Egypt animal mummies showcased at Saqqara near Cairo
- Published
Watch footage of the mummified big cats on display at the exhibition
A large cache of mummified animals found in an ancient Egyptian necropolis have been displayed for the first time near the capital Cairo.
Archaeologists discovered the trove last year near the Step Pyramid of Saqqara, south of the capital.
They uncovered hundreds of artefacts, including masks, statues and mummified cats, crocodiles, cobras and birds.
Egyptian authorities unveiled the artefacts at an exhibition near the Saqqara necropolis on Saturday.
Tests are being carried out to verify whether two of the mummified animals are lion cubs, Egypt's ministry of antiques said.
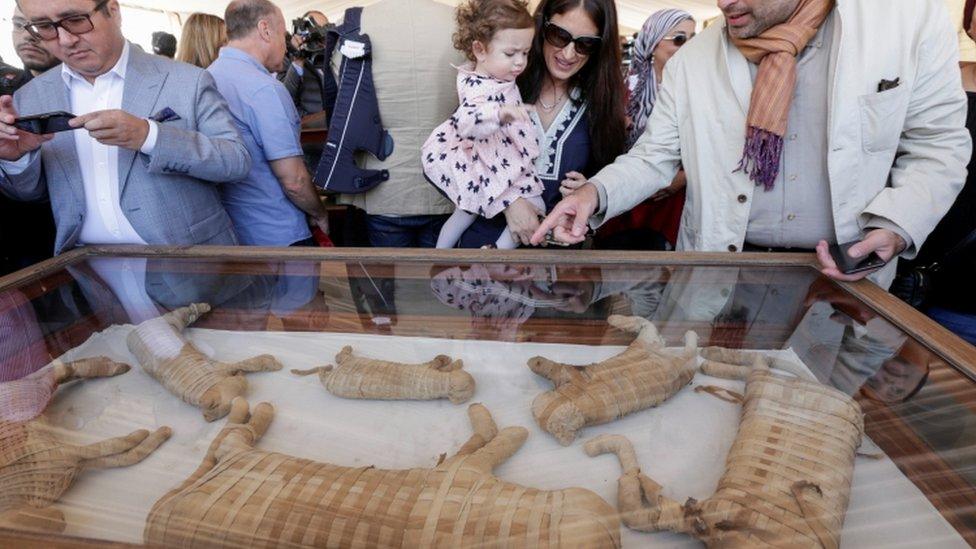

The animal mummies were found at Saqqara, an ancient burial ground south of Egypt's capital Cairo
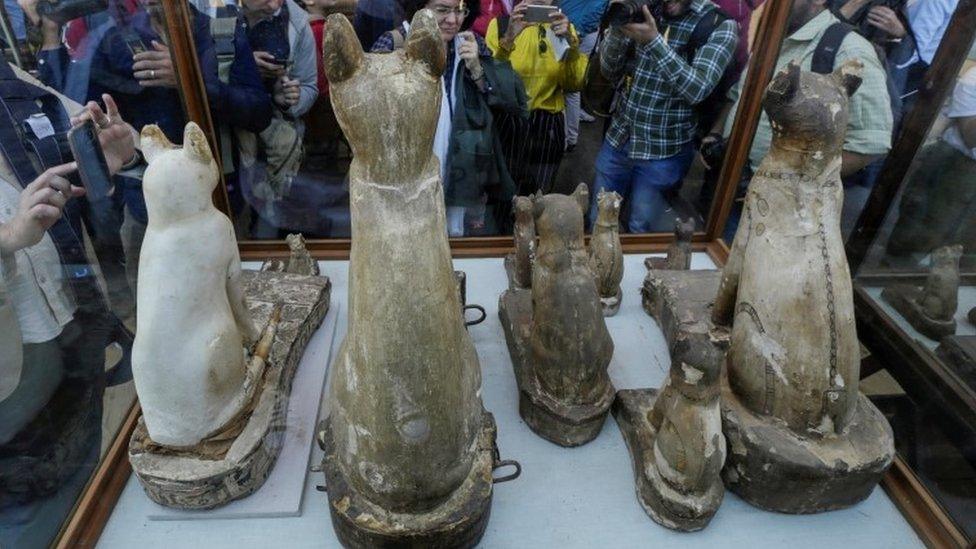

Tourists showed up in large numbers to see the artefacts on display
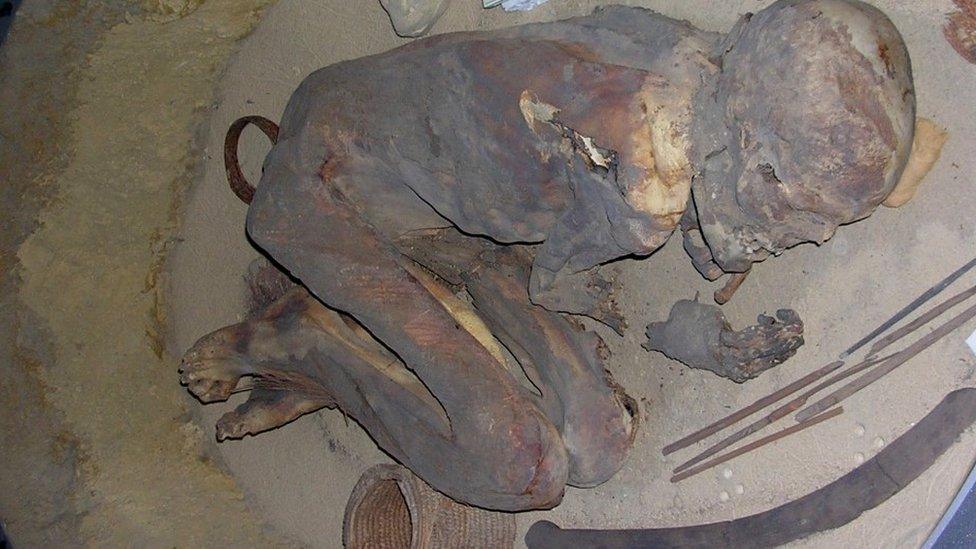
Unlike mummified cats, which are frequently found by archaeologists, the discovery of intact lions is considered rare.
At a news conference on Saturday, one Egyptian official touted a large scarab statue as one of the most significant discoveries.
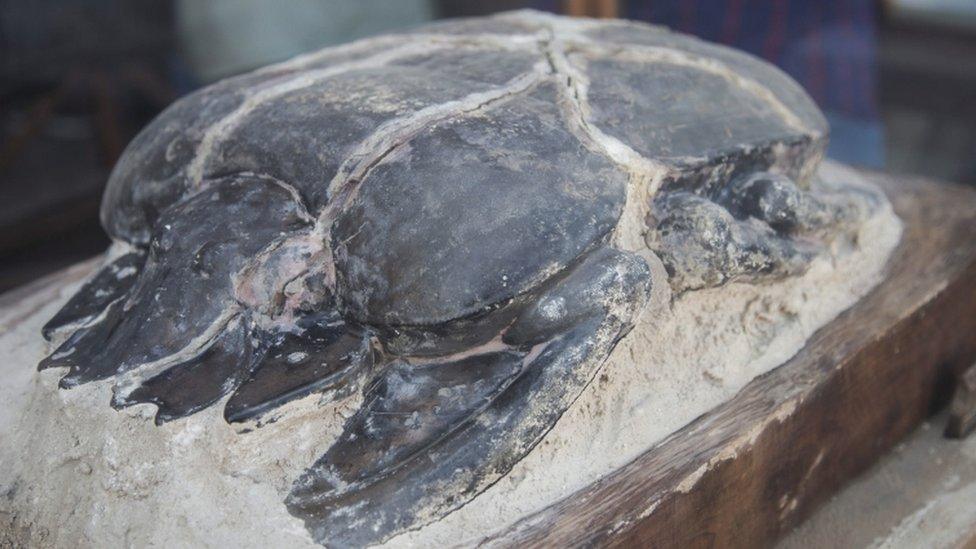

A large scarab statue was among the hundreds of artefacts discovered
"The most lovely discovery out of those hundreds: that scarab," said Mostafa Waziri, secretary-general of Egypt's Supreme Council of Antiquities.
"It is the biggest and [largest] scarab all over the world."
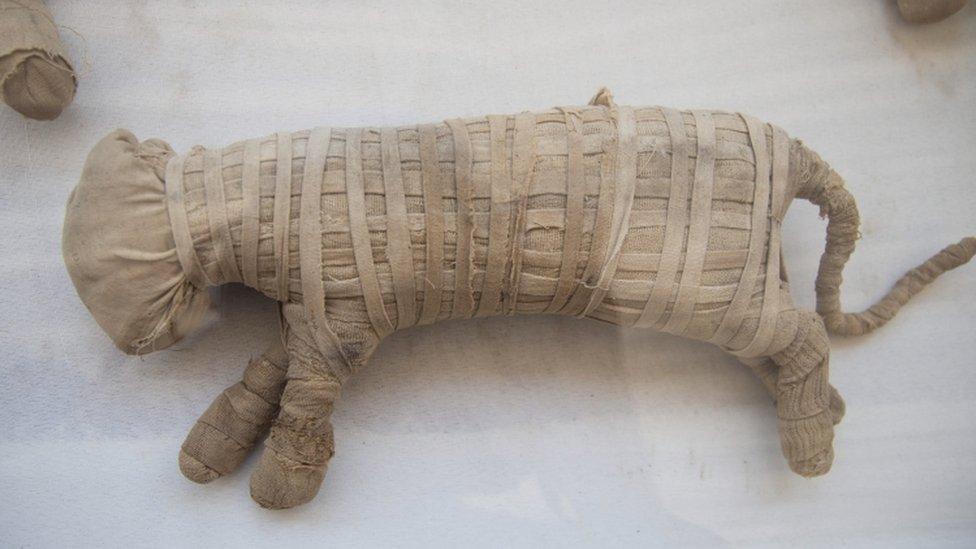

Archaeologists suspect two of the mummified animals are lion cubs
Saqqara is an ancient burial ground that served as the necropolis for Memphis, the capital of ancient Egypt for more than two millennia.
Located around 30km (18 miles) south of Cairo, Saqqara was an active burial ground for more than 3,000 years and has been designated a Unesco World Heritage Site.
In recent years, Egypt has ramped up its promotion of its archaeological finds in a bid to revive its vital but flagging tourism industry.
- Published15 December 2018

- Published16 October 2019

- Published16 August 2018
