Ancient 'New York': 5,000-year-old city discovered in Israel
- Published

The city was described by archaeologists as the New York of its time

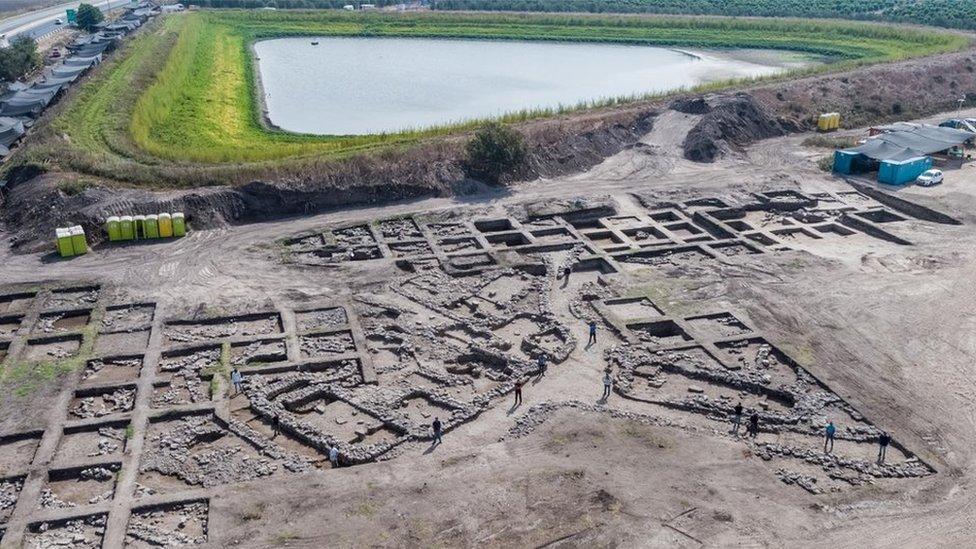
The remains of a 5,000-year-old city have been discovered in Israel - the largest and oldest such find in the region.
The city was home to 6,000 people and included planned roads, neighbourhoods, a ritual temple and fortifications.
An even earlier settlement, believed to be 7,000 years old, was discovered beneath the city.
Israeli archaeologists said the discovery was the most significant in the region from that era.
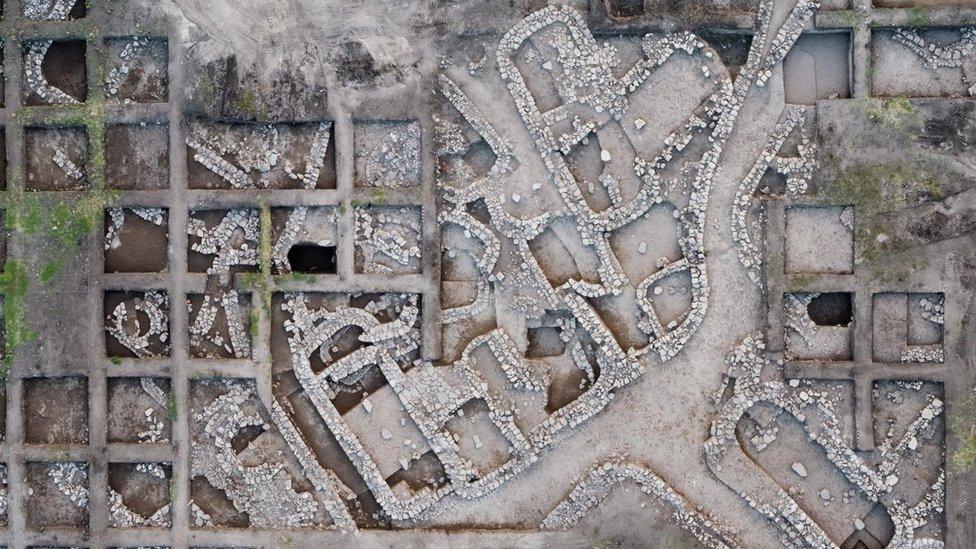


The impressive planning, diverse facilities and public buildings suggest a well-organized society, Israeli authorities said
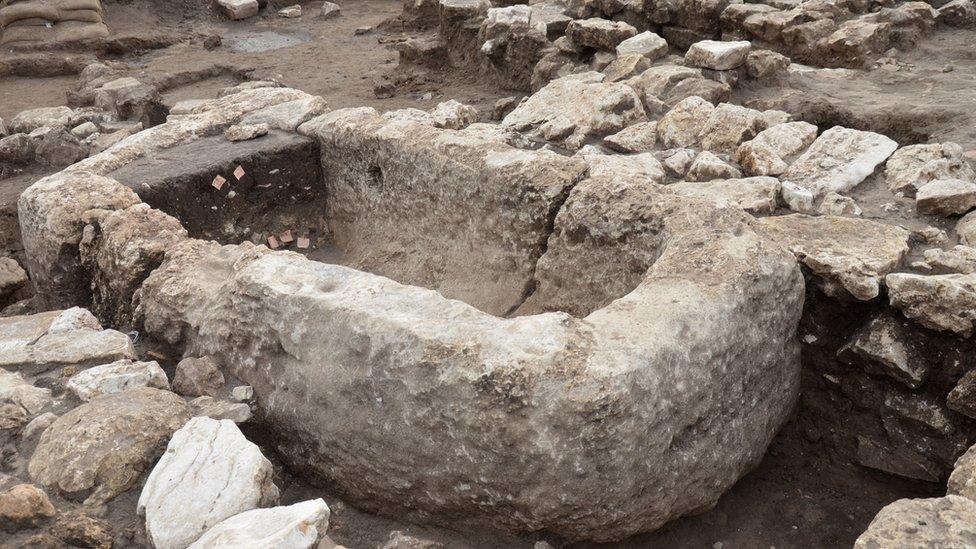

The stone basin for holding liquids was likely used during religious rituals

"This is the Early Bronze Age New York of our region; a cosmopolitan and planned city where thousands of inhabitants lived," the excavation directors said in a statement.
"There is no doubt that this site dramatically changes what we know about the character of the period and the beginning of urbanization in Israel," the statement added.
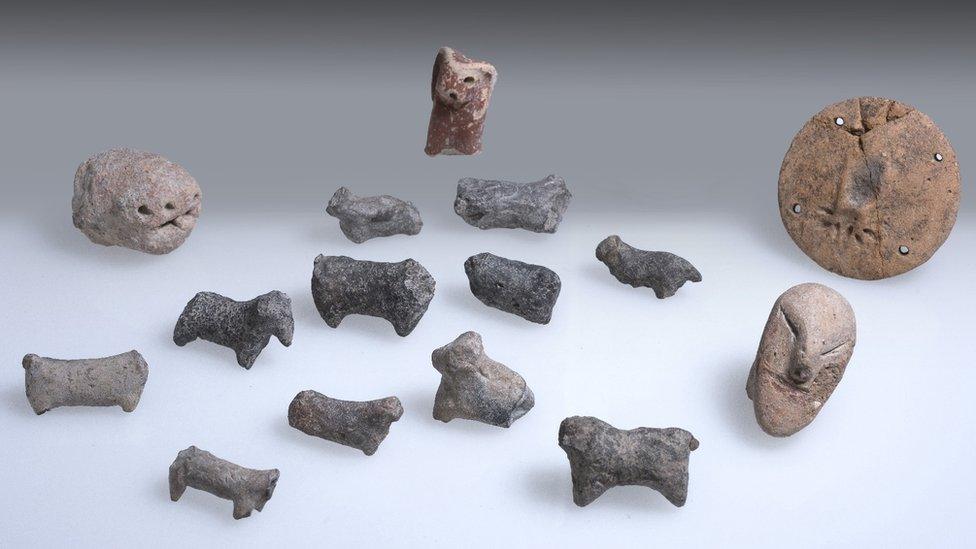


Rare figurines, often depicting people or animals, were discovered inside the temple

Known as En Esur, the site spans 650 dunams (161 acres), about double the size of previous similar findings. The design of the city included designated residential and public areas, streets and alleys, the Israel Antiquities Authority said.
About four million fragments were found at the site, including rare figurines of humans and animals, pieces of pottery and various tools, some of which came from Egypt.
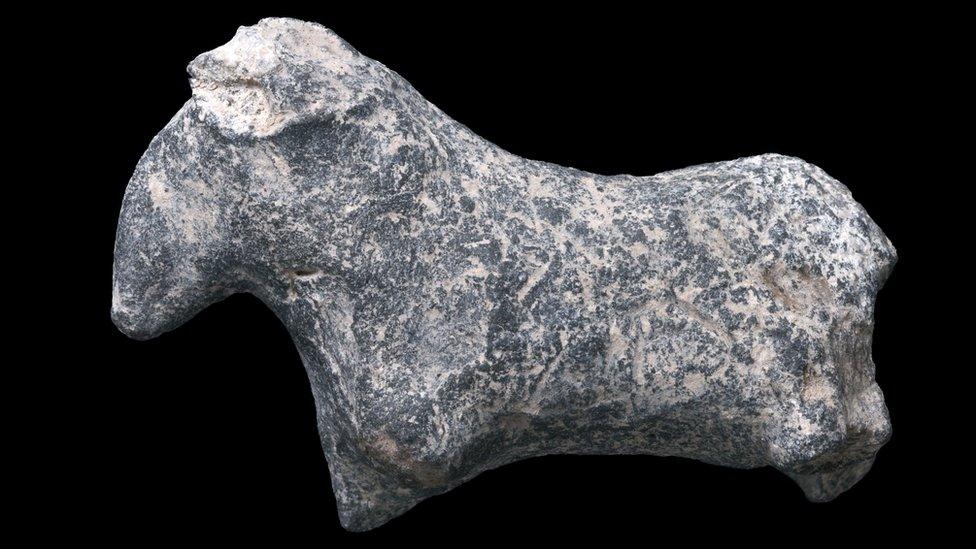


Authorities said the figurines offer valuable insight into the spiritual life of the community
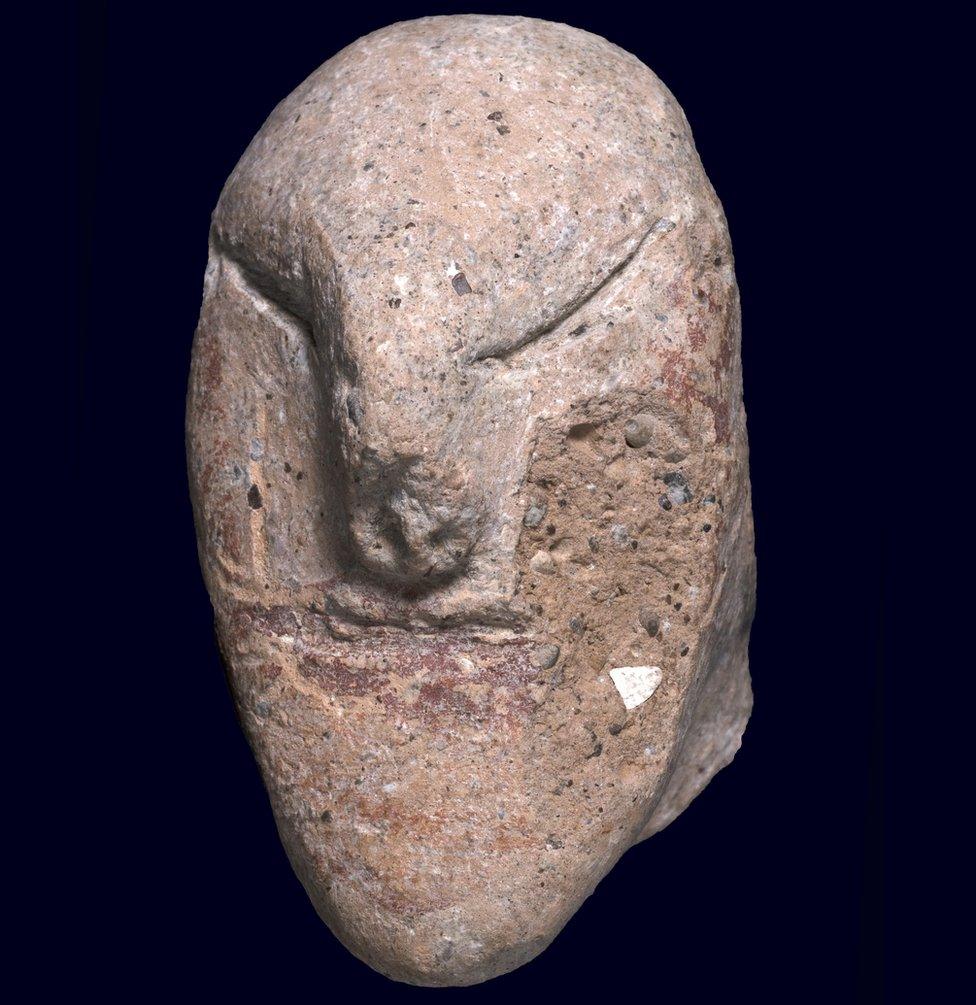

Some of the figurines have been preserved with great detail

Burnt animal bones found on the site provided evidence of sacrificial offerings. Inhabitants of the city - who were likely drawn to the area by two fresh water springs, fertile land and proximity to trade routes - made their living from agriculture, trading with different regions and cultures.
Archeologists had been excavating the site for more than two and a half years, with 5,000 teenagers and volunteers participating. The settlement was discovered during excavations preceding the construction of a new road.
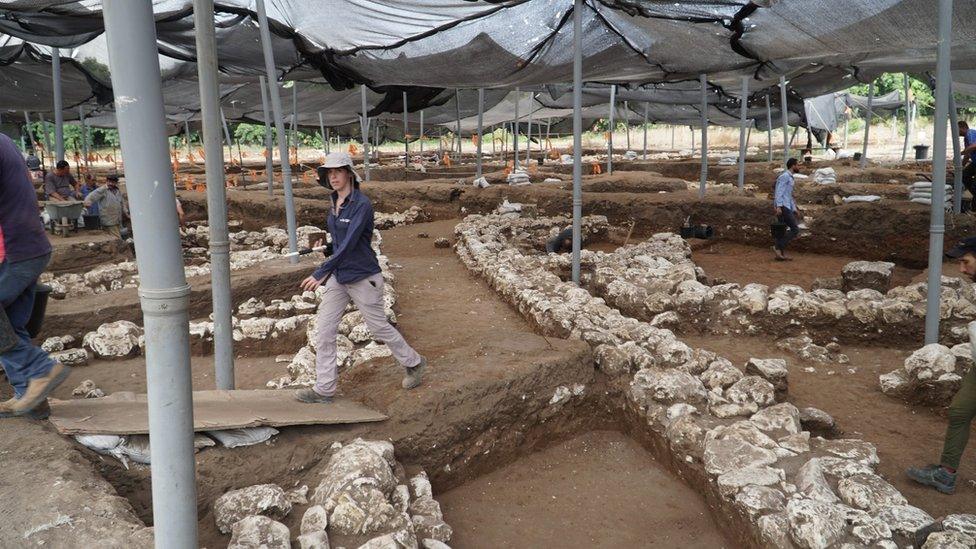

About 5,000 teenagers and volunteers have contributed to the excavation, which has been going on for over two and half years
.
- Published3 October 2019

- Published14 November 2018

- Published24 November 2016

- Published23 September 2014