Egypt declares state of emergency after deadly church attacks
- Published
Footage shows the scene following an explosion at a church in Tanta in northern Egypt
Egypt's President Abdul Fattah al-Sisi has announced a three-month state of emergency after attacks on two Coptic churches that left at least 44 dead.
The measure allows authorities to make arrests without warrants and search people's homes. It needs to be approved by parliament before it is implemented.
So-called Islamic State (IS) said it was behind the blasts in Tanta and Alexandria on Palm Sunday.
The group has targeted Copts in Egypt recently and warns of more attacks.
Mr Sisi made a defiant speech at the presidential palace after a meeting of the national defence council to discuss the explosions.
He warned that the war against the jihadists would be "long and painful", and said that the state of emergency would come into force after all "legal and constitution steps" were taken. The majority in parliament backs Mr Sisi.
The president had earlier ordered the deployment of the military across the country to protect "vital and important infrastructure".
The move by Mr Sisi is likely to raise concerns among human rights activists, observers say. The president, a former army chief, has been criticised by local and international groups for severe restrictions on civil and political rights in Egypt.
Human Rights Watch says, external tens of thousands of people have been arrested in a crackdown on dissent, and that security forces have committed flagrant abuses, including torture, enforced disappearances and likely extrajudicial executions.

State of emergency measures include:
Further restrictions on freedom of movement and gatherings
Monitoring of all forms of communication
Entitles president to confiscate or shut down media outlets
Allows any property to be placed under control of security forces
Deployment of security forces to enforce measures
Arrest of anyone suspected of violating state of emergency

The attacks coincided with one of the holiest days in the Christian calendar, marking the triumphal entry of Jesus Christ into Jerusalem.
IS said that two suicide bombers carried out the blasts. One targeted St George's Coptic church in the northern city of Tanta, where 27 people were killed, the health ministry said.
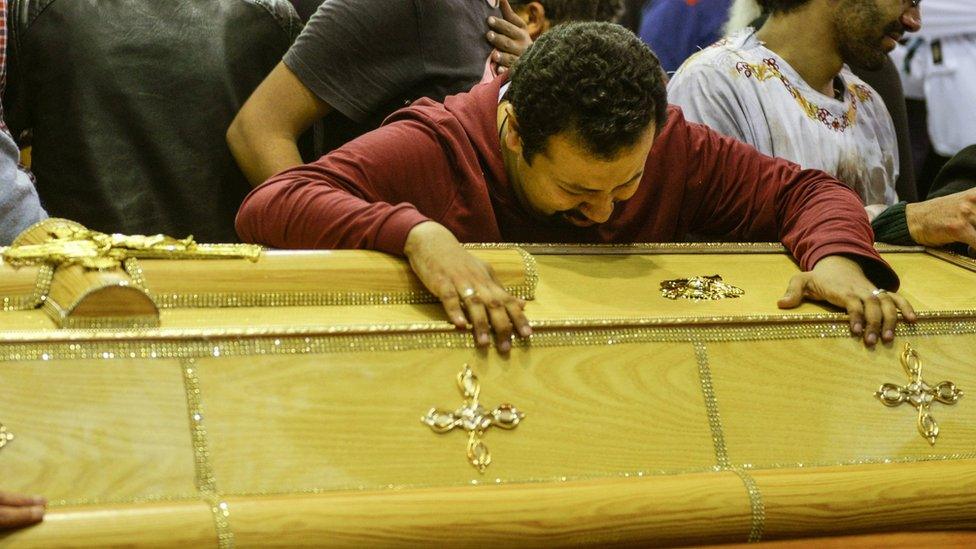

So-called Islamic State said it was behind the attacks targeting Coptic churches
Hours later, police stopped the bomber from entering the St Mark's Coptic church in Alexandria, also in the north. He detonated his explosives outside, leaving 17 dead, including several police officers.
"Crusaders and their apostate allies should know the bill between us and them is very big and they will pay it with rivers of blood from their children, god willing. Wait for us, for we will wait for you," the jihadist group said in a statement quoted by Reuters news agency.

Copts in Egypt: Recent developments
December 2016: 25 people died when a bomb exploded at the Coptic cathedral in Cairo during a service. IS said it was behind the attack
February 2016: A court sentenced three Christian teenagers to five years in prison for insulting Islam. They had appeared in a video, apparently mocking Muslim prayers, but claimed they had been mocking IS following a number of beheadings
April 2013: Two people were killed outside St Mark's cathedral in Cairo when people mourning the death of four Coptic Christians killed in religious violence clashed with local residents

The blasts came weeks before an expected visit by Pope Francis intended to show support for the country's Christians, who make up about 10% of Egypt's population and have long complained of being vulnerable and marginalised.
This sense of precariousness has only increased in recent years, with the rise of violent jihadism in parts of Egypt, the BBC's Arab affairs editor Sebastian Usher says.
The community's trust in the state's ability and willingness to protect them will now be even more deeply shaken after the attacks, our correspondent adds.
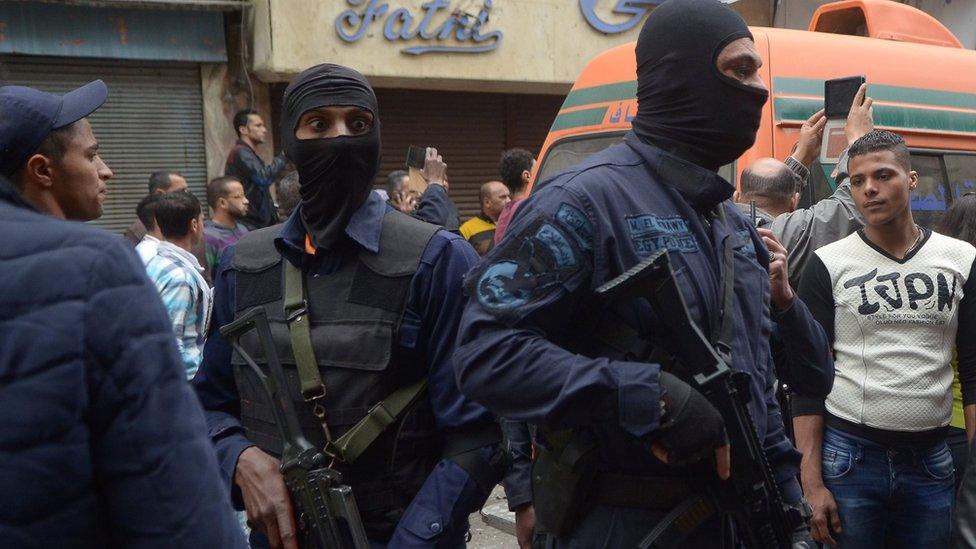

Security forces were deployed in Alexandria following the attack

What is the Coptic Christian faith?

The Coptic Orthodox Church is the main Christian Church in Egypt. While most Copts live in Egypt, the Church has about a million members outside the country.
Copts believe that their Church dates back to around 50 AD, when the Apostle Mark is said to have visited Egypt. The head of the Church is called the Pope and is considered to be the successor of St Mark.
This makes it one of the earliest Christian groups outside the Holy Land.
The Church separated from other Christian denominations at the Council of Chalcedon (451 AD) in a dispute over the human and divine nature of Jesus Christ.
The early Church suffered persecution under the Roman Empire, and there were intermittent persecutions after Egypt became a Muslim country. Many believe that continues to this day.
- Published9 April 2017
- Published16 February 2015

- Published25 February 2017

- Published2 January 2024