crackdown like that could ignite an even greater rage on the streets - and further tarnish France's international standing.
Mr Macron was forced by this crisis to leave last week's summit of EU leaders where they discussed Europe's biggest emergency: Russia's invasion of Ukraine. And this weekend, the president had to cancel a much discussed state visit to important EU ally Germany - the first by a French president in 23 years.
While in the world of sport, questions are being asked as to whether France can be trusted to safely host international events like the world's biggest cycling championship, the Tour de France. It concludes in three weeks on the Champs Elysées - a favourite spot for rioters, as we learned at the start of this article. The Rugby World Cup is due to begin in France in September. France is also set to host next year's summer Olympics. It escaped no-one's attention here that an Olympic swimming complex was targeted by rioters on one of the first nights of turmoil following Nahel's death.
Talk to the protesters themselves and many say staying home on their housing estates is far from straightforward. They feel unsafe, they say, because of regular confrontations with police. The UN has accused France's security forces of systemic racism.
Watch: Nahel's family say violence won’t bring justice for the boy they lost
Activists like Assa Traore - whose brother died seven years ago following his arrest, told us being a young black or Arab man on a housing estate in France means being regularly exposed to police brutality and racial profiling. Until France recognises the problem is endemic, she says, there will be a lot more Nahels.
But the secretary general of one of France's powerful police unions, Unité SGP, flatly denies the allegations of systemic racism.
Jean-Christophe Couvy says France is "not the US. We don't have ghettos", he told me. "Our forces represent France's multicultural society with officers from all backgrounds. You'll find maybe 1% of racists - like in the rest of society - but no more."
Mr Couvy didn't want to discuss the specifics of Nahel's case as it's an open investigation.
So I asked him how he would go about improving police relations with the estates.
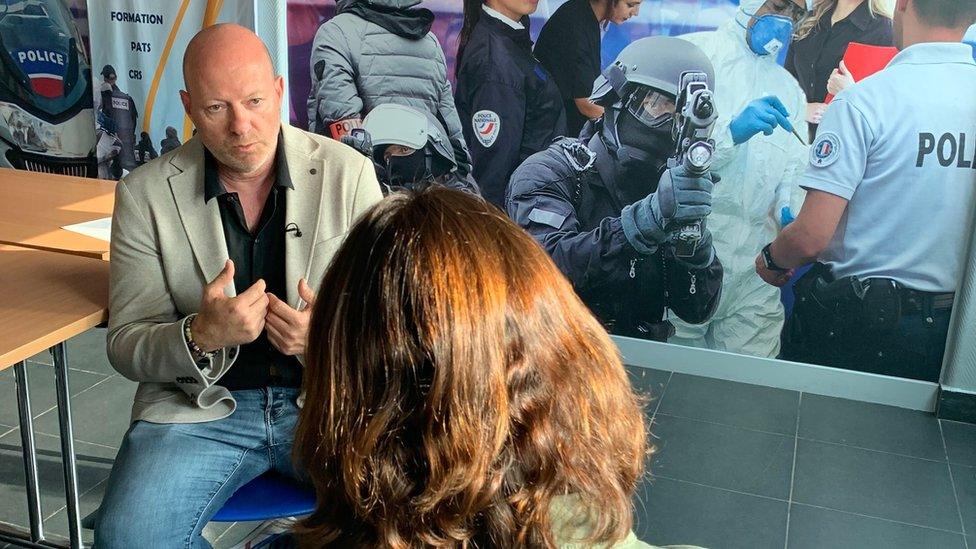

Jean-Christophe Couvy denies there is systemic racism in the police force
"The best way forward is to return to a system of community policing in France, where we know each other by our first names."
Right now in France, he told me, policing has become a box-ticking exercise of showing how many people each officer detains for questioning - to demonstrate he or she is working hard.
"The problem with that is it becomes like two opposing gangs on the streets: police vs the inhabitants of the estates."
Back in January, French Prime Minister Elisabeth Borne launched a new action plan against racism but it's been criticised for its silence on racial profiling by French police. Last summer, the Council of Europe's European Commission against Racism and Intolerance released its sixth report on France, highlighting "little progress" on curtailing the use of ethnic profiling by law enforcement officers.
Not all the rioters on France's streets were triggered by Nahel's death, but those who were say loud protests are the only way that people like them get their voices heard in France. That's why, they say, they shouldn't sit quietly at home.
France may be calming down. The large majority of the country fervently hopes so.
But the spectre of potential renewed violence hangs over France. On the streets and across social media here, French men and women predict, if relations between the authorities and housing estates such as Nahel's remain unchanged, France's streets could easily ignite again - as they've done many times in the past.
Have you been affected by the unrest in France? You can contact us by emailing haveyoursay@bbc.co.uk, external.
Please include a contact number if you are willing to speak to a BBC journalist. You can also get in touch in the following ways:
WhatsApp: +44 7756 165803
Tweet: @BBC_HaveYourSay, external
Please read our terms & conditions and privacy policy
If you are reading this page and can't see the form you will need to visit the mobile version of the BBC website to submit your question or comment or you can email us at HaveYourSay@bbc.co.uk, external. Please include your name, age and location with any submission.
Related topics
- Published30 June 2023

- Published1 July 2023
